UNIVERSITY OF GOTHENBURG THIS IS FREDRIK BACKHED, PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, UNIVERSITY OF GOTHENBURG. view more CREDIT: PHOTO BY JOHAN WINGBORG The individual mix of microorganisms in the human gastrointestinal tract provides vital clues as to how any future incidence of type 2 diabetes can be predicted, prevented and treated. This is demonstrated in a population...
Tag: <span>microbiota</span>
Location, location, location: Even gut immune response is site-specific
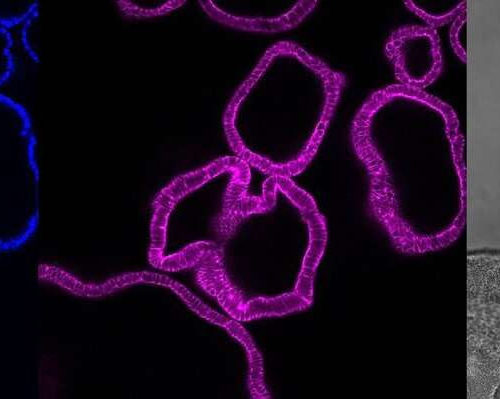
by Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg The pictures show the same stomach organoids: It shows the cell nuclei (blue) and the skeleton of the cell (pink) as a cross-section of the organoids. In grey is the microscopic picture of the organoids. A single organoid here is about a quarter millimeter in size. Credit: Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg, JMU Why is...
SARS-CoV-2: New insights on antibody testing and RNA testing
Washington, DC – June 20, 2020 – Two types of tests are used to track SARS-CoV-2. Reverse transcriptase PCR (rt-PCR) tests for current infection. Antibody tests reveal that an infection has taken place, even long after the fact. Each of 2 papers published in the Journal of Clinical Microbiology (JCM) addresses one of these testing...
Improved gut microbiota with cholesterol-lowering medication
by Margareta Gustafsson Kubista, University of Gothenburg There is a clear link between improved gut microbiota and one of our most common cholesterol-lowering drug groups: statins. This is evident from a European study involving researchers from the University of Gothenburg. Scientists have previously found an association between the gut microbiota and various metabolism-related and cardiovascular...
Researchers discover key player in hepatitis A virus infection
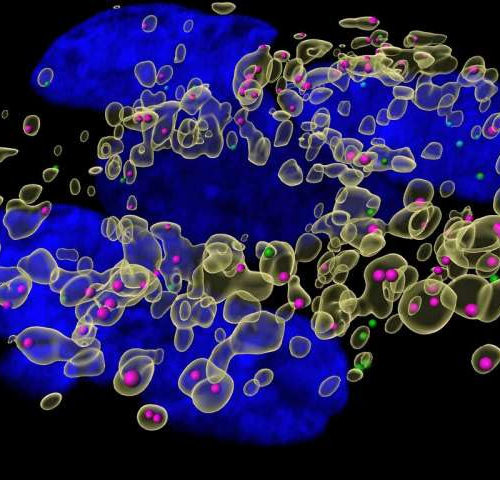
by University of North Carolina Health Care Hepatitus A virus particles (pink) trapped in lysosomes (yellow intracellular organelles), unable to initiate replication in the cytoplasm of cells due to UCGC enzyme being knocked out. Credit: Maryna Kapustina, PhD, UNC School of Medicine How hepatitis A virus (HAV) manages to enter liver cells called hepatocytes and...
New testing system predicts septic shock outcomes
by Emily Ayshford, University of Chicago More than 1.7 million Americans develop sepsis each year, and more than 270,000 die from it. The condition—which happens when the body has an extreme response to a bacterial or viral infection, causing a chain reaction that can lead to organ failure and death—has few strategies for treatment. That’s...
Effects of a Gluten-Free Diet on the Gut Microbiota
By Dr. Maho Yokoyama, Ph.D.Reviewed by Michael Greenwood, M.Sc. Why a Gluten Free Diet? Gluten is a protein found in grains such as wheat, barley, and rye, and is comprised of gliadins. For some people, eating foods that contain gluten can cause digestive problems due to gluten-related disorders. Gluten-related disorders can range from mild to severe in symptoms, and include celiac disease...
How whipworms wreak havoc on the gut
Signaling through interleukin-10 (IL-10) receptors on gut immune cells plays a critical role in protecting the gut lining and microbiota from disruption caused by whipworms, according to a study published January 31 in the open-access journal PLOS Pathogens by María Duque-Correa of the Wellcome Sanger Institute in the UK, and colleagues. The human gut is...
Probiotics, Fecal Transplant Promising in Ulcerative Colitis
PHILADELPHIA — The probiotic VSL#3 and fecal microbiota transplantation could help induce remission in patients with ulcerative colitis, according to a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. There is “abundant evidence” that the intestinal microbiome plays an integral role in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis, said Mina Fransawy Alkomos, MD, from New York...
Improved early diagnosis and treatment for Graves’ orbitopathy
Despite Graves’ disease and Graves’ orbitopathy affecting around 3 million Europeans and costing billions of euros, treatments can only control symptoms. INDIGO identified risk factors, studied microbiota composition and tested probiotics to improve health outcomes. Credit: Perception7, Shutterstock Graves’ disease (GD)—the commonest cause of an overactive thyroid gland—is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by the...