Marilynn Larkin December 30, 2024 0322 TOPLINE: Fragmented sleep — that is, increased wakefulness and reduced sleep efficiency — is a sign of metabolic dysfunction—associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), a study using actigraphy showed. METHODOLOGY: TAKEAWAY: IN PRACTICE: “We concluded from our data that sleep fragmentation plays a role in the pathogenesis of human MASLD....
Tag: <span>Metabolic Dysfunction</span>
Pipeline of new drug treatment for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
News Release 25-Sep-2024 Peer-Reviewed PublicationXia & He Publishing Inc. ACC, Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor; MPC, mitochondrial pyruvate carrier; THR, thyroid hormone receptor; ASK-1, apoptosis signaling kinase-1; GLP-1R, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; GCGR, glucagon receptor; GIPR, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor; PDE, phosphodiesterase; SGLT, sodium–glucose cotransporter; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; SCD1, stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1; FGFR4/1, fibroblast...
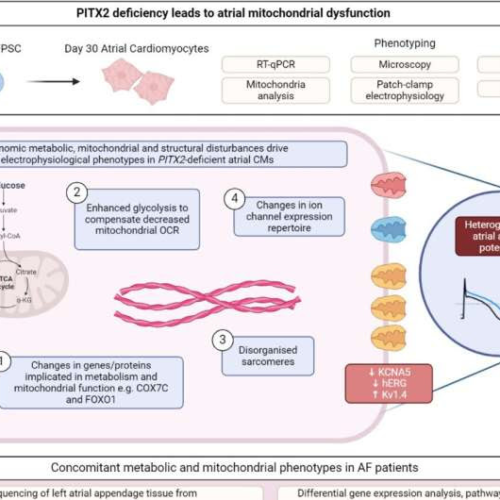
Gene-related metabolic dysfunction may be driving heart arrhythmia
August 12, 2024 by University of Birmingham Graphical Abstract. Credit: Cardiovascular Research (2024). DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvae169Patients with a common heart arrhythmia called atrial fibrillation could benefit from future treatments that target inefficiencies in heart cell metabolism, a new paper has found. A study published in Cardiovascular Research Journal discovered that a gene deficiency found in patients...
How obesity dismantles our mitochondria: Study reveals key mechanism behind obesity-related metabolic dysfunction
by University of California – San Diego These colored streaks are mitochondrial networks within fat cells. Researchers from UC San Diego discovered that a high-fat diet dismantles mitochondria, resulting in weight gain. Credit: UC San Diego Health SciencesThe number of people with obesity has nearly tripled since 1975, resulting in a worldwide epidemic. While lifestyle factors...
Study reveals how excess carbohydrates may contribute to metabolic dysfunction
BRIGHAM AND WOMEN’S HOSPITAL A high body mass index (BMI) is closely correlated with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. For decades, nutrition guidelines have emphasized the necessity of decreasing intake of dietary fats. Yet, even as studies demonstrate ties between foods laden with simple carbohydrates and metabolic dysfunction, much remains unknown about how the...
Excessive Mitochondrial Point Mutations Do Not Lead to Obvious Metabolic Dysfunction
Every cell contains a herd of hundreds of mitochondria, organelles descended from ancient symbiotic bacteria. The primary purpose of mitochondria is to package the chemical energy store molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) that is needed to power cellular processes. Each mitochondrion contains one more copies of a small circular genome, the mitochondrial DNA. This mitochondrial DNA is unfortunately poorly protected and repaired in...