HEBREW SENIORLIFE HINDA AND ARTHUR MARCUS INSTITUTE FOR AGING RESEARCH BOSTON – A new study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism found that age-related accumulation of abdominal fat is associated with lower muscle density. Low muscle density means the muscle has more fat in it, which can lead to less effective muscle function that...
Tag: <span>muscle function</span>
Getting to the heart of heart muscle function
by Nancy Fliesler, Children’s Hospital Boston The heart muscle is studded with tiny dyads that coordinate our heartbeats. New research uncovers a vital component that arranges dyads and holds them together. Credit: Medical images: William Pu, MD. Illustrations: Patrick Bibbins, Boston Children’s Hospital Every heart muscle cell, or cardiomyocyte, is studded with tiny, intricate structures called...
Krill oil may be beneficial to muscle function and size in healthy people over the age of 65
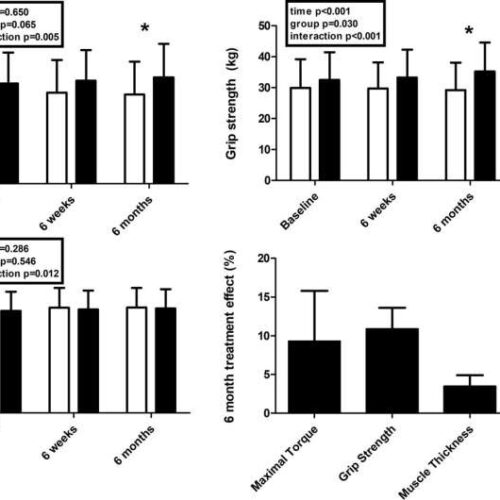
by University of Glasgow Knee extensor maximal torque, grip strength and vastus lateralis muscle thickness at baseline, 6 weeks and 6 months and corresponding 6-month treatment effects in control and krill oil groups. Data are mean (SD) for baseline 6 week and 6-month data and mean (95%CI) for 6-month treatment effects. ∗ denotes a significant...
Researchers Develop Injectable Microtissue to Preserve Muscle Function in Rats with Severed Sciatic Nerves
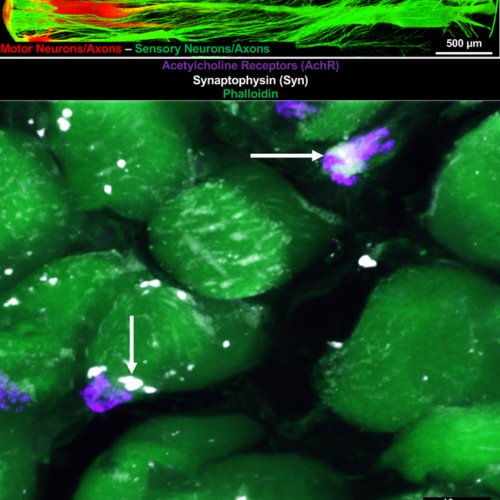
Researchers engineered the first injectable microtissue containing motor and sensory neurons encased in protective tissue, called tissue-engineered neuromuscular interfaces (TE-NMIs). The TE-NMI neurons provide a source of axons to muscles in rats who suffered nerve injuries and “babysit” the muscles to prevent degeneration and loss of function. In contrast, the damaged nerve regrows, according to...
Penn Researchers Develop Injectable Microtissue to Preserve Muscle Function in Rats with Severed Sciatic Nerves
UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE IMAGE: A TE-NMI IN VITRO AND REINNERVATED MUSCLE FIBER AFTER DELAYED NERVE REPAIR FOLLOWING TE-NMI EXCISION. CREDIT: PENN MEDICINE PHILADELPHIA— Researchers engineered the first injectable microtissue containing motor and sensory neurons encased in protective tissue, called tissue engineered neuromuscular interfaces (TE-NMIs). The TE-NMI neurons provide a source of axons...
Tongue Exercise Does Not Help with the Age-Related Decline of Tongue Muscle Function in Rats
Exercise in the form of strength training creates such broad changes in metabolism and produces such diverse benefits to health that it is interesting to see a specific example in which it doesn’t help at all. That is possibly a path to better understanding which of the results of exercise are important, versus which are not, when it comes to functional...
What are electrolyte drinks and how to make them
Electrolytes are minerals such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium. They are present in tissue, blood, and other bodily fluids and are critical for nerve and muscle function, blood pressure regulation, and hydration. Some drinks are naturally rich in electrolytes, while others undergo special formulation to provide electrolytes. The term electrolyte refers to the fact that...
Vitamin D deficiency may impair muscle function
SOCIETY FOR ENDOCRINOLOGY Vitamin D deficiency may impair muscle function due to a reduction in energy production in the muscles, according to a mouse study published in the Journal of Endocrinology. Vitamin D deficient mice were found to have impaired muscle mitochondrial function, which may have implications for muscle function, performance and recovery. This may suggest...
Molecular gatekeepers that regulate calcium ions key to muscle function
CHILDREN’S NATIONAL HOSPITAL Calcium ions are essential to how muscles work effectively, playing a starring role in how and when muscles contract, tap energy stores to keep working and self-repair damage. Not only are calcium ions vital for the repair of injured muscle fibers, their controlled entry into the mitochondria, the cell’s energy powerhouses, spells...