CENTRO NACIONAL DE INVESTIGACIONES CARDIOVASCULARES CARLOS III (F.S.P.) IMAGE: FROM LEFT TO RIGHT: REBECA ACÍN-PÉREZ, SALVADOR IBORRA, JOSÉ ANTONIO ENRÍQUEZ AND DAVID SANCHO. Macrophages are immune system cells. They are essential in the early response to infections, and they also have a key role in the proper functioning of our tissues and the regulation of...
Tag: <span>mechanism</span>
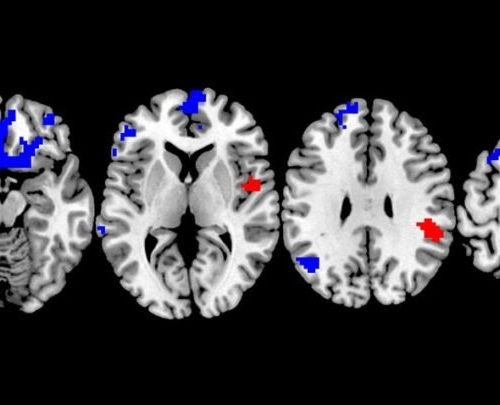
Which OCD Treatment Works Best? New Brain Study Could Lead to More Personalized Choices
New research could improve the odds that people with the obsessive-compulsive disorder will receive a therapy that really works for them – something that eludes more than a third of those who currently get OCD treatment. The study, performed at the University of Michigan, suggests the possibility of predicting which of two types of therapy...
People with increased risk of Alzheimer’s have deficits in navigating
by Ruhr-Universitaet-Bochum Animals and humans have the ability to follow their own position in space through self-motion cues, even in the absence of any other sensory information. “If you get up at night and want to find your way to the bathroom in the dark, you need—in addition to knowing the arrangement of your own...
New connections reveal how cancer evades the immune system
by University of Michigan If cancer is a series of puzzles, a new study pieces together how several of those puzzles connect to form a bigger picture. One major piece is the immune system and the question of why certain immune cells stop doing their job. Another piece involves how histones are altered within immune...
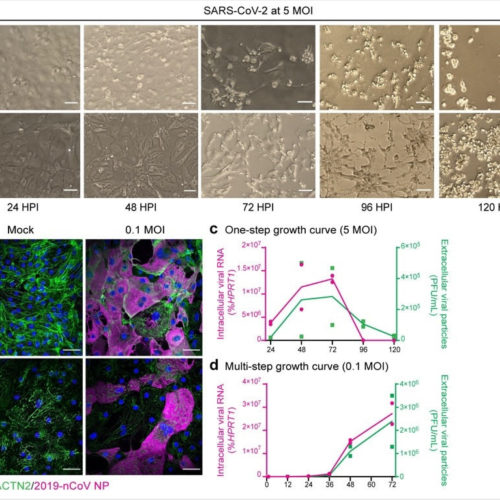
COVID-19 patients may experience long-term cardiovascular complications
By Sally Robertson, B.Sc. Researchers at the University of Washington in Seattle have conducted a study suggesting that infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) can directly infect heart tissue and contribute to whole-organ cardiac dysfunction. Charles Murry and colleagues found that the virus directly infected cardiomyocytes, impaired their electrophysiological and contractile properties,...
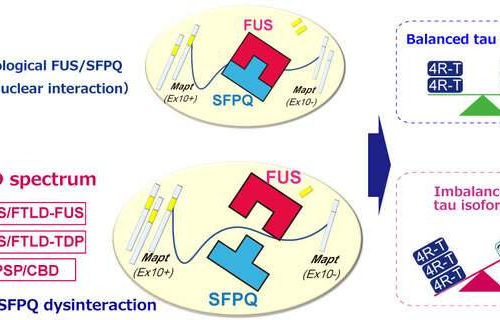
Unlocking the mystery of tau for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases
by Nagoya University Under normal physiological conditions, FUS and SFPQ interact in the nucleus of nerve cells and regulate the alternative splicing of MAPT by excising exon 10. When this functional machinery is impaired, the splicing ratio of MAPT exon 10+/exon 10- is increased, which in turn results in an increased 4R-Tau/3R-Tau ratio. The findings...
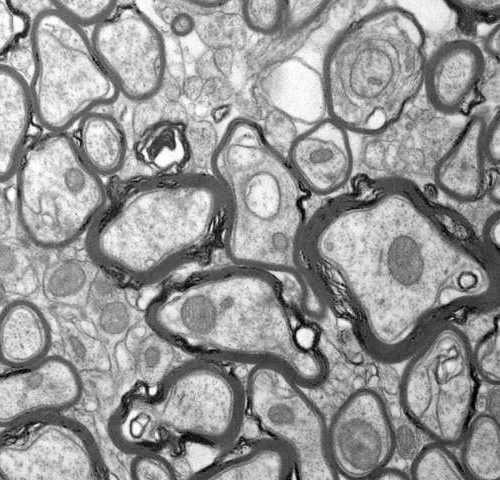
Mechanisms identified to restore myelin sheaths after injury or in multiple sclerosis
by Universitaet Mainz Remyelination in the spinal cord after experimental focal degradation of myelin sheaths, simulating a lesion caused by multiple sclerosis. In young adults, the myelin sheath (dark rings) around axons (light gray circular structures) can be rebuilt, but this process is not fully efficient and its efficiency decreases sharply with age and as...
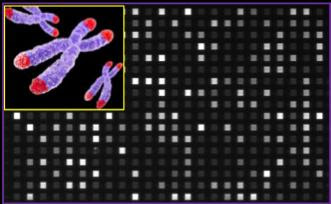
NUS researchers develop new system for accurate telomere profiling in less than 3 hours
The novel STAR assay can rapidly determine telomere dysregulation in cancers and age-related diseases in clinical settings A MAGNIFIED IMAGE CAPTURED BY THE DEVICE USED TO PERFORM STAR ASSAY. DIFFERENT FLUORESCENT INTENSITIES REFLECT THE LENGTH VARIATIONS IN INDIVIDUAL TELOMERE MOLECULES. view more CREDIT: NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE The plastic tips attached to the ends of...
New tool identifies which cancer patients are most likely to benefit from immunotherapy
A new prognostic tool developed by an international team led by CTI-Bath paves the way for personalised medicine for cancer patients. A new diagnostic tool that can predict whether a cancer patient would respond to immunotherapy treatment has been developed by scientists at the University of Bath. This advance in precision medicine will allow clinicians...
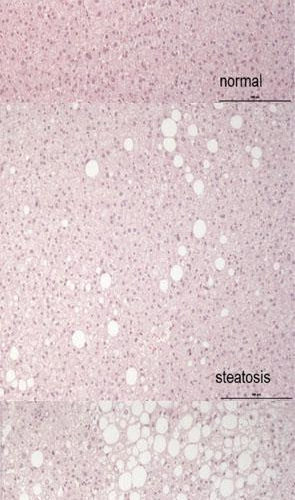
How protein protects against fatty liver
DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER DIABETESFORSCHUNG DZD MICROSCOPIC IMAGES OF LIVER BIOPSIES OF THREE INDIVIDUALS WITH DIFFERENT DEGREES OF LIVER FAT ACCUMULATION view more CREDIT: DIFE Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is the most common chronic liver disease in the world, with sometimes life-threatening consequences. A high-protein, calorie-reduced diet can cause the harmful liver fat to melt away...