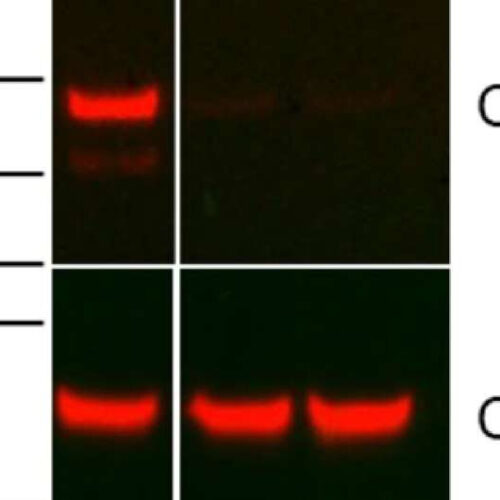
by Sarah Avery, Duke University School of Nursing Fig 1. CFH in EVs from CMT167 wild type vs. CFH knockout lung cancer cell lines. EVs were isolated from cell line conditioned media and 7.5 μg protein were western blotted and probed with GT103 and an anti-human IgG-HRP, then stripped and probed with anti-CD63 (SBI Biosystems) and...
Tag: <span>Lung cancer</span>
Immunotherapy drug can beat back early-stage lung cancer
by Dennis Thompson An immunotherapy drug is the first to significantly reduce the risk of cancer recurrence or death in people with early-stage lung cancer, researchers report. Atezolizumab reduced by 34% the risk of disease recurrence or death in a certain group of people with stage II to IIIA non-small cell lung cancer —those whose tumors carry a protein...
Study Suggests Path to Blocking Common Genetic Driver of Lung Cancer
KRAS is one of the most common drivers of cancer and is involved in one-third of non-small cell lung cancers. It’s proved an elusive target thanks to its smooth structure and biochemistry. And although new inhibitors are demonstrating some success against one type of KRAS, new paths are needed. A study from University of Michigan...
Capsaicin analog could help treatment-resistant lung cancer
EXPERIMENTAL BIOLOGY A new study found that non-pungent synthetic analog of capsaicin — the compound that makes chili peppers hot — made small cell lung cancer cells more responsive to treatment. Small cell lung cancer is a very aggressive form of cancer with a low survival rate. Cisplatin-based combination chemotherapy is typically the first-line treatment...
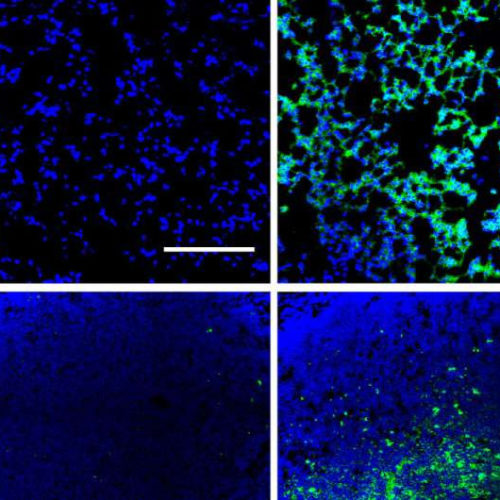
Delivering vaccines directly to the lungs can boost immune responses to respiratory infections or lung cancer: study
by Sarah McDonnell, Massachusetts Institute of Technology Antigen peptides (green) from the novel albumin-binding vaccine (amphiphile, right column) were better retained in the lungs and draining lymph nodes of mice than the control vaccine (soluble, left column). Credit: Rakhra et al., Sci. Immunol. 6, eabd8003 (2021) Many viruses infect their hosts through mucosal surfaces such as...
Enzymatic danse macabre of lung cancer
by King Abdullah University of Science and Technology Through international collaborations with Stanford University and the University of Texas in the U.S., KAUST scientists identified the enzyme NSD3 as a main driver of cancer. Credit: KAUST; Anastasia Serin A chromatin-regulating enzyme has been shown by in-depth interdisciplinary investigations to be a key driver of a common...
Missing protein helps small cell lung cancer evade immune defenses
by UT Southwestern Medical Center Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a highly metastatic cancer. The liver is one of the common sites of metastases, as seen in this image of mouse liver with metastatic SCLC lesions. SCLC tumors are composed of tightly packed epithelial cells with few immune cells infiltrating inside the tumor. Credit: UT...
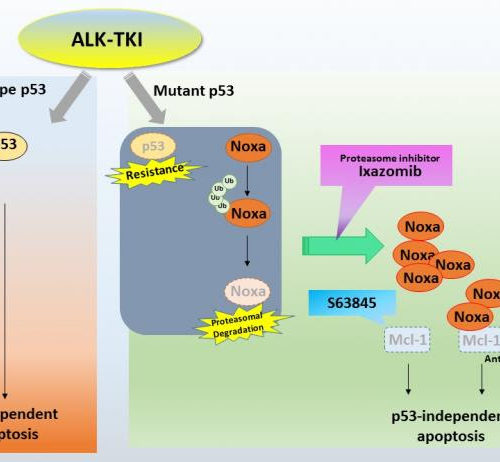
Potential combined drug therapy for lung cancer
KANAZAWA UNIVERSITY IMAGE: GRAPHICAL SCHEMA SHOWING THE MECHANISM FOR OVERCOMING INTRINSIC RESISTANCE TO ALK-TKIS OWING TOTP53 MUTATIONS CREDIT: KANAZAWA UNIVERSITY Most lung cancers are of a type called non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). This type of cancer is relatively insensitive to chemotherapy, so NSCLC therapies are usually based on drug treatment. Alectinib is a drug commonly...
Researchers uncover a potential treatment for an aggressive form of lung cancer
UT SOUTHWESTERN MEDICAL CENTER IMAGE: THE IMAGE DEPICTS A NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER TUMOR SURROUNDED BY METABOLITES INVOLVED IN THE HEXOSAMINE BIOSYNTHESIS PATHWAY. CREDIT: CREDIT: ELIZABETH LIEU DALLAS – Jan. 5, 2021 – Researchers at the Children’s Medical Center Research Institute at UT Southwestern (CRI) have discovered a new metabolic vulnerability in a highly aggressive form of non-small cell lung cancer...
Low-dose CT for lung cancer screening: benefit outweighs potential harm
INSTITUTE FOR QUALITY AND EFFICIENCY IN HEALTH CARE For heavy (ex-)smokers, lung cancer screening using low-dose computed tomography (low-dose CT, LDCT) offers more benefit than harm: The procedure can save a number of people from dying of lung cancer; for some of them, it might also prolong overall survival. This is the conclusion drawn by...