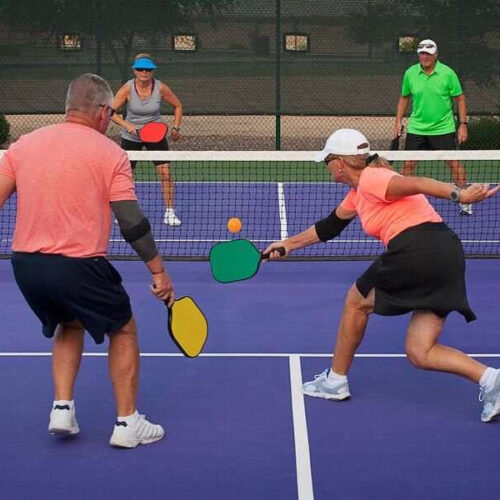
by Cara Murez Pickleball has burst onto the scene, inspiring people of all ages to pick up a paddle. But as with any sport, it’s possible to get hurt. Some best practices can help prevent injuries, according to a sports medicine expert. For pickleball players, the most common injury is to the rotator cuff tendon in the shoulder. This can...
Tag: <span>Injuries</span>
The suffering of those who cannot feel pain
by Isabelle Tourne and Daniel Lawler Pain of the painless: Abela’s daughters can only move around using crutches or a wheelchair because of injuries due to their condition. Patrice Abela first knew something was wrong when his eldest daughter was learning to walk and her feet left trails of blood behind her, yet she showed...
Antifreeze cream prevents frostbite injuries to skin
AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY Skiers, hikers, soldiers and others exposed to extreme cold temperatures can experience frostbite — a painful injury that occurs when ice crystals form in the skin. Many extremely cold areas are also remote, and delays in frostbite treatment can result in severe wounds, scarring and even limb amputation. Now, researchers reporting in...
Avoid opioid prescriptions for sprains and strains, evidence reviews say
Two new evidence reviews related to acute musculoskeletal injuries like strains and sprains suggest other forms of treatments are as effective as opioids and have less risk of harms to patients. The details of the systematic reviews and meta-analyses, led by McMaster, were published August 17 in the Annals of Internal Medicine. The first article...
FDA Approves Oliceridine, An Intravenous Opioid Severe Acute Pain Relievers for Clinical Use
The United States Food and Drug Administration recently approved Oliceridine, also known as “Olinvyk,” an opioid primarily concerned in treating severe acute pain, by biopharmaceutical company, Trevena, last August 7, 2020. After years of getting the FDA to approve the drug, Trevena, Inc., finally received approval this year. Trevena initially submitted the drug for review...
High school athletes require longer recovery following concussions
Epidemiologic findings from a high school population HENRY FORD HEALTH SYSTEM HIGH SCHOOL ATHLETES REQUIRE LONGER RECOVERY FOLLOWING CONCUSSIONS. view more CREDIT: GETTY IMAGES DETROIT – Young athletes are sidelined for at least one month after suffering a concussion, according to a Henry Ford Hospital study that provides new perspective on concussions and brain injuries....
Nuclear Softening Allows Cells to Move Into Dense Tissue, Encouraging Injury Repair
Using an enzyme inhibitor in meniscus cells, a Penn team was able to soften their nucleus and promote access to previously impassible areas. By softening a cell’s nucleus so that it can squeeze its way through dense connective tissues, a group of researchers believes they’ve demonstrated a new way to help the body efficiently repair...
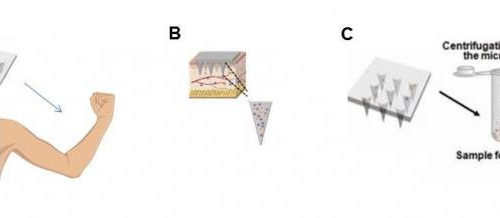
Extraction of skin interstitial fluid using microneedle patches
Researchers at the Terasaki Institute enhance tool for extraction of samples used in monitoring patient health (LOS ANGELES) – The interstitial fluid is a major component of the liquid environment in the body and fills the spaces between the body’s cells. In contrast, blood circulates only within the circulatory vessels of the body and is...
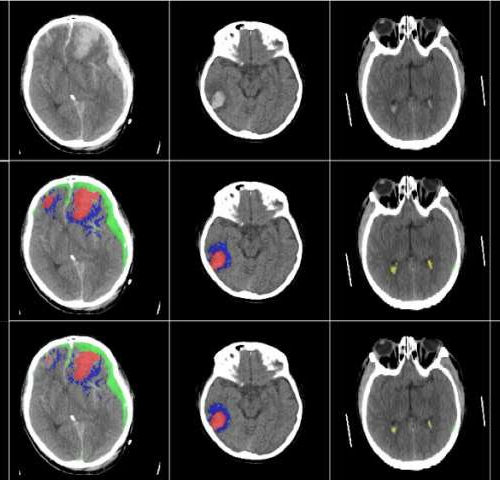
AI successfully used to identify different types of brain injuries
by University of Cambridge Researchers have developed an AI algorithm that can detect and identify different types of brain injuries. The researchers, from the University of Cambridge and Imperial College London, have clinically validated and tested the AI on large sets of CT scans, and found that it was successfully able to detect, segment, quantify...
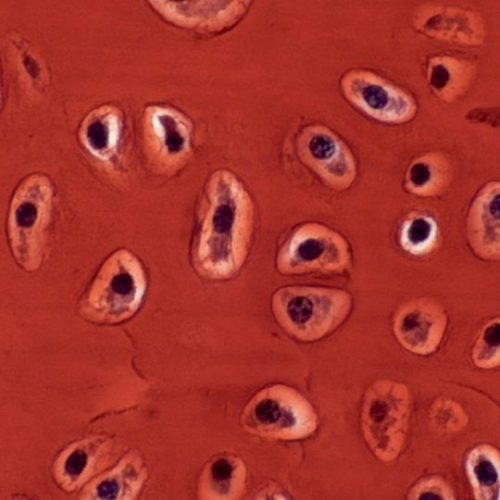
Adult skates can spontaneously repair cartilage injuries
Researchers have found that adult skates have the ability to spontaneously repair injured cartilage, using a type of cartilage stem cell. Human cartilage has very limited capacity for repair, and the finding may lead to new stem cell treatments for human cartilage injuries. Published in the journal eLife, the study identified a new type of...
- 1
- 2