by Cleveland Clinic An international team of researchers co-led by Cleveland Clinic have identified why patients without PTEN mutations may still experience the high cancer risk associated with PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome (PHTS). In a new study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, a research team co-led by Charis Eng, MD, Ph.D., Cleveland...
Tag: <span>inhibitors</span>
Type 2 diabetes medication could prevent SARS-CoV-2 from replicating in host cells
As advanced as medical science is, there are still many diseases we cannot treat. For example, there is no cure for COVID-19. However, this doesn’t mean that we cannot help people recover from this disease. Scientists at the University of Waterloo have found that type-2 diabetes helps stopping the spread of the COVID-19 virus in...
A roadmap for effective treatment of COVID-19
Due to the devastating worldwide impact of COVID-19, the illness caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, there has been unprecedented efforts by clinicians and researchers from around the world to quickly develop safe and effective treatments and vaccines. Given that COVID-19 is a complex new disease with no existing vaccine or specific treatment, much effort is...
Some recommended cardiovascular medications prescribed less frequently to women
DALLAS, May 20, 2020 — Women receiving treatment in primary care received some cardiovascular medication prescriptions at a lower rate than men, according to new research published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open access journal of the American Heart Association. “Additional efforts need to be taken to ensure that everyone,...
New test strip could provide accurate point-of-care diagnostics for cancer, COVID-19
by James Ives, M.Psych. (Editor) A new synthetic paper for finger-prick blood tests could provide accurate point-of-care diagnostics for cancer, COVID-19, and other serious diseases. Researchers at KTH Royal Institute of Technology say the innovation allows the detection of important biomarker proteins that might otherwise evade the blood plasma screening process. There are proteins in...
Scientists find a new way to reverse symptoms of Fragile X
by Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT scientists have identified a potential new strategy for treating Fragile X syndrome, a disorder that is the leading heritable cause of intellectual disability and autism. In a study of mice, the researchers showed that inhibiting an enzyme called GSK3 alpha reversed many of the behavioral and cellular features of...
Eyes send an unexpected signal to the brain
The eyes have a surprise. For decades, biology textbooks have stated that eyes communicate with the brain exclusively through one type of signaling pathway. But a new discovery shows that some retinal neurons take a road less traveled. New research, led by Northwestern University, has found that a subset of retinal neurons sends inhibitory signals...
Researchers discover key mechanism of cytokine storm in Castleman disease
by Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania When Castleman Disease patients have a flare of their symptoms, they experience a cytokine storm inside their bodies—a hyper-response from the immune system that can cause a fever, organ failure, and even death. Now researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of...
Newly discovered mechanism can explain increased risk of dementia
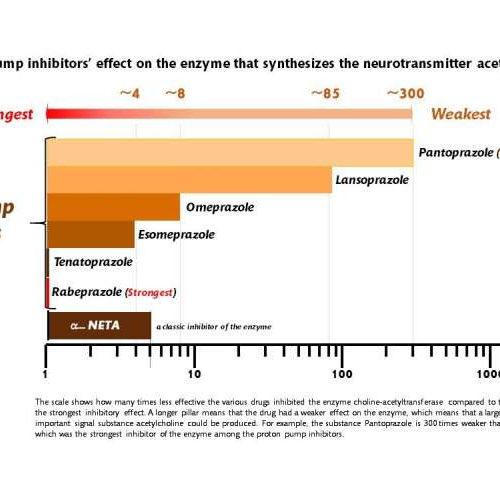
by Karolinska Institutet Millions of people around the world use proton pump inhibitors for conditions like heartburn, gastritis and stomach ulcers. Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden now report that the long-term use of these drugs could increase the risk of developing dementia. Their results are published in the journal Alzheimer’s & Dementia. “We’ve been...
Overlooked researchers researchers researchers could play important part in pneumonia and COVID-19, researchers say
by Karolinska Institutet In severe cases of COVID-19, a massive release of the endogenous protein HMGB1 in the lungs may contribute to pulmonary inflammation and tissue damage, according to a review article published today in the scientific journal Molecular Medicine. The researchers conclude that the inflammation could hypothetically be treated with an HMGB1 inhibitor. Severe...