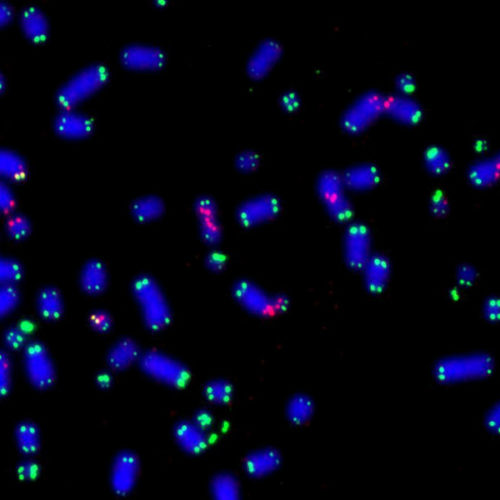
by Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT scientists have identified a potential new strategy for treating Fragile X syndrome, a disorder that is the leading heritable cause of intellectual disability and autism. In a study of mice, the researchers showed that inhibiting an enzyme called GSK3 alpha reversed many of the behavioral and cellular features of...
Tag: <span>molecular</span>
ONE PROTEIN EASES PROBLEMS WHEN CANCER CELLS DIVIDE
Two important functions of the protein RTEL1 during cancer cell division could help pinpoint new cancer treatments, researchers report. One of the body’s most important processes is cell division, which occurs throughout life. Normal cells only have a limited number of divisions, while in cancer cells the cell division goes awry and is uncontrollable. Therefore,...
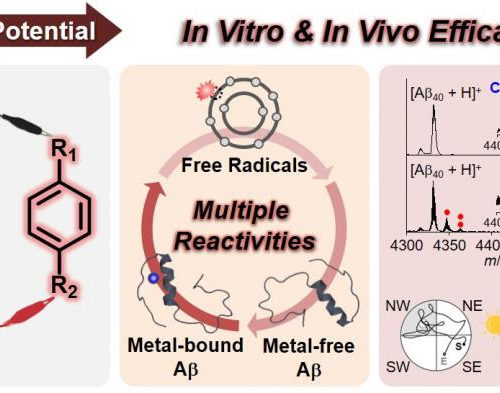
Simple molecular reagents to treat Alzheimer’s disease
CREDIT: PROFESSOR MI HEE LIM, KAIST Sometimes the most complex problems actually have very simple solutions. A group of South Korean researchers reported an efficient and effective redox-based strategy for incorporating multiple functions into simple molecular reagents against neurodegenerative disorders. The team developed redox-active aromatic molecular reagents with a simple structural composition that can simultaneously...
Unraveling one of prion disease’s deadly secrets
AMHERST, Mass. – A molecular biologist at the University of Massachusetts Amherst who has for decades studied the nightmarish group of fatal diseases caused by prions – chronic wasting disease in deer, mad cow in cattle and its human analog – credits a middle-of-the-night dream for a crucial insight, a breakthrough she hopes could lead...
COMBINE COTTON AND SILK FOR THE BEST HOMEMADE MASK
If the fit is right, face masks made of a combination of high thread-count cotton and natural silk fabric or a chiffon weave can effectively filter out aerosol particles, researchers report. In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that people wear masks in public. Because N95...
Reducing early brain inflammation could slow Alzheimer’s progression
CREDIT: GIORGIA MENEGONI, SAPIENZA, UNIVERSITY OF ROME Bethesda, MD – In a new animal study examining Alzheimer’s disease, researchers found that disease progression could be slowed by decreasing neuroinflammation in the brain before memory problems and cognitive impairment were apparent. The new findings point to the importance of developing therapies that target very early stages...
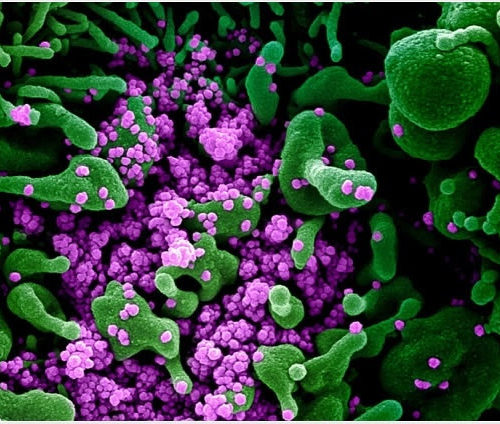
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein discovery could pave way for COVID-19 vaccine
By Sally Robertson, B.Sc Researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati, have made an important discovery about a viral fusion protein found on the surface of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) that could help researchers develop a vaccine. Their finding that a mutation in the protein’s cleavage site disrupts binding to host...
Molecular basis of rare neurological disorder reveals potential treatment
Now, his team has figured out how mutations in this protein, called synaptotagmin-1 or syt1, can lead to a rare condition known as syt1-associated neurodevelopmental disorder. The scientists’ discovery led them to identify a possible treatment, Chapman and his colleagues report May 1, 2020, in the journal Neuron. An email prompted the team’s investigation. In...
Proteins may halt the severe cytokine storms seen in Covid-19 patients
Team designs antibody-like receptor proteins that can bind to cytokines, as possible strategy for treating coronavirus and other infections. One of the defining features of Covid-19 is the excessive immune response that can occur in severe cases. This burst of immune overreaction also called a cytokine storm, damages the lungs and can be fatal. A...
Proteins may halt the severe cytokine storms seen in COVID-19 patients
CAMBRIDGE, MA — One of the defining features of Covid-19 is the excessive immune response that can occur in severe cases. This burst of immune overreaction, also called a cytokine storm, damages the lungs and can be fatal. A team of MIT researchers has developed specialized proteins, similar in structure to antibodies, that they believe...