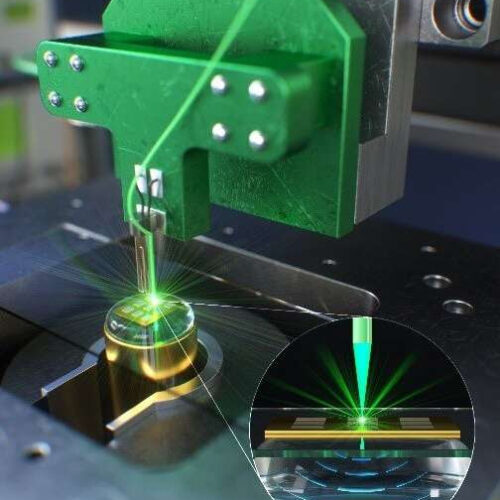
by Pohang University of Science & Technology (POSTECH) A microscope system that uses optical fibers instead of lenses. Credit: POSTECH Newly developed photoacoustic microscopy uses vibrations generated when light is absorbed and captures images of cells or blood vessels. This development has increased the possibility of peering inside the body without contrast agents. However, obtaining...
Tag: <span>microscope</span>
What causes long COVID symptoms? Clues from under the microscope
by University of New South Wales The findings may validate some of the symptoms that people with long COVID experience, the authors say. Credit: Shutterstock A team from UNSW’s Kirby Institute and St Vincent’s Hospital Sydney have uncovered an immune profile for long COVID, potentially paving the way for tailored treatment for those with ongoing...
Fat crystals trigger chronic inflammation
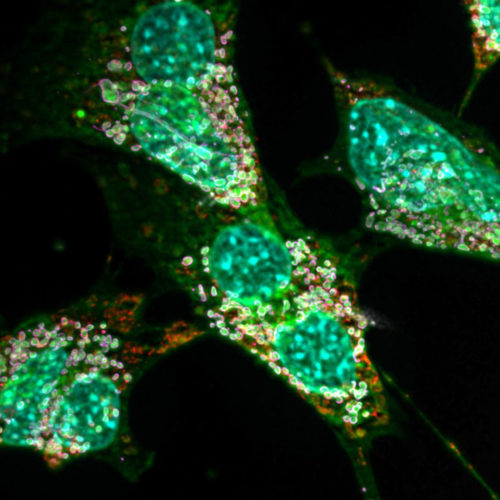
Scientists at the University of Bonn identify previously unknown disease mechanism UNIVERSITY OF BONN DEOXYSPHINGOLIPIDS (GREEN) INTERFERE NOT ONLY WITH THE WORK OF THE MITOCHONDRIA (RED) BUT ALSO WITH CELL DIVISION. SOME OF THEM THEREFORE HAVE TWO NUCLEI (TURQUOISE). view more CREDIT: © AG KÜRSCHNER/UNIVERSITÄT BONN A congenital disorder of the fat metabolism can apparently...
Scientists say Hong Kong man got coronavirus a second time
by Marilynn Marchione This electron microscope image made available and color-enhanced by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Integrated Research Facility in Fort Detrick, Md., shows Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 virus particles, orange, isolated from a patient. University of Hong Kong scientists claim to have the first evidence of someone being reinfected with the...
Silky material uses magnetic particles to regrow bone
Silky material uses magnetic particles to regrow bone By Ben Coxworth August 10, 2020 It was just a couple of months ago that we heard about an implantable material that electrically stimulates bone cells, causing them to reproduce. Now, scientists have created a similar substance that utilizes magnetism. There are already a number of experimental...
Mechanically Stimulating Neurons Using Magnetic Nanodiscs
Electrical stimulation and chemical pharmaceuticals are the two ways that doctors and scientists routinely use to manipulate neural cells. Chemicals have their side effects, are slow to take effect, and are usually systemically delivered, while electrical stimulation usually requires invasive wires, is limited in its resolution, and is nearly impossible to administer within certain parts...
New technique in which drugs make bacteria glow could help fight antibiotic resistance
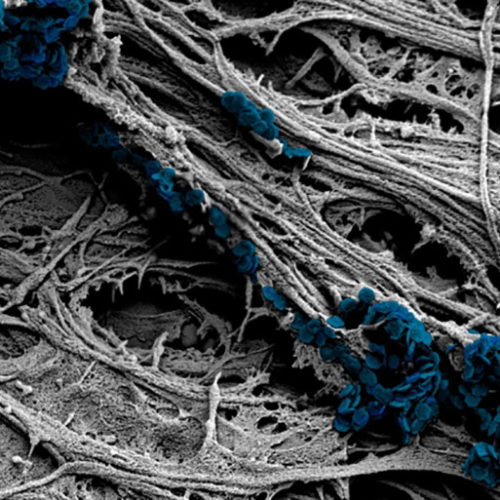
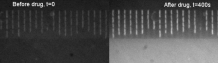
A new technique could help reduce antibiotic prescribing by predicting which drugs could be effective in fighting bacteria within minutes. Scientists at the University of Exeter have developed the method, which allows users to see whether a bacterium is likely to respond to antibiotics. The research is currently in early stages of development, and the...
Researchers develop microscopy technique for noninvasive evaluation of wound healing
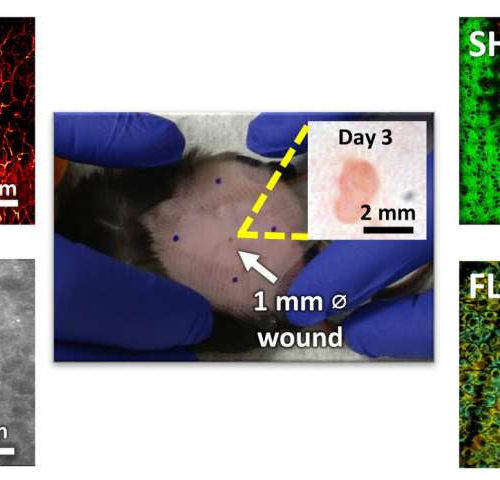
by Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology Researchers at the GSK Center for Optical Molecular Imaging have developed a new microscope that looks at the different parameters that change during wound healing. They hope to use this technique to understand how skin disorders, such as foot ulcers in diabetic patients and psoriasis, can be...
CAR T cell therapy: potential for considerable savings
GERMAN CANCER RESEARCH CENTER (DEUTSCHES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENTRUM, DKFZ) Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy is a new and in some cases highly effective form of immunotherapy to treat certain types of cancer of the blood and lymph system. This promising treatment comes at a cost, however: The manufacturers charge up to EUR 320,000 for the...
How chandelier cells light up the brain
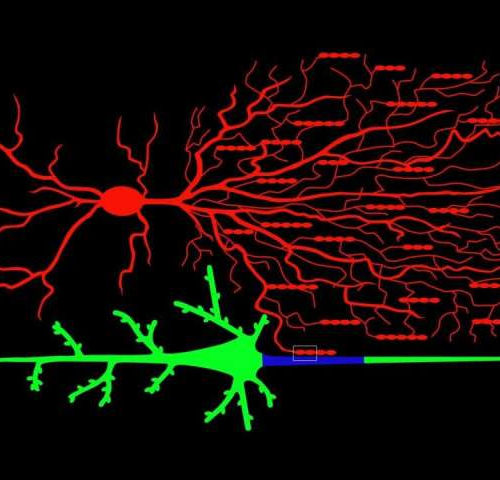
by Jennifer Michalowski, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Illustration of a chandelier cell (on top in red) connecting to a pyramidal neuron (in green on the bottom) on its axonal initial segment (in blue). Credit: CSHL Within the intricate network of cells that make up the brain, chandelier cells stand out for their elaborate, branching structure....
- 1
- 2