The aging of the vasculature has detrimental effects on organs throughout the body. The most structurally apparent issue is that of atherosclerosis, the buildup of fatty deposits that narrow and weaken blood vessels. This ultimately leads to heart failure, stroke, heart attack, and death. A close second is the stiffening of blood vessels, due to a variety of processes such as cross-linking to reduce elasticity in...
Tag: <span>mice</span>
Hope for infertile men; mice could hold the secret
THE COMPANY OF BIOLOGISTS Male infertility affects more than 20 million men globally and is a contributing cause to around 50% of infertility in couples. Frequently, male infertility is the result of defects in the sperm tail, the flagellum, which allows the sperm to swim toward an egg. Males with severe infertility can experience multiple...
An asthma vaccine effective in mice
INSTITUT PASTEUR Inserm teams led by Laurent Reber (Infinity, Toulouse) and Pierre Bruhns (Humoral Immunity, Institut Pasteur, Paris) and French company NEOVACS have developed a vaccine that could induce long-term protection against allergic asthma, reducing the severity of its symptoms and thus significantly improving patient quality of life. Their research in animals has been published in the...
New strategy blocks chronic lung disease in mice
WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE IMAGE: Shown is a transmission electron microscope image of exosomes purified from fluid from the lungs of a patient with COPD. A new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis has uncovered a previously unknown role for exosomes in inflammatory respiratory diseases. The study has implications for...
Scientists reverse deadly impacts of asthma in mice
by CU Anschutz Medical Campus Credit: CC0 Public Domain Mucus in the lungs can be fatal for asthma patients, but scientists at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have broken up those secretions at the molecular level and reversed their often deadly impacts. In a study published Monday in the journal Nature Communications, the researchers explained how they...
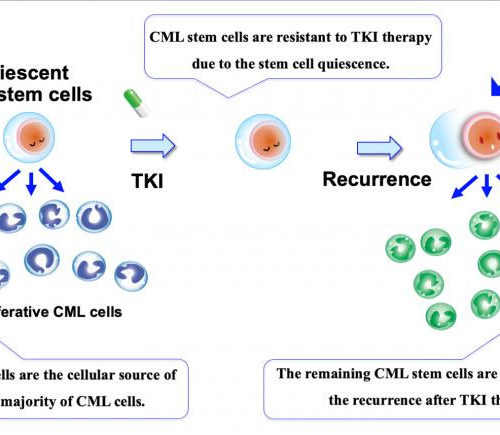
New way to halt leukemia relapse shown promising in mice
HIROSHIMA UNIVERSITY IMAGE: CML STEM CELLS, WHICH ARE THE CELLULAR SOURCE OF THE VAST MAJORITY OF CML CELLS, ARE REPORTEDLY RESISTANT TO TKI THERAPY DUE TO THE STEM CELL QUIESCENCE. THUS, THE REMAINING. Researchers have identified a second path to defeating chronic myelogenous leukemia, which tends to affect older adults, even in the face of...
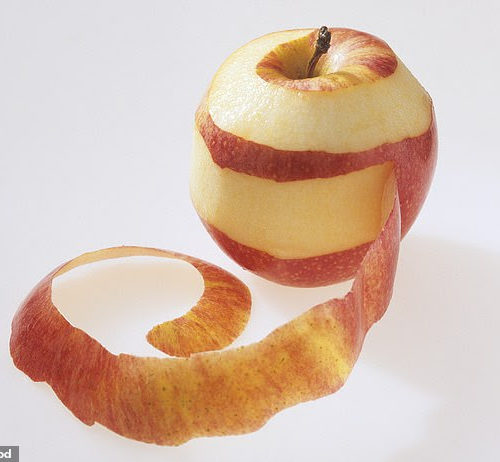
Why an apple a day could keep multiple sclerosis away: Compound that gives the fruit’s skin its sheen could help reverse devastating damage caused by the disease
Chemical found in apple peel could transform multiple sclerosis treatment Compound could be turned into the first drug that reverses disease’s damage Testing on mice, paralysed animals given ursolic acid were able to walk again A chemical in apple peel could transform the treatment of multiple sclerosis, research reveals. The compound that gives apple skin...
Inhalation therapy shows promise against pulmonary fibrosis in mice, rats
NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIVERSITY A new study from North Carolina State University shows that lung stem cell secretions – specifically exosomes and secretomes – delivered via nebulizer, can help repair lung injuries due to multiple types of pulmonary fibrosis in mice and rats. The work could lead to more effective, less invasive treatment for human...
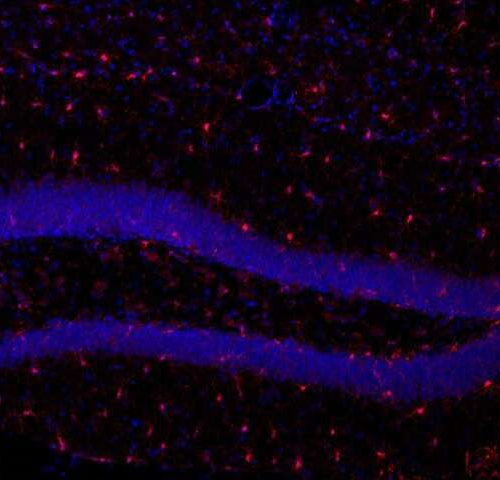
Study in mice: Brain cells long thought of as passive play key role in memory
by Mark Dallas, The Conversation Microglia are resident immune cells in your brain that act as first responders, always on the lookout for trouble. Accounting for about 10% of our brain cells, they were historically thought of as passive bystanders in the brain until injury or infection kicked them into action. These cells were first...
Inputs to the motor cortex make dexterous movements possible in mice
HOWARD HUGHES MEDICAL INSTITUTE In a sleepy haze, reaching out and grabbing the coffee cup in front of you seems to happen on autopilot. But your caffeine-deprived brain is working hard. It’s collecting sensory information and other kinds of feedback – clues about where your arm is in space relative to the mug – and...