Health13 January 2025 ByDavid Nield (Maria Korneeva/Moment/Getty Images) Being able to erase bad memories and traumatic flashbacks could help in the treatment of a host of different mental health issues, and scientists have found a promising new approach to do just this: weakening negative memories by reactivating positive ones. In an experiment covering several days, an international...
Tag: <span>memories</span>
Cells all over the body store ‘memories’: What does this mean for health?
Share on PinterestDo all our cells have a type of memory, and if so, how might this influence health? We investigate. Design by MNT; Photography by Grant Faint/Getty Images & Ed Reschke/Getty Images. Memory is one of the most crucial aspects of our health and human identity. Through memory, we create our individuality, our specific relationships...
MUSIC CAN ENHANCE LEARNING AND CHANGE OUR MEMORIES
SEPTEMBER 11TH, 2024POSTED BY GEORGIA TECH (Credit: Getty Images) TAGS : LEARNINGMEMORYMUSICUNIVERSITY : GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY New research demonstrates music’s impact on learning and memory, with possible therapeutic applications for mental health. The music we know and might love, music that feels predictable or even safe—that music can help us study and learn. Yiren...
Erasing ‘bad memories’ to improve long term Parkinson’s disease treatment – Parkinson’s
by Katherine Gaither, University of Alabama at Birmingham Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Common treatments for Parkinson’s disease can address short-term symptoms, but can also cause extensive problems for patients in the long run. Namely, treatments can cause dyskinesia, a form of uncontrollable movements and postures. In a recent study published in The Journal of Neuroscience,...
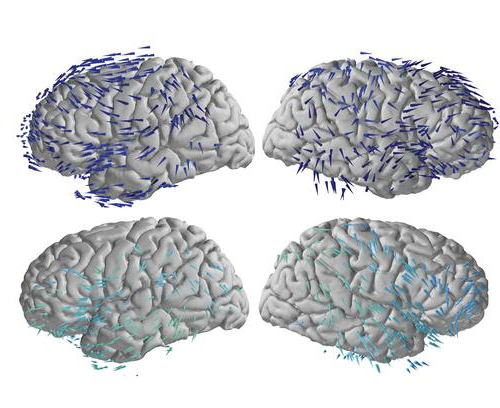
Brain waves travel in one direction when memories are made and the opposite when recalled
Peer-Reviewed Publication COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE TRAVELING WAVE PROPAGATION DIRECTIONS IN THE MEMORY TASK REVEAL HOW THE BRAIN QUICKLY COORDINATES ACTIVITY AND SHARES INFORMATION ACROSS MULTIPLE REGIONSCREDIT: HONGHUI ZHANG In the space of just a few seconds, a person walking down a city block might check their phone, yawn, worry about...
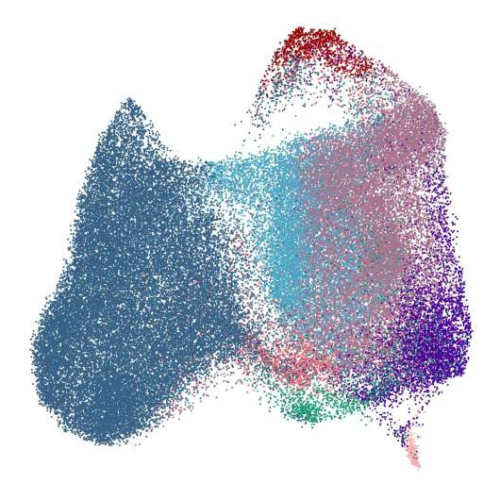
Researchers discover new cell that remembers allergies
by McMaster University Image depicting UMAP of mass cytometry data analyzing human B cell subsets. Credit: Depiction generated by David R. Glass, project lead by Joshua F.E. Koenig, Peter Sejer Andersen, Niels Peter H. Knudsen, Allyssa Phelps, and Kelly Bruton.Researchers with McMaster University and Denmark-based pharmaceutical company ALK-Abello A/S have made a groundbreaking discovery: a new...
Study reveals fatty acids hold clue to creating memories
by University of Queensland L to R: Dr. Isaac Akefe and Professor Fred Meunier in the lab. Credit: Queensland Brain InstituteResearchers at the University of Queensland have revealed the crucial role of saturated fatty acids in the brain’s consolidation of memories. Dr. Isaac Akefe from UQ’s Queensland Brain Institute has uncovered the molecular mechanism and identifies...
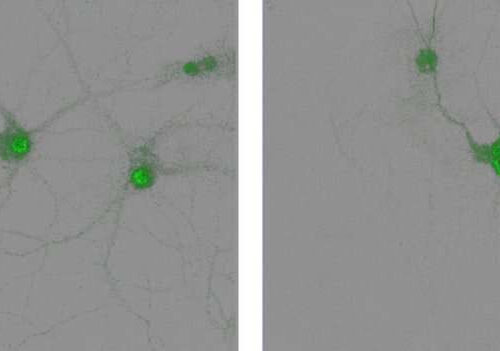
New mouse study reveals a key process in how the brain forms memories
by UC Davis The left panel shows PDE4D5 in the nucleus of hippocampal neurons. The right panel shows PDE4D5 in the cytoplasm of hippocampus neurons after activation of an adrenaline receptor. Credit: University of California The process by which memories are formed in the hippocampus region of the brain is complex. It relies on a...
Self-assembling proteins can store cellular “memories”
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MA — As cells perform their everyday functions, they turn on a variety of genes and cellular pathways. MIT engineers have now coaxed cells to inscribe the history of these events in a long protein chain that can be imaged using a light microscope. Cells programmed to produce these chains...
Scientists identify how the brain links memories
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – LOS ANGELES HEALTH SCIENCES Our brains rarely record single memories—instead, they store memories into groups so that the recollection of one significant memory triggers the recall of others connected by time. As we age, however, our brains gradually lose this ability to link related memories. Now UCLA researchers have discovered...