New research indicates that taking vitamin D supplements may help prevent a potentially serious side effect of a revolutionary form of anti-cancer therapy. The findings are published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society (ACS). Immune checkpoint inhibitors help the immune system recognize and combat cancer cells, and although these...
Tag: <span>inhibitors</span>
Nuclear softening allows cells to move into dense tissue, encouraging injury repair
by Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania By softening a cell’s nucleus so that it can squeeze its way through dense connective tissues, a group of researchers believe they’ve demonstrated a new way to help the body efficiently repair injuries. The team of researchers from the University of Pennsylvania tested this theory...
Immune cells infiltrating tumors may play bigger cancer role than previously thought
by University of California – San Diego Most traditional cancer therapies target either the tumor cells themselves or indiscriminately kill any rapidly dividing cell. New findings by researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine indicate that manipulating macrophages, a type of immune cell found abundantly in the tissues surrounding a tumor, could...
Promising treatment to slow kidney disease doesn’t prove out in clinical trial
Scientists find that reducing levels of uric acid in the blood does not guard against complication in type 1 diabetes. JOSLIN DIABETES CENTER BOSTON – (June 25, 2020) – Historically, half or more of people with type 1 diabetes develop kidney disease, which frequently progresses to kidney failure requiring hemodialysis or a kidney transplant for...
Two new, powerful small molecules may be able to kill cancers that other therapies can’t
Using human cell and mouse models, City of Hope scientists demonstrate that the cancer inhibitors they’re developing could destroy acute myeloid leukemia and tumors from brain, pancreatic and breast cancers PRINT E-MAIL DUARTE, Calif. — City of Hope scientists have identified and developed two potent small molecules that appear to suppress tumor growth in multiple...
Antidepressant fluoxetine (Prozac) suppresses replication of SARS-CoV-2
By Sally Robertson, B.Sc A study conducted by researchers at Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg has shown that the antidepressant agent fluoxetine may be an effective drug for the early treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) among at-risk groups. Jochen Bodem and colleagues found that the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) fluoxetine significantly inhibited viral...
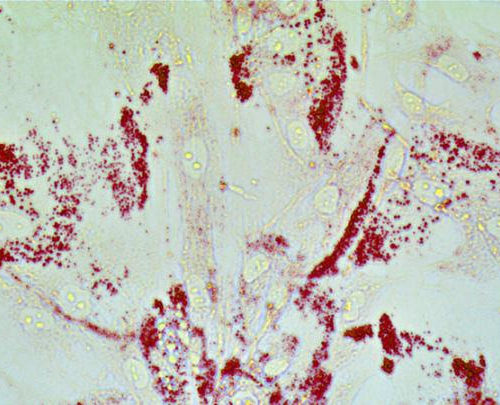
Loss of lipid-regulating gene fuels prostate cancer spread
JOHNS HOPKINS MEDICINE ANCER CELLS GOBBLE UP LIPIDS. PROSTATE CELLS ARE STAINED WITH OIL-RED O TO DETECT LIPID DROPLETS. OUR WORK SHOWS THAT REDISTRIBUTION OF LIPIDS FROM PROSTATE CANCER MICROENVIRONMENT TRIGGERS INFLAMMATION AND… view more CREDIT: NICK (JIN-YIH) LOW Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Centerresearchers from the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular Radiation Sciences identified...
Anaphylaxis-preventing pill offers new hope for severe allergy sufferers
By Rich Haridy June 07, 2020 Promising new research from Northwestern University is reporting progress in the development of an anaphylaxis-preventing pill. The drug, initially designed as an alternative to chemotherapy for some types of cancer, could hypothetically be taken before meals to prevent serious allergic reactions. BTK inhibitors are relatively new drugs, originally designed...
Antibiotic-destroying genes widespread in bacteria in soil and on people
Chemical compound restores tetracycline’s effectiveness by blocking bacterial resistance. The latest generation of tetracyclines — a class of powerful, first-line antibiotics — was designed to thwart the two most common ways bacteria resist such drugs. But a new study from researchers at Washington University in St. Louis and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has...
Researchers identify two marine molecules with therapy potential against Alzheimer’s disease
by University of Barcelona An interdisciplinary research study of the University of Barcelona identified two potential candidates to treat Alzheimer’s disease. These are two marine molecules, meridianine and lignarenone B, able to alter the activity of GSK3B activity, a protein associated with several neurodegenerative diseases. The researchers used several biocomputational techniques to detect these so...