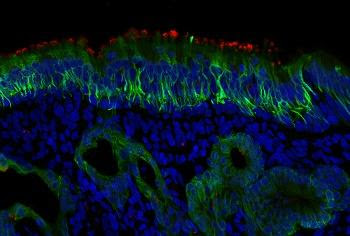
JOHNS HOPKINS MEDICINE RED STAIN IS ACE2. THE GREEN PROBE IS STAINING CK18, WHICH IS FOUND IN SUPPORTING CELLS AND MUCUS GLANDS. view more CREDIT: PHOTO BY MENGFEI CHEN Scientists at Johns Hopkins Medicine, experimenting with a small number of human cell samples, report that the “hook” of cells used by SARS-CoV-2 to latch onto...
Tag: <span>MICROSCOPY</span>
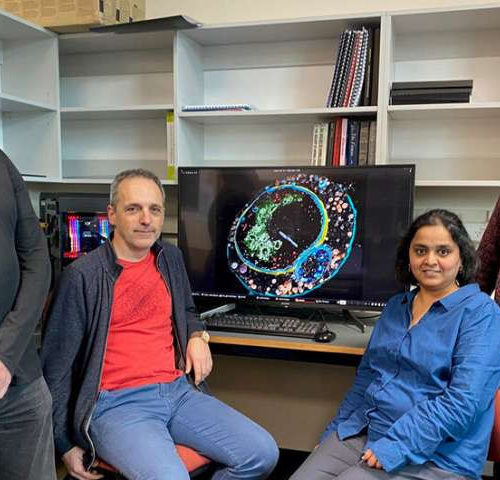
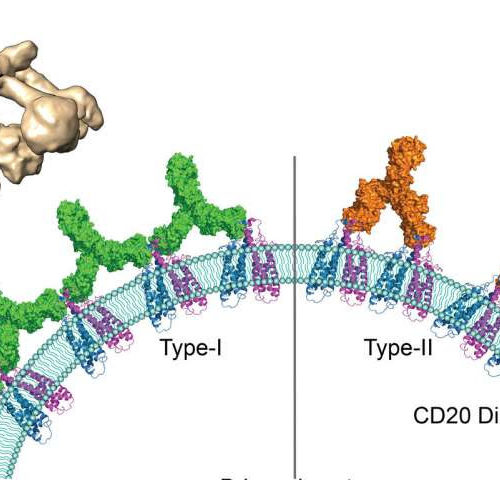
The behaviour of therapeutic antibodies in immunotherapy
Since the late 1990s, immunotherapy has been the frontline treatment against lymphomas where synthetic antibodies are used to stop the proliferation of cancerous white blood cells. However, in the more than 20 years since their use began, the molecular mechanisms that underlie this therapy are still little understood. For the first time, scientists from the...
The behavior of therapeutic antibodies in immunotherapy
by CNRS Human antigen CD20 molecules (blue and pink) expressed on the surface of B cells are recognised by type 1 (green), and type 2 (orange) therapeutic antibodies. Only type 1 antibodies can potently recruit complement C1 component (light brown) to elicit complement pathway. Credit: Nicolas Reyes Since the late 1990s, immunotherapy has been the...
Virus uses decoy strategy to evade immune system, research reveals
by University of Otago University of Otago researchers have learnt more about how viruses operate and can evade the immune system and are now using their discovery to help learn more about COVID-19. The recent research, led by Dr. Mihnea Bostina and Ph.D. student Sai Velamoor from the Department of Microbiology and Immunology and Otago...
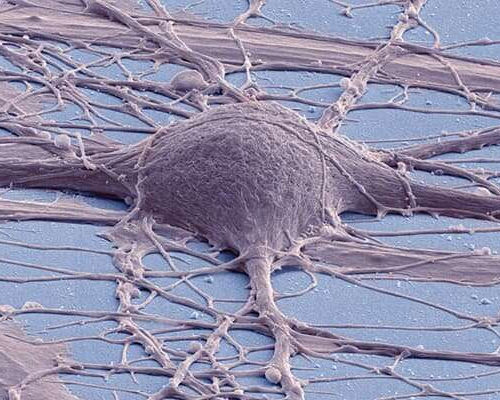
Implanted neural stem cell grafts show functionality in spinal cord injuries
by University of California – San Diego Colorized scanning electron micrograph of a cultured human neuron. Credit: Thomas Deerinck, UC San Diego National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Using stem cells to restore lost functions due to spinal cord injury (SCI) has long been an ambition of scientists and doctors. Nearly 18,000 people in the...
New indication of a link between Alzheimer’s and diabetes
by Forschungszentrum Juelich Pathological protein clumps are characteristic of a series of diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and type 2 diabetes. Scientists at Forschungszentrum Jülich, Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf, and Maastricht University have now used cryo-electron microscopy to obtain a sharp image for the first time of how individual molecules are arranged in...
‘It opens up a whole new universe’: Revolutionary microscopy technique sees individual atoms for first time
A game-changing technique for imaging molecules known as cryo-electron microscopy has produced its sharpest pictures yet — and, for the first time, discerned individual atoms in a protein. By achieving atomic resolution using cryogenic-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), researchers will be able to understand, in unprecedented detail, the workings of proteins that cannot easily be examined by...
BLUE LIGHT COULD BE THE ‘NEXT FRONTIER’ IN SUPERBUG FIGHT
Scientists are locked in a high-stakes race against bacterial evolution, racing against adversaries that can spawn a new generation in less time than it takes to wash a load of laundry. New strains of antibiotic-resistant pathogens emerge faster than we can develop drugs to fight them, and experts warn that there may come a day...
Ultra-precision nano-sensor could detect iron disorders
Chronic iron imbalances – having either too little or too much iron in the blood – can result in medical conditions ranging from anaemia and haemochromatosis through to more severe diseases, such as cancer, Parkinson’s Disease and Alzheimer’s Disease. Haemochromatosis is one of Australia’s most common hereditary diseases and the Australian Bureau of Statistics estimates...
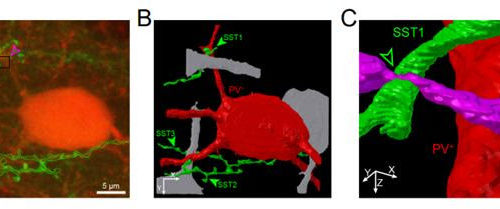
A study finds neuropeptide somatostatin enhances visual processing?
By: PROFESSOR SEUNG-HEE LEE, KAIST Researchers have confirmed that neuropeptide somatostatin can improve cognitive function in the brain. A research group of Professor Seung-Hee Lee from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST found that the application of neuropeptide somatostatin improves visual processing and cognitive behaviors by reducing excitatory inputs to parvalbumin-positive interneurons in the...
- 1
- 2