by Ebony Williams, The Atlanta Journal-Constitution Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public DomainBeet juice has been linked to lower blood pressure and reduced inflammation. It’s often sweet and can pair well with a hearty meal, or the powder supplement can be perfectly blended into a shake or smoothie. “A nutritional powerhouse, beets are also packed with fiber and...
Tag: <span>mystery</span>
Unlocking the mysteries of a heart disease trigger
by NIH/National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public DomainAs the body ages, it is normal for changes in cells to occur. “Cells divide every day and mutations happen,” said Emma M. Groarke, M.D., an attending hematologist and researcher in NHLBI’s Hematopoiesis and Bone Marrow Failure Laboratory. “Most of the time they don’t have any...
Uncovering the mysteries of milk allergy
by Madeline McCurry-Schmidt, La Jolla Institute for Immunology Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public DomainCow’s milk allergy is the most common type of food allergy in children—it’s also the weirdest. In all allergies, a person gets sick when immune cells overreact to normally harmless molecules, such as milk proteins, peanut proteins, or cat dander. Immune cells think the offending...
Unraveling the Mystery of Long COVID
Debby Waldman August 09, 2023 After catching COVID-19 for the second time in July 2022, Daniel Lewis suffered persistent headaches, chest pain, and a dangerously high heart rate. He recalls that he was also so exhausted packing for a family wedding that he had to take a break to rest each time he put something into his...
Researchers solve mystery of how statins improve blood vessel health
by Nina Bai, Stanford Cardiovascular Institute Researchers at Stanford Medicine and their colleagues have discovered how statins improve cardiovascular health beyond lowering cholesterol. Credit: Roger Ashford/Shutterstock.com Using new genetic tools to study statins in human cells and mice, Stanford Medicine researchers and collaborators have uncovered how the cholesterol-lowering drugs protect the cells that line blood vessels....
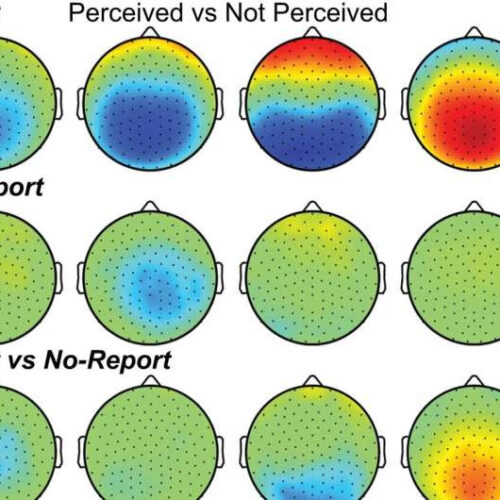
Eyes offer a window into the mystery of human consciousness
by Bill Hathaway, Yale University Cortical and thalamic electrophysiology signals in conscious perception. A–C Scalp topographical plots of high-density scalp EEG showing mean voltage (microvolts; µV) for all statistically significant samples by cluster-based permutation tests (p < 0.05) in four time windows corresponding with the event-related potentials (ERPs) N100 (75-125 milliseconds; ms), visual awareness negativity (VAN; 175–225 ms),...
Study may have solved a mystery surrounding Crohn’s disease
Reviewed by Emily Henderson, B.Sc. Oct 5 2022 A new study may have solved a mystery surrounding Crohn’s disease, a type of inflammatory bowel disease in which immune defenses meant to attack invading microbes instead mistakenly target the body’s own digestive tract. Norovirus, a common infection that causes vomiting and diarrhea, is one of several...
A new theory in physics claims to solve the mystery of consciousness
by Bar-Ilan University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain How do 1.4 kg of brain tissue create thoughts, feelings, mental images, and an inner world? The ability of the brain to create consciousness has baffled some for millennia. The mystery of consciousness lies in the fact that each of us has subjectivity, something that is like to...
“A mystery across the centuries” solved
Since the 1800s, scientists have noted the configuration of centromeres, a special chromosomal region vital for cell division, in the nucleus. However, until this point, the determining mechanisms and the biological significance of centromere distribution were poorly understood. A team led by researchers from the University of Tokyo and their collaborators recently proposed a two-step regulatory...
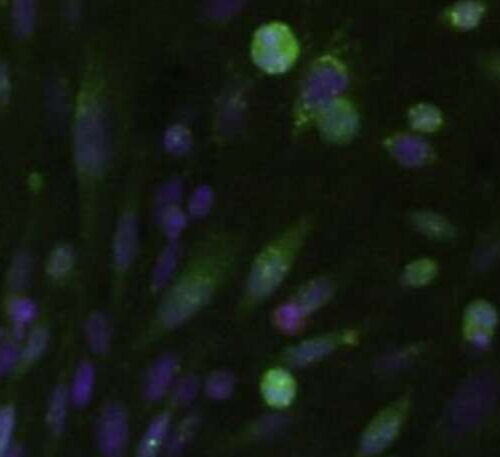
Solving the mystery of a stubborn, and common, cancer gene
by Robin Marks, University of California, San Francisco Microscopic image showing parts of the HER2 receptor touching each other inside the cells (green) and outside the cells (red) in a process called dimerization. The lack of red shows that cells with high levels of HER2 can have a lot of dimerization of their inside halves,...
- 1
- 2