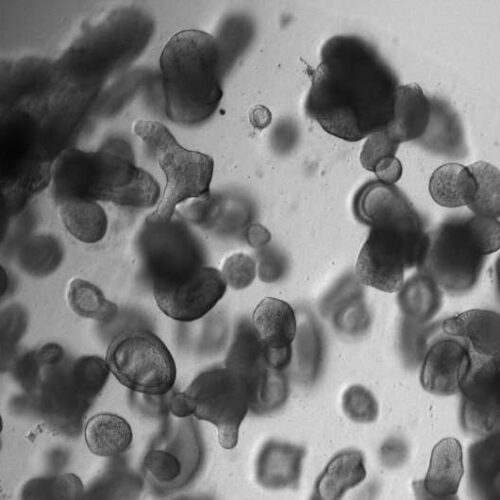
by Hubrecht Institute Human intestinal organoids used in this study to model the impact of BMP signaling on differentiation. Credit: Joep Beumer, Jens Puschhof and Fjodor Yousef Yengej, Copyright Hubrecht Institute. Intestinal cells can change specializations during their lives. The BMP signaling pathway—an important communication mechanism between cells—appears to be the driver of these changes....
Tag: <span>intestinal cells</span>
Can we harness intestinal cells to treat endocrine disorders?
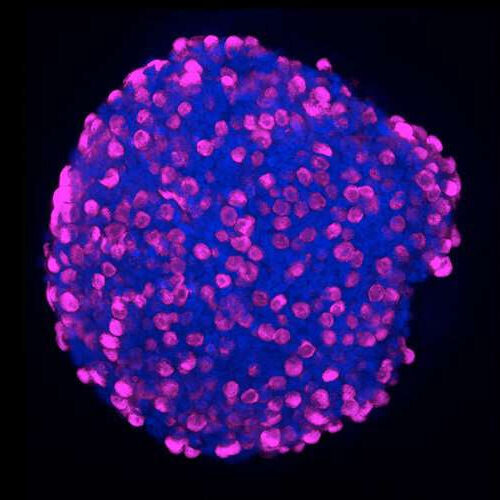
by Nancy Fliesler, Children’s Hospital Boston Using a newly developed protocol, Daniel Zeve, MD, and David Breault, MD, have been able to derive human enteroendocrine cells from human intestinal stem cells via intestinal organoids. Credit: Daniel Zeve, Boston Children’s Enteroendocrine cells punch above their weight. Constituting just about 1 percent of intestinal cells, they produce,...
New tech could reverse diseases, including IBS and diabetes, using intestinal cells
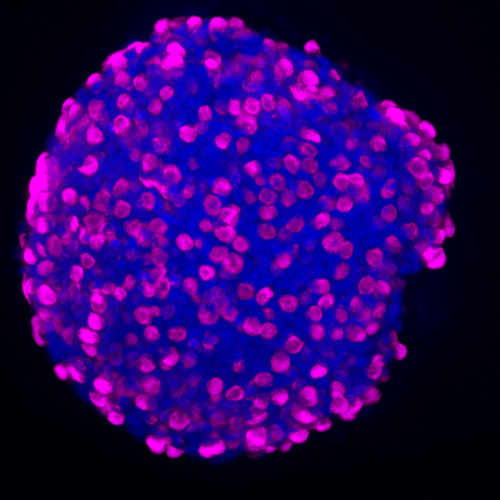
A newly developed technology platform has the potential to treat diseases like diabetes, IBS, and obesity by using enteroendocrine (EE) cells found in human intestinal cells, according to a recent study. Although enteroendocrine cells make up only about 1% of intestinal cells, they produce around fifteen different hormones that play a role in regulating digestion...
Following your gut: The remarkable role of intestinal cells
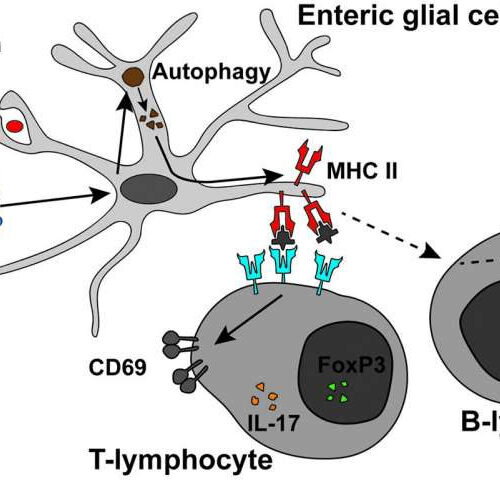
by Michigan State University This image is a 3-D volume rendering of a myenteric ganglion with enteric glia labeled in blue and MHC-II labeled in red. Credit: Aaron Chow and the Gulbransen Lab Food is essential for life—a daily source of calories and comfort. But for the more than 3 million adults in the United States...
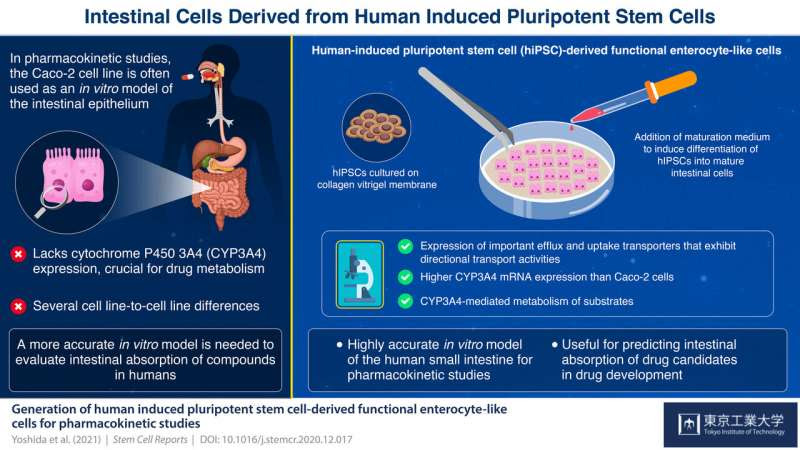
Researchers grow intestinal cells from human-induced pluripotent stem cells
by Tokyo Institute of Technology Human-induced pluripotent stem cells derived enterocyte-like cells exhibit P-gp- and BCRP-mediated efflux and cytochrome P450 (CYP3A4)-mediated metabolism. We concluded that hiPS cell-derived enterocyte-like cells can be used as a model for the evaluation of drug transport and metabolism studies in the human small intestine. Credit: Tokyo Tech A team of scientists...
The role of Klumpfuss in intestinal cell differentiation
by Leibniz Institute on Aging Stem cells are essential for homeostasis and cell renewal in organs like skin, lung or intestine. During the course of life, their function decreases steadily, making this decline a main factor for the development of age-associated diseases. Researchers of the Leibniz Institute on Aging in Jena, Germany, and their colleagues of the...
Surprising research result: All immature cells can develop into stem cells
by University of Copenhagen A sensational new study conducted at the University of Copenhagen disproves traditional knowledge of stem cell development. The study reveals that the destiny of intestinal cells is not predetermined, but instead determined by the cells’ surroundings. The new knowledge may make it easier to manipulate stem cells for stem cell therapy. The results have been published in Nature. All cells in the foetal gut have...