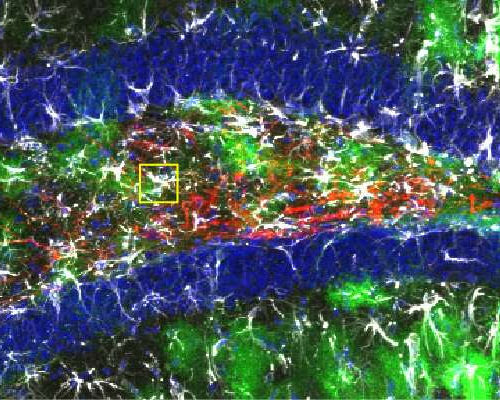
by Mark Derewicz, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine The dentate gyrus houses neural stem cells in a thin zone near the blue-labeled granule cells. Cholecystokinin interneurons (red) extend elaborate processes and release neuropeptide onto astrocytes (green) to induce neurogenesis in brain of adult mouse. Credit: University of North Carolina at Chapel...
Tag: <span>neuroinflammation</span>
Immune Cells in Spinal Fluid of Multiple Sclerosis Patients Identified as Likely Disease Drivers
Results Lay Groundwork for New, More Targeted Immune Therapies. New UC San Francisco research sheds light on how immune system B cells that infiltrate the central nervous system may drive multiple sclerosis (MS), pointing the way to a new generation of targeted immune therapies to halt the progression of the disease. MS is a common...
Study leads to potential for new treatment approach to Alzheimer’s
by University of Kentucky Research looking at a possible new therapeutic approach for Alzheimer’s disease was recently published in the Journal of Neuroinflammation. The paper out of the University of Kentucky’s Sanders-Brown Center on Aging (SBCoA) is titled “Therapeutic Trem2 activation ameliorates amyloid-beta deposition and improves cognition in the 5XFAD model of amyloid deposition”. The...
55% of coronavirus patients still have neurological problems three months later: study
Could the coronavirus lead to chronic illness? While lung scarring, heart and kidney damage may result from COVID-19, doctors and researchers are starting to clock the potential long-term impact of the virus on the brain also. Younger COVID-19 patients who were otherwise healthy are suffering blood clots and strokes. And many “long-haulers,” or COVID-19 patients...
AsEH enzyme: A new pharmacological target against Alzheimer’s disease
Drugs with neuroprotector effects UNIVERSITY OF BARCELONA FROM LEFT TO RIGHT, SANTIAGO VÁZQUEZ, CARLES GALDEANO, MERCÈ PALLÀS AND CHRISTIAN GRIÑÁN-FERRÉ (FACULTY OF PHARMACY AND FOOD SCIENCES/UNIVERSITY OF BARCELONA)…. view more CREDIT: UNIVERSITY OF BARCELONA A UB study published in the journal Neurotherapeutics has validated a new pharmacological target for Alzheimer’s disease. The results show the...
Reducing early brain inflammation could slow Alzheimer’s progression
CREDIT: GIORGIA MENEGONI, SAPIENZA, UNIVERSITY OF ROME Bethesda, MD – In a new animal study examining Alzheimer’s disease, researchers found that disease progression could be slowed by decreasing neuroinflammation in the brain before memory problems and cognitive impairment were apparent. The new findings point to the importance of developing therapies that target very early stages...
Connecting interferon, neuroinflammation and synapse loss in Alzheimer’s disease
by Ana María Rodríguez, Ph.D., Baylor College of Medicine When immunologist Dr. Wei Cao joined Baylor College of Medicine three-and-a-half years ago, her first project was to investigate how inflammation contributes to Alzheimer’s disease. “Alzheimer’s is the most common cause of dementia among older adults. The current understanding is that, in addition to having beta-amyloid...
How stem cell therapy could be a future cure for alcoholism
An animal study has found that stem cell treatment could dramatically reduce alcohol intake suggesting a new treatment for alcoholism An intriguing new study has found that a single dose of human mesenchymal stem cells administered to rats bred to be high alcohol drinkers significantly reduced their voluntary alcohol intake. The research bolsters the growing...
- 1
- 2