By Michael Irving September 13, 2020 Researchers have shown how to grow gold inside cancer cells in order to kill them Gold isn’t just a pretty face – it’s shown promise in fighting cancer in many studies. Now researchers have found a way to grow gold nanoparticles directly inside cancer cells within 30 minutes, which...
Tag: <span>nanoparticles</span>
Nanoparticles show promise in defeating antibiotic-resistant bacteria, U of T researchers find
A new therapy developed by researchers at the University of Toronto may bring us one step closer to effectively killing deadly drug-resistant superbugs. “The threat posed by pathogens that are increasingly becoming resistant to all known antibiotics is an alarming and pressing health care problem,” says Ruby Sullan, assistant professor in the department of physical...
U of T researchers discover how to get more cancer-fighting nanoparticles to where they’re needed
Researchers in the University of Toronto’s Faculty of Applied Science & Engineering have discovered a dose threshold that greatly increases the delivery of cancer-fighting drugs into a tumour. The findings, published recently in the journal Nature Materials, provide a potentially universal method for gauging nanoparticle dosage and could help advance a new generation of cancer...
How to use ventilation and air filtration to prevent the spread of coronavirus indoors
by Shelly Miller, The Conversation The vast majority of SARS-CoV-2 transmission occurs indoors, most of it from the inhalation of airborne particles that contain the coronavirus. The best way to prevent the virus from spreading in a home or business would be to simply keep infected people away. But this is hard to do when...
Scientists work to freeze-dry synthetic platelets
A Case Western Reserve University scientist, who has for more than a decade pioneered research into synthetic platelet substitutes, has been awarded a $3.8 million grant by the U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) to develop freeze-dried artificial platelets that can treat bleeding in wounded soldiers in the battlefield before they can be taken to a...
Skin cancer treatments could be used to treat other forms of the disease
by Institut national de la recherche scientifique – INRS The creation of a silica nanocapsule could allow treatments that use light to destroy cancerous or precancerous cells in the skin to also be used to treat other types of cancer. Such are the findings of a study by INRS (Institut national de la recherche scientifique)...
Exhaled biomarkers can reveal lung disease
Specialized nanoparticles create a ‘breath signal’ that could be used to diagnose pneumonia and other infectious or genetic diseases MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MA — Using specialized nanoparticles, MIT engineers have developed a way to monitor pneumonia or other lung diseases by analyzing the breath exhaled by the patient. In a study of mice,...
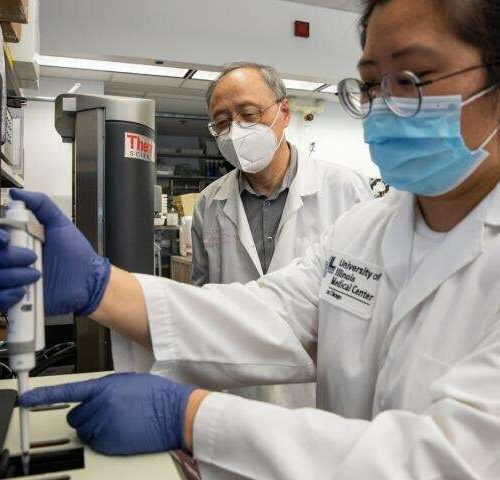
New antiplatelet drug shows promise for treating heart attack
by University of Illinois at Chicago UIC’s Xiaoping Du oversees Ph.D. student Yaping Zhanga enter a sample in an aggregometer in his lab at the College of Medicine Research Building Credit: Joshua Clark/University of Illinois at Chicago Researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago have developed a new drug that prevents blood clots without...
Nanoparticles for Large Gene Therapy to Cure Common Eye Diseases
MEDGADGET EDITORS GENETICS, NANOMEDICINE, OPHTHALMOLOGY Wet age-related macular degeneration and a number of other eye diseases, including congenital conditions, are related to mutated genes that result in blood vessel abnormalities. These can be treated with gene therapy, but delivering genetic material has proven to be difficult when dealing with large gene sequences that are common...
Researchers find more precise way to target tumours with anti-cancer drugs
by Adrianna MacPherson, University of Alberta Researchers at the University of Alberta have found a way to deliver anti-cancer drugs with more precision, which could increase the effectiveness of many cancer treatments. U of A oncologist Frank Wuest altered the surface of nanoparticles, which are well suited to deliver drugs, with epidermal growth factor (EGF),...