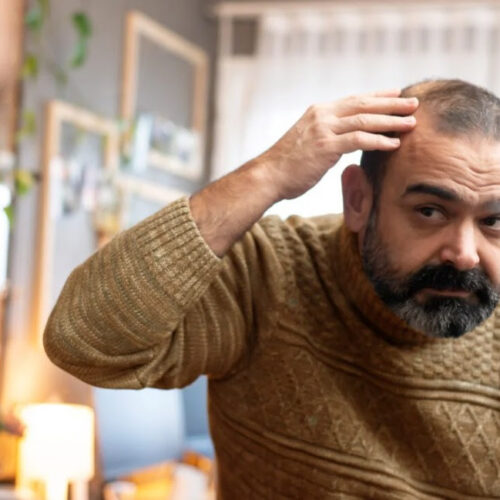
SScientists may have discovered a breakthrough treatment that could help reverse hair loss by using microRNA. herkisi/Getty Images Scientists have discovered that a type of microRNA may help treat hair loss. This microRNA could aid hair regrowth by softening hair follicles, which naturally become stiffer as we age and contribute to hair loss. According to...
Tag: <span>microRNA</span>
Softening stiff hair follicle stem cells with a microRNA regrows hair
by Northwestern University Credit: CC0 Public Domain Just as people’s joints can get stiff as they age and make it harder for them to move around, hair follicle stem cells also get stiff, making it harder for them to grow hair, reports a new Northwestern Medicine study. But if the hair follicle’s stem cells are softened, they are...
Boosting the effects of a particular microRNA may benefit patients with cervical cancer
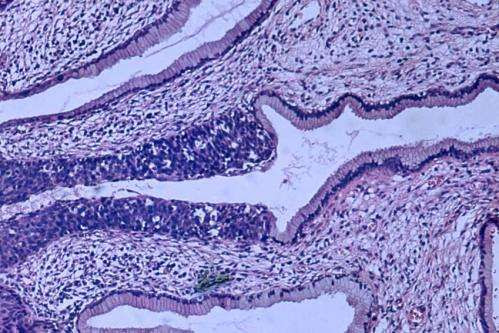
by Wiley High grade dysplasia (carcinoma in situ) in the uterine cervix. The abnormal epithelium is extending into a mucus gland to the left of centre. This disease can progress to invasive cancer (squamous cell carcinoma) of the cervix. Credit: Haymanj/public domain Dysregulation of microRNAs, which are molecules involved in controlling gene expression, can promote...
MicroRNA can help predict which breast cancer patients are more likely to see their cancer come back
by American College of Surgeons Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain MicroRNA (miRNA) can be used as a biomarker to predict which patients are likely to face breast cancer recurrence and mortality, according to study results published online ahead of print in the Journal of the American College of Surgeons (JACS). While long-term outcomes have improved for patients...
The MicroRNA Content of Exosomes in the Context of Aging
Much of the communication between cells is carried in extracellular vesicles, membrane-wrapped packages of signaling molecules. Vesicles are classified by size at present, though the nomenclature is often used confusingly and inconsistently. Exosomes are one class of smaller and frequently studied vesicle. Since it is now comparatively cheap to analyze the contents of vesicles obtained from blood samples,...
Silencing of an ALS gene safely delivered to patients in new study
by Jim Fessenden, University of Massachusetts Medical School UMass Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital are the first to safely treat two research participants with a synthetic microRNA, delivered into the spinal fluid, designed to silence a human disease-causing gene. Details of the treatment, which targeted the mutant SOD1 gene that causes ALS, appear in...
How a microRNA protects vascular integrity
by Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich Short RNA molecules known as microRNAs (miRNAs) play a vital role in the regulation of gene expression. Anomalies in miRNAs expression and function have been implicated in pathological processes, such as the development of chronic diseases like atherosclerosis. The regulatory functions of miRNAs usually take place in the cytoplasm,...
Breakthrough article on mechanistic features of microRNA targeting and activity
Confocal microscopy image of worms carrying fluorescent reporters that allow monitoring of miRNA activity in vivo. Giovanna Brancati and Helge Grosshans from the FMI have described target specialization of miRNAs of the let-7 family. They identified target site features that determine specificity, and revealed that specificity can be modulated in a manner that allows cells...
Newly Discovered MicroRNA Regulates Mobility of Tumor Cells
Cancer cells can reactivate a cellular process that is an essential part of embryonic development. This allows them to leave the primary tumor, penetrate the surrounding tissue and form metastases in peripheral organs. In the journal Nature Communications, researchers from the University of Basel’s Department of Biomedicine provide an insight into the molecular networks that regulate...
microRNA may reduce stroke risk
The molecule microRNA-210 stabilises deposits in the carotid artery and can prevent them from tearing. Thus, it may prevent dangerous blood clots from forming. This is what scientists headed by Prof. Lars Mägdefessel, Professor of Vascular Biology at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and head of a junior scientist group in the German Centre...