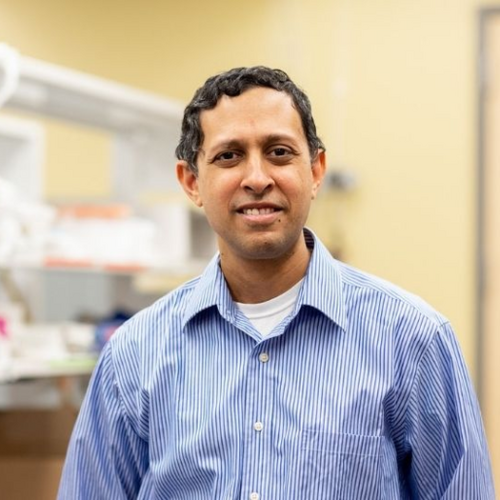
UNIVERSITY OF HOUSTON IMAGE: NAVIN VARADARAJAN, UNIVERSITY OF HOUSTON M.D. ANDERSON PROFESSOR OF CHEMICAL AND BIOMOLECULAR ENGINEERING, STUDIED THE DYNAMIC INTERACTIONS BETWEEN T CELLS AND TUMOR CELLS TO DETERMINE WHICH PATIENTS ARE LIKELY TO RESPOND TO CAR T-CELL THERAPY TO TREAT LYMPHOMA. CREDIT: UNIVERSITY OF HOUSTON In the war against cancer, one of the most...
Tag: <span>Lymphoma</span>
Towards a cure for lymphoma: new research brings hope
New light is being shed on the mechanisms underlying the malignant transformation of lymphomas, paving the way for a promising therapeutic target, thanks to research conducted by a team led by Université de Montréal professor Tarik Möröy. Director of the hematopoiesis and cancer research unit at the Montreal Clinical Research Institute (IRCM), affiliated with UdeM, Möröy...
Study reveals cause, potential precision therapies for aggressive type of lymphoma
WEILL CORNELL MEDICINE DNA mutations are essential to the rapid development of an array of antibody-producing immune cells called B cells that collectively can recognize a vast number of specific targets. But this process can go awry in people with a mutation in a gene called SETD2, leading to a type of aggressive blood cancer,...
NK cells combined with bispecific antibody showed strong response for patients with lymphoma
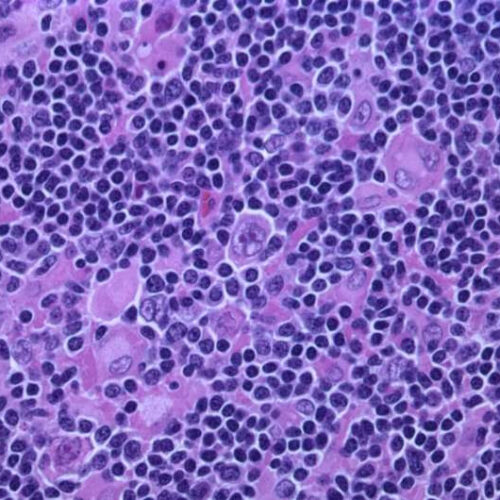
by University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Hodgkin lymphoma, nodular lymphocyte predominant (high-power view) Credit: Gabriel Caponetti, MD./Wikipedia/CC BY-SA 3.0 Researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center showed that natural killer (NK) cells derived from donated umbilical cord blood, combined with a novel bispecific antibody known as AFM13 that targets...
Lymphoma cell metabolism may provide new cancer target
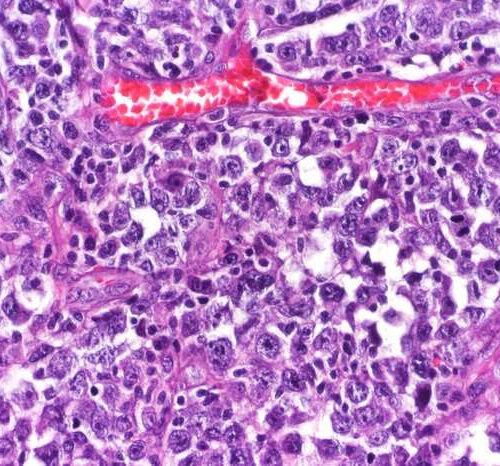
by Weill Cornell Medical College Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Credit: CoRus13, distributed under a CC BY-SA 4.0 license Aggressive and relatively common lymphomas called diffuse large B cell lymphomas (DLBCLs) have a critical metabolic vulnerability that can be exploited to trick these cancers into starving themselves, according to a study from researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine...
International collaboration set to investigate new treatment strategy for lymphoma
QUEEN MARY UNIVERSITY OF LONDON An international collaboration involving researchers from Queen Mary University of London, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK), New York, and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston has secured a €1M research grant from Dutch blood cancer charity, Lymph&Co, to investigate a new treatment target for lymphoma. The aim of the project is...
Clinical feasibility of individualized therapy in leukemia and lymphoma patients
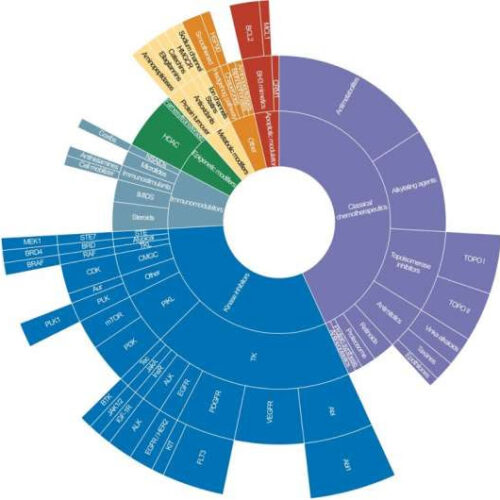
by Johannes Angerer, Medical University of Vienna Figure S1. Sunburst plot showing the classes of drugs tested by scFPM. Drugs can be broadly classified into kinase inhibitors, immunomodulatory drugs, epigenetic modifiers, metabolic modifiers, apoptotic modulators, classical chemotherapeutics and other drugs. Credit: DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-0538 Standard therapy for advanced recurring aggressive, hematological malignancies, such as leukemias and lymphomas,...
Researchers discover a novel class of drugs that may help treat a deadly type of lymphoma
THE MOUNT SINAI HOSPITAL / MOUNT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE New York, NY (June 22, 2021) – A new class of drugs that inhibits a “master switch” involved in the vast majority of cases of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), a fatal subtype of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, has been discovered by researchers at Mount Sinai. In a study in Clinical...
Newly identified gut cells nurture lymph capillaries
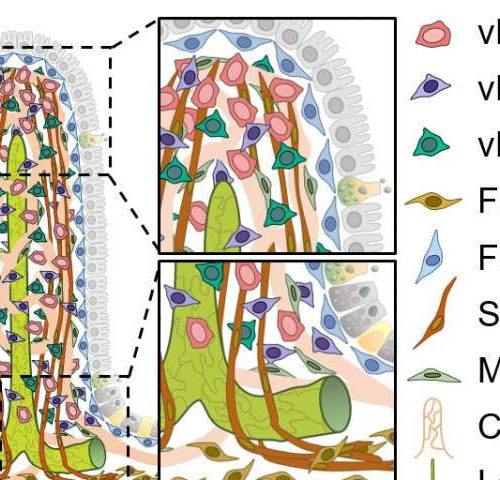
by Institute for Basic Science Fingerlike projections that cover the intestinal wall and absorb nutrients in the small intestine.During digestion, hydrophilic nutrients, such as glucose and amino acids, are absorbed by blood capillaries. On the other hand, hydrophobic nutrients, such as lipids, are taken in by specialized lymphatic capillaries called lacteals. The graphics also shows...
Better vaccines are in our blood
by Harvard University Red blood cells do more than shuttle oxygen from our lungs to our organs: they also help the body fight off infections by capturing pathogens on their surfaces, neutralizing them, and presenting them to immune cells in the spleen and liver. Now, a team of researchers from Harvard’s Wyss Institute for Biologically...