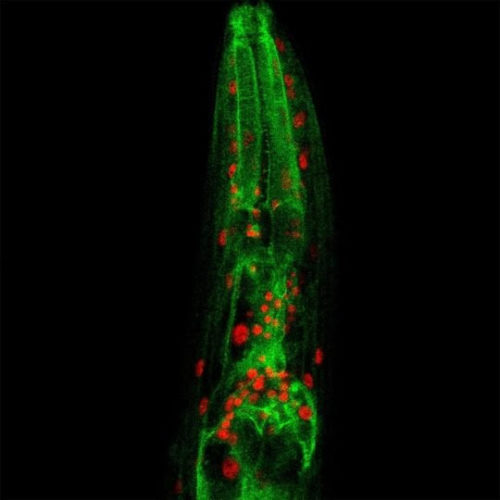
by Karuna Meda, Thomas Jefferson University Patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, lose muscle control as nerve cells or neurons in the brain and spinal cord degenerate and can no longer send signals to muscles. Previous studies have identified that problems at the synapse, the point where signals jump...
Tag: <span>molecular</span>
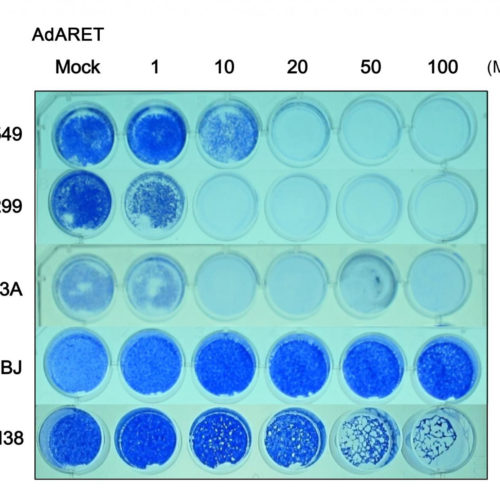
Exploiting viruses to attack cancer cells
An adenovirus is now better able to target and kill cancer cells due to the addition of an RNA stabilizing element. Hokkaido University scientists have made an adenovirus that specifically replicates inside and kills cancer cells by employing special RNA-stabilizing elements. The details of the research were published in the journal Cancers. Much research in...
The self-synthesizing ribosome
As the cell’s protein factory, the ribosome is the only natural machine that manufactures its own parts. That is why understanding how the machine, itself, is made, could unlock the door to everything from understanding how life develops to designing new methods of drug production. An intensive, long research effort at the Weizmann Institute of...
What if we could design powerful drugs without unwanted side effects?
Psychedelics such as LSD and magic mushrooms have proven highly effective in treating depression and post-traumatic stress disorders, but medical use of these drugs is limited by the hallucinations they cause. “What if we could redesign drugs to keep their benefits while eliminating their unwanted side effects?” asks Ron Dror, an associate professor of computer...
New liver cancer research targets non-cancer cells to blunt tumor growth
by Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania “Senotherapy,” a treatment that uses small molecule drugs to target “senescent” cells, or those cells that no longer undergo cell division, blunts liver tumor progression in animal models according to new research from a team led by Celeste Simon, Ph.D., a professor of Cell and...
Novel tool developed to diagnose and monitor autoimmune disorders
Researchers from Prokhorov General Physics Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences and the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology have developed a novel method for diagnosing and monitoring autoimmune disorders. Within a mere 25 minutes, their new biosensor not only measures the concentration of autoantibodies in human blood serum with extremely high sensitivity, but...
Subcellular chatter regulates longevity
As people get older, they often feel less energetic, mobile or active. This may be due in part to a decline in mitochondria, the tiny powerhouses inside of our cells, which provide energy and regulate metabolism. In fact, mitochondria decline with age not only in humans, but in many species. Why they do so is...
HKBU scientists eliminate drug side effects by manipulating molecular chirality
Scientists from Hong Kong Baptist University (HKBU) have developed a novel technique that can produce pure therapeutic drugs without the associated side effects. The approach, which uses a nanostructure fabrication device, can manipulate the chirality of drug molecules by controlling the direction a substrate is rotated within the device, thus eliminating the possible side effects...
Unusual immune response in bladder appears to drive repeat UTIs
by Sarah Avery, Duke University As many people know, bladder infections can be a painful and recurring condition, and those who are prone to the infections often report they have to “go” with greater frequency and urgency. These two related conditions are caused by an aberrant immune response that prioritizes repairing tissue in the bladder...
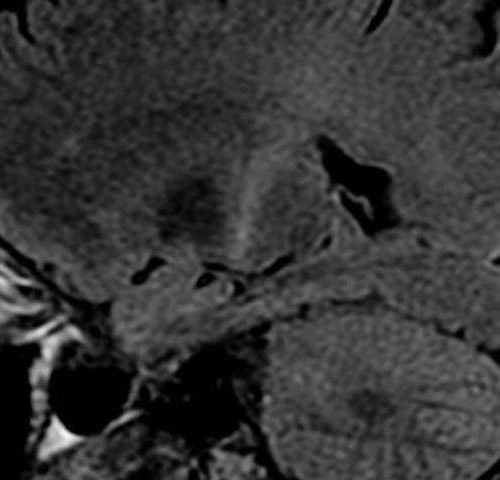
Mechanism behind upper motor degeneration revealed
CHICAGO — Scientists from Northwestern Medicine and the University of Belgrade have pinpointed the electrophysiological mechanism behind upper motor neuron (UMN) disease, unlocking the door to potential treatments for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and other neurodegenerative diseases, such as Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia and Primary Lateral Sclerosis. The study, published in Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience on...