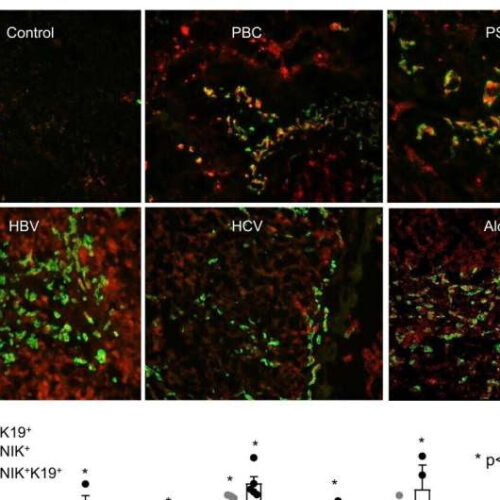
by Kelly Malcom, University of Michigan Chronic liver disease is associated with NIK upregulation in cholangiocytes. A, B Human liver sections were stained with antibodies to NIK and K19. A Representative images. Scale bar: 200 μm. B NIK+, K19+, and NIK+K19+ cells were counted and normalized to total cells. Control: n = 3 subjects, PBC: n = 3 subjects, PSC: n = 3 subjects, HBV: n = 5 subjects, HCV: n = 3 subjects, Alcohol: n = 3 subjects. C, D C57BL/6J male mice were...
Tag: <span>liver fibrosis</span>
Liver fibrosis: The fatal signaling pathway
by Medizinische Hochschule Hannover Professor Dr. Ingmar Mederacke. Credit: Medizinische Hochschule Hannover At least 5 million people in Germany suffer from liver disease. Fibrosis, the pathological proliferation of connective tissue, plays an important role in many complications of chronic liver problems. Activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are massively involved in this tissue remodeling. An international...
Selective, toxin-bearing antibodies could help treat liver fibrosis
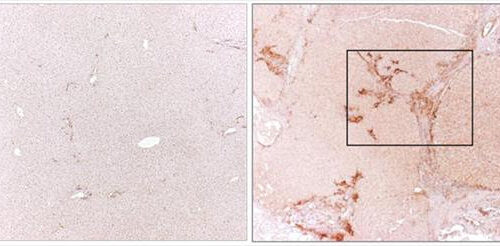
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – SAN DIEGO IMAGE: Normal liver tissues (left) do not produce mesothelin, while liver tissue from patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis does (right, darker staining). Mesothelin is a marker of liver fibrosis and the target of a potential new therapy for liver disease. CREDIT: UC SAN DIEGO HEALTH SCIENCES Chronic alcohol abuse...
Yale studies suggest new path for reversing type-2 diabetes and liver fibrosis
YALE UNIVERSITY New Haven, Conn. — In a pair of related studies, a team of Yale researchers has found a way to reverse type-2 diabetes and liver fibrosis in mice, and has shown that the underlying processes are conserved in humans. The studies appear in the Feb. 4 edition of Cell Reports and in the...
T2DM is risk factor for liver fibrosis progression in NAFLD
Toshifumi Tada, M.D., from Ogaki Municipal Hospital in Japan, and colleagues examined clinical risk factors for progression of liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Data were included for 1,562 patients with NAFLD (aged 36 to 64 years) and less severe liver fibrosis (FIB-4 index, <1.3). The researchers found that 186 patients progressed to advanced fibrosis (FIB-4 index, >2.67) during follow-up. For progression to advanced fibrosis, the three-, five-, seven-, and 10-year cumulative incidence rates...
- 1
- 2