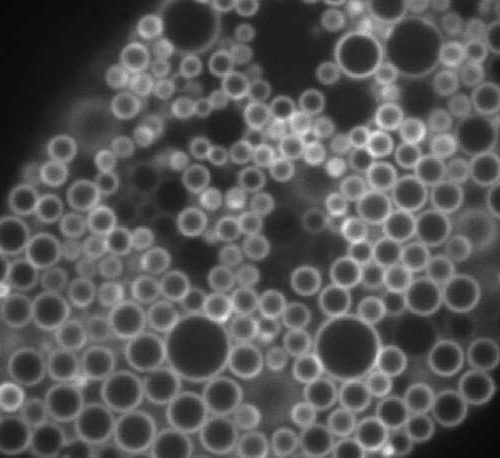
by Howard Hughes Medical Institute In suspense novels, the most unassuming character sometimes turns out to be a mastermind, influencing events without attracting attention. That same storyline may be afoot in cells as well: an unglamorous fat-storing droplet appears to have a surprise role in controlling gene activity. The droplets prevent cells from activating genes...
Tag: <span>metabolism</span>
Targeting cholesterol metabolism in macrophages to eliminate viral infection
CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES HEADQUARTERS Recent evidence suggests a link between cholesterol metabolism and innate immunity. Upon viral infection, macrophages show reduced cholesterol synthesis accompanied by enhanced expression of antiviral genes, including type I interferon (IFN-I). IFN-I can induce 25-hydroxycholesterol (25-HC) accumulation, which blocks viral entry. However, it has been unclear whether other cholesterol-associated metabolic...
New automated method helps identify cancer cell metabolism inhibitors
Reviewed by James Ives, M.Psych. (Editor) UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center researchers have developed a new automated method for testing hundreds of molecules at a time to find out which ones block cancer cells from consuming glucose – the sugars they need to spread and grow. Using robotics, the researchers tested 3,555 compounds on non-small-cell...
Nutrition or pathogen? Balancing healthy metabolism and stress resistance
by Beth Newcomb, University of Southern California A new study led by the USC Leonard Davis School of Gerontology indicates that the negative long-term metabolic effects of fighting off infections could be mitigated by tweaking how a gene called SKN-1 directs cells to respond to stressors. A previous study in Caenorhabditis elegans in the laboratory...
Anti-obesity effect of resveratrol and quercetin metabolites
by University of the Basque Country Resveratrol and quercetin are two functional ingredients to which a fat-reducing effect has been attributed in experiments conducted in vivo and in vitro. Yet their rapid metabolism means that only a tiny fraction of these compounds reach organs and tissue. Now, a new study suggests that their metabolism should...
Scientists discover new way to promote insulin production in pre-diabetes phase
by Nanyang Technological University Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) scientists have discovered that a type of immune cell known as a pancreatic islet macrophage is capable of promoting insulin production during the pre-diabetes phase. The scientists believe that the macrophages could be harnessed through new targeted treatments to prevent type 2 pre-diabetic patients from...
New finding offers possibility for preventing age-related metabolic disease
by Brita Belli, Yale University A study by researchers at Yale has uncovered why belly fat surrounding organs increases as people age, a finding that could offer new treatment possibilities for improving metabolic health, thereby reducing the likelihood for diseases like diabetes and atherosclerosis that stem from inflammation. Led by Dr. Vishwa Deep Dixit, the...
Brain-to-pancreas signalling axis links nicotine and diabetes
The discovery of a signalling axis that connects nicotine responses in the brain with glucose metabolism by the pancreas sheds light on why cigarette smoking increases the risk of diabetes. One of the many dangers of smoking is an increased risk of diabetes, because nicotine uptake leads to altered glucose metabolism and increased blood sugar...
Increase health benefits of exercise by working out before breakfast
by University of Bath According to a new study, published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, health scientists at the Universities of Bath and Birmingham found that by changing the timing of when you eat and exercise, people can better control their blood sugar levels. The six-week study, which involved thirty men classified...
A comprehensive atlas of genetic regulation of lipid metabolism published
UNIVERSITY OF HELSINKI An international research team has identified several novel genetic variants associated with plasma levels of lipid species and cardiovascular disease risk in humans. The study demonstrates that genetic studies focusing on circulating molecular lipid levels over traditional lipid measures can help improve cardiovascular risk prediction and treatment. The results of the study...