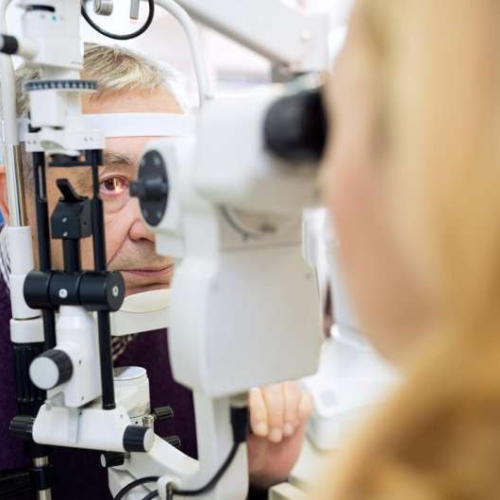
Atrophic macular degeneration, or geographic atrophy, is an advanced stage of dry age-related macular degeneration. Destruction of the cells — known as atrophy — in the retina can eventually lead to dim or blind spots in vision. Age-related macular degeneration affects the macula, the central portion of the retina that enables people to see. Over...
Tag: <span>macular degeneration</span>
Common diabetes drug shows promise for treating macular degeneration
October 1, 2024 by University of Chicago Medical Center Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is one of the leading causes of vision loss in adults over 50 in the United States. According to estimates from the National Eye Institute, approximately 11 million people in the U.S. are affected by some form of AMD, and that number...
Diagnosed with macular degeneration? Here’s what you need to know
by Dennis Thompson Age-related macular degeneration can lead to vision loss in seniors, but new therapies have offered fresh hope for preserving eyesight later in life, eye experts say. These cutting-edge therapies benefit both the dry and wet types of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), says the American Society of Retina Specialists (ASRS). Eleven million people...
Does more outdoor light at night help cause macular degeneration?
by Ernie Mundell As levels of nighttime artificial outdoor light rise, so do the odds for a leading cause of vision loss, age-related macular degeneration (AMD). South Korean researchers found that people living in areas of that country with the highest levels of streetlights and other artificial light had more than double the odds for...
QUANTUM CHEMISTRY PROTECTS AGAINST MACULAR DEGENERATION
Age-related macular degeneration is the leading cause of vision loss in Western countries. The condition, a deterioration of central vision, begins when droplets of lipids and proteins called lipofuscin accumulate in the retina and damage cells. Effective treatments for age-related macular degeneration (AMD) are not available and it remains unclear how healthy eyes prevent this...
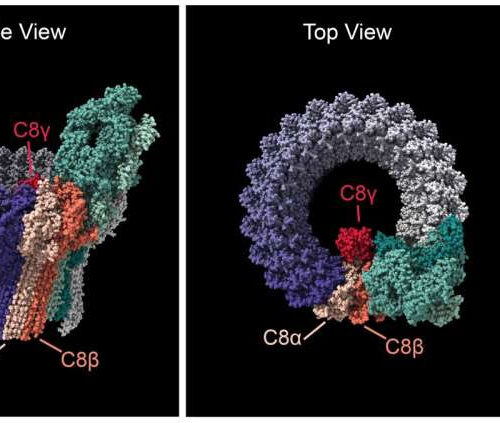
Extremely rare gene variants point to a potential cause of age-related macular degeneration
by National Eye Institute The complement membrane attack complex is a pore that inserts into the cell membrane. The complex is formed by up to 18 C9 subunits (purple), the C5, C6, and C7 subunits (various shades of green), and the C8-alpha, C8-beta, and C8-gamma subunits (shades of red). Side (left) and Top (center) views show...
An antibody-based drug triggers rare inflammatory eye problems in macular degeneration patients
by Delthia Ricks , Medical Xpress Neutralizing and non-neutralizing ADAs in complex with brolucizumab. A structural model of a complex comprised of one neutralizing anti-brolucizumab antibody in blue, and two non-neutralizing antibodies in light yellow. Brolucizumab is shown in gray, with the VEGF-A-binding CDRs highlighted in magenta. ADA, anti-drug antibody; CDR, complementarity-determining region; VEGF-A, vascular...
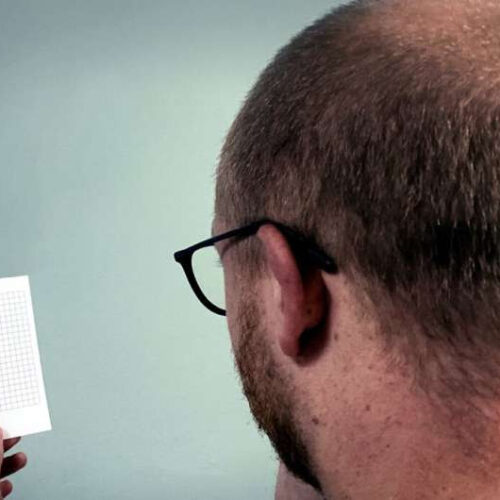
Commonly used self-test for age-related macular degeneration found to be inaccurate
by Yousif Subhi, Medical Xpress The Amsler grid test is a small piece of paper with horizontal and vertical lines held at a reading distance with the observer looking with each eye separately and focusing on the dot in the center. Credit: Yousif Subhi Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is one the most prevalent eye diseases....
Age-related macular degeneration a risk factor for COVID-19 infection, severe disease
BOSTON UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE (Boston)— Recent evidence has emerged to suggest that age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a clinical risk factor for increased risk for infection and mortality. AMD has been reported to confer higher risk of severe complications of SARS-CoV-2 infection, including respiratory failure and death (25 percent), a risk which is higher than Type 2...
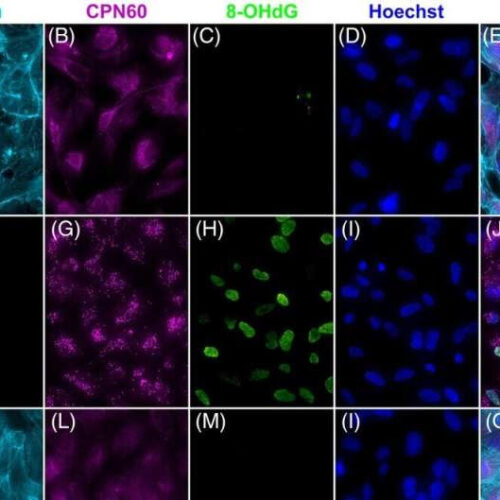
New gene therapy shows promise for treating age related macular degeneration
by Trinity College Dublin Rescue of ARPE19 cells insulted with NaIO3. 5.0 × 104 ARPE19 cells were transduced with AAV2/8-ophNdi1 5-h post-seeding; MOI = 5.4 × 105 (K–O). Twenty-eight-hour post-transduction cells were insulted with 5-mM NaIO3 (F–O) and 24-h post-insult cells were fixed and stained with Phalloidin-iFluor 647 (F-actin, light blue), and CPN60 (mitochondrial marker, magenta) and 8-OHdG-Alexa Fluor 488 (oxidative stress marker, green) immunocytochemistries;...