by Radboud University Nijmegen Silicone molecules from breast implants can initiate processes in human cells that lead to cell death. Researchers from Radboud University have demonstrated this in a new study published on 12 June in Scientific Reports. “However, there are still many questions about what this could mean for the health effects of silicone...
Tag: <span>molecular</span>
New indication of a link between Alzheimer’s and diabetes
by Forschungszentrum Juelich Pathological protein clumps are characteristic of a series of diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and type 2 diabetes. Scientists at Forschungszentrum Jülich, Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf, and Maastricht University have now used cryo-electron microscopy to obtain a sharp image for the first time of how individual molecules are arranged in...
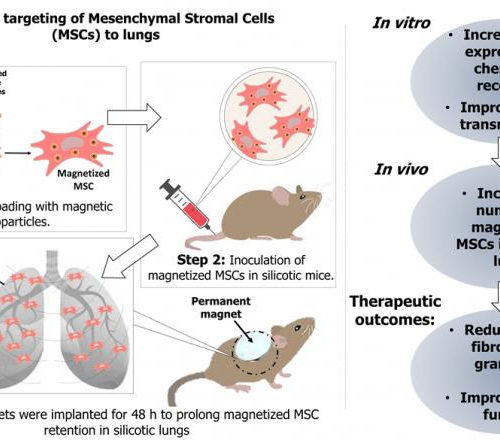
Magnetic guidance improves stem cells’ ability to treat occupational lung disease
Durham, NC – Results of a study released today in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine(SCTM) may point the way to a cure for a serious lung disease called silicosis that affects millions of workers worldwide. Silicosis results from years of breathing in dust microparticles of silica by workers in professions such as construction and sand blasting....
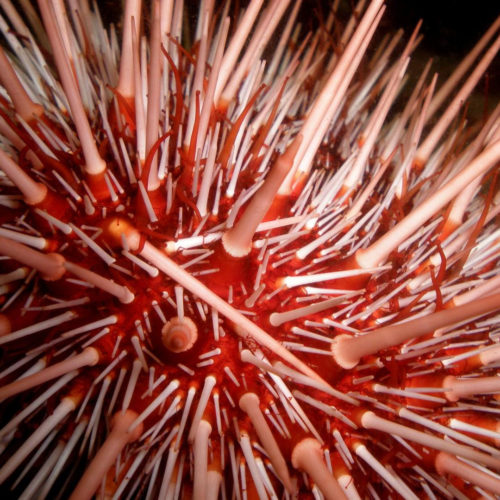
Warburg effect: Sugar-tagging helps drug compounds to target human prostate cancer cells
Scientists of Far Eastern Federal University (FEFU), together with German and Russian colleagues, have developed a lead compound to fight chemotherapy-resistant prostate cancer. The original design comes out as scientists combine biologically active molecules from the chemically modified pigment of sea urchins with glucose molecules to deliver the active drug substance inward the tumor cells....
Creating a new paradigm for understanding the individual effects of diet
by Murdoch University Researchers at the Australian National Phenome Centre at Murdoch University and partners at Imperial College London have made a major breakthrough in understanding how individuals can have different reactions to the same diets. For decades, nutritionists and scientists have been debating whether weight loss is down to sheer will power and healthiness...
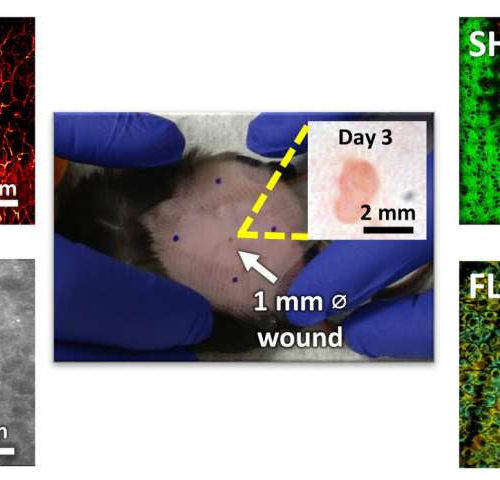
Researchers develop microscopy technique for noninvasive evaluation of wound healing
by Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology Researchers at the GSK Center for Optical Molecular Imaging have developed a new microscope that looks at the different parameters that change during wound healing. They hope to use this technique to understand how skin disorders, such as foot ulcers in diabetic patients and psoriasis, can be...
Coronavirus antibodies may last only two to three months after infection, study suggests
Berkeley Lovelace Jr. @BERKELEYJR Coronavirus antibodies may last only two to three months after a person becomes infected with Covid-19, according to a new study published Thursday in Nature Medicine. Researchers in the Wanzhou District of China compared the antibody response of 37 asymptomatic people with that of 37 symptomatic people. The researchers found people...
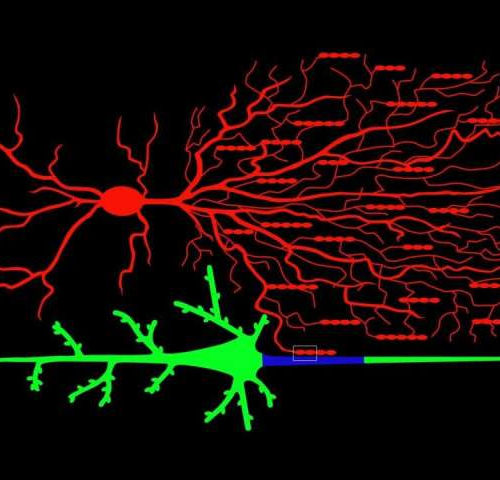
How chandelier cells light up the brain
by Jennifer Michalowski, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Illustration of a chandelier cell (on top in red) connecting to a pyramidal neuron (in green on the bottom) on its axonal initial segment (in blue). Credit: CSHL Within the intricate network of cells that make up the brain, chandelier cells stand out for their elaborate, branching structure....
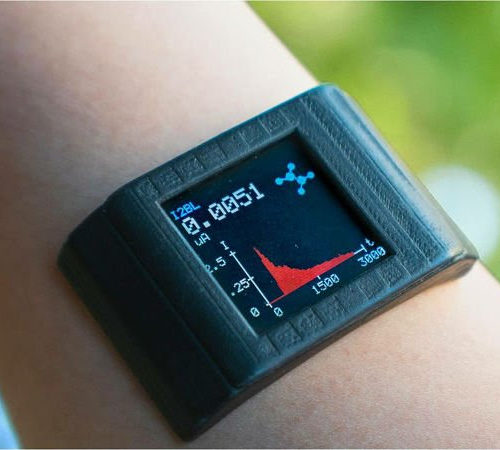
Adhesive film turns smartwatch into biochemical health monitoring system
UCLA engineers have designed a thin adhesive film that could upgrade a consumer smartwatch into a powerful health monitoring system. The system looks for chemical indicators found in sweat to give a real-time snapshot of what’s happening inside the body. A study detailing the technology was published in the journal Science Advances. Smartwatches can already...
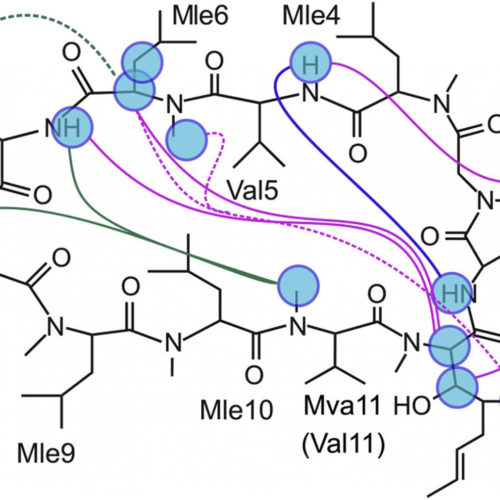
Cyclosporin study may lead to novel ways of approaching mitochondrial dysfunction
Cyclic peptide molecules of the fungal origin called cyclosporins were discovered in 1970’s, and cyclosporin A soon became an important drug due to its immunosuppressive activity. The details of the biochemical reactions involving cyclosporin were elucidated by the beginning of 1990s, but still some aspects of the behavior of this molecule raise questions. Investigation started...