by University College London Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain High levels of ammonia kill liver cells by damaging the mitochondria that power the cells. But this can be prevented using an existing drug due to start clinical trials, finds a new study in mice led by researchers from UCL. The study, published in Science Advances, is the first to observe...
Tag: <span>liver cells</span>
Intermittent fasting spurs proliferation of liver cells in lab mice, study finds
by Krista Conger, Stanford University Medical Center A study led by researchers at Stanford Medicine questions the long-held belief that adult liver cells rarely divide. Credit: Marko Aliaksandr/Shutterstock.com Intermittent fasting—abstaining from eating for lengthy periods of time—spurs liver cells in laboratory mice to divide rapidly, according to a study led by researchers at Stanford Medicine. The finding challenges the long-standing...
Liver cancer: How liver cells go astray
by University of Basel One of the main causes of liver cancer is excessive alcohol consumption. Credit: Biozentrum, University of Basel The causes of liver cancer are manifold. In addition to metabolic disorders such as those associated with obesity, the main causes in the western world are infections with hepatitis C virus and high alcohol...
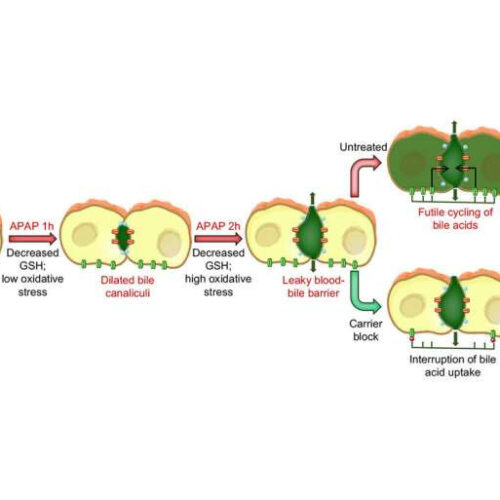
Interruption of bile acid uptake by liver cells after paracetamol overdose mitigates liver damage
by Anne Rommel, Leibniz-Institut für Arbeitsforschung an der TU Dortmund Graphical abstract. Credit: Journal of Hepatology (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.01.020 Poisoning with paracetamol (acetaminophen—APAP) is a common cause of liver failure. However, not all the correlations that lead to liver damage from APAP are yet known. Especially the role of bile acids is unclear. The Leibniz Research Center...
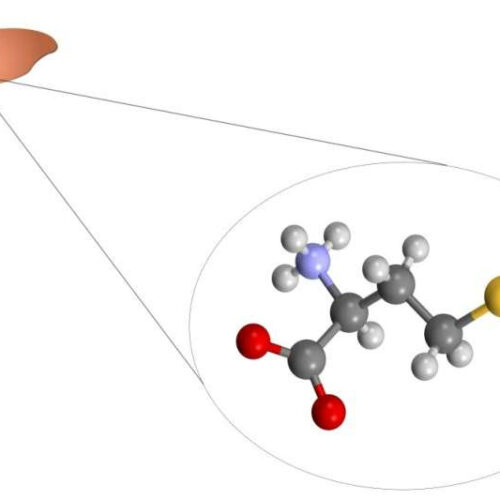
Lack or excess of amino acid methionine in diet can affect liver cells, study shows
by Mônica Tarantino, FAPESP Research reveals the mechanisms whereby methionine-deficient and methionine-supplemented diets can alter gene expression and damage liver cells. Credit: DBCLS and Ben Mills/Wikimedia Commons Having shown that diet can influence gene expression, science is starting to find out more about how this happens. According to an article recently published in Food and Chemical Toxicology, a...
Mutations in liver cells linked to liver disease and fat metabolism
by Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute Credit: CC0 Public Domain For the first time, DNA mutations in liver cells have been identified that impact metabolism and insulin sensitivity in patients with liver disease. These mutations are specific to liver disease that is associated with obesity, type 2 diabetes, and chronic alcohol consumption. The study, from the Wellcome...
New bioink for cell bioprinting in 3D
A research group led by Daniel Aili, associate professor at LiU, has developed a bioink to print tissue-mimicking material in 3D printers. The scientists have developed a method and a material that allow cells to survive and thrive. “Bioprinting is a new and exciting technology to manufacture three-dimensional tissue-mimicking cell cultures. It has been a...
Virus co-opts immune protein to avoid antiviral defences
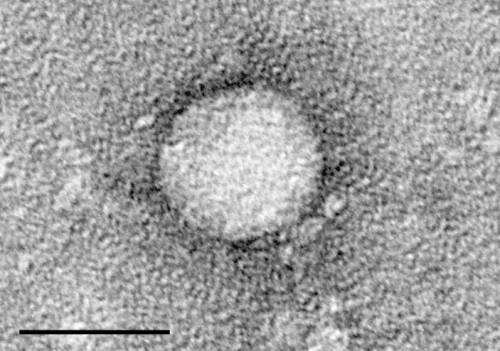
by eLife Electron micrographs of hepatitis C virus purified from cell culture. Scale bar is 50 nanometers. Credit: Center for the Study of Hepatitis C, The Rockefeller University. By discovering a trick the hepatitis C virus uses to evade the immune system, scientists have identified a new antiviral defense system that could be used to...
New liver cancer research targets non-cancer cells to blunt tumor growth
by Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania “Senotherapy,” a treatment that uses small molecule drugs to target “senescent” cells, or those cells that no longer undergo cell division, blunts liver tumor progression in animal models according to new research from a team led by Celeste Simon, Ph.D., a professor of Cell and...
Chemicals often found in consumer products could lead to obesity and fatty liver diseases
While poor nutrition and lack of exercise contribute to obesity, exposure to these compounds could trigger lifelong susceptibility to weight gain, Baylor University researcher says Chemical compounds found in many consumer products could be major contributors to the onset of lipid-related diseases, such as obesity, in humans, according to a Baylor University study. Until recently,...
- 1
- 2