by The Mount Sinai Hospital Influence of histone monoaminylation dynamics on circadian gene expression. Credit: Benjamin Weekley, Ph.D., Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai A collaborative effort between Mount Sinai and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center has shed valuable light on how monoamine neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and now histamine help regulate brain physiology...
Tag: <span>neurotransmitter</span>
A calming neurotransmitter can also be excitatory, study finds
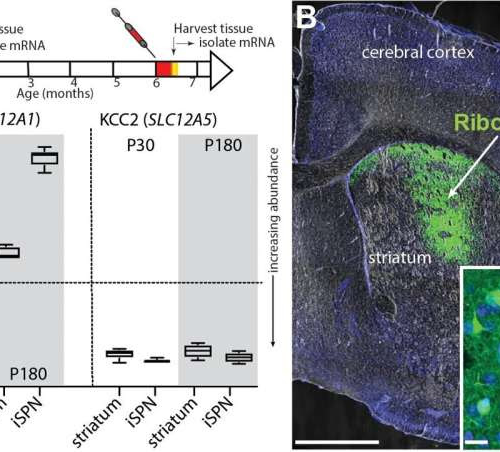
by Olivia Dimmer, Northwestern University KCC2 mRNA is robustly expressed in SPNs, but not NKCC1. Credit: PLOS Biology (2024). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002483A neurotransmitter previously thought only to calm neurons may also play a role in waking them up, according to a study published in the journal PLOS Biology, a discovery which challenges the textbook view of how...
Using brain scans of people on mind-altering drugs to learn more about neurotransmitter systems
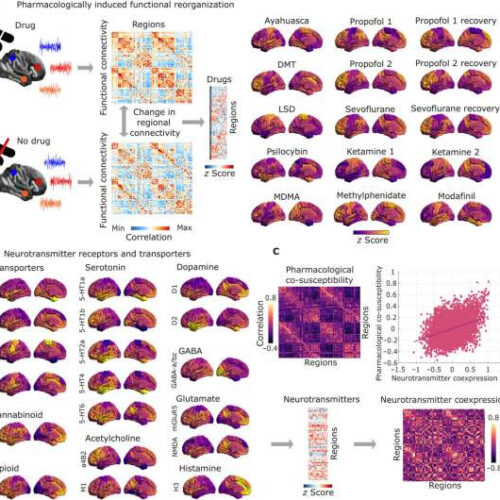
by Bob Yirka , Medical Xpress Overview of receptors and pharmacological rs-fMRI data. (A) For each psychoactive drug, its pattern of pharmacologically induced functional reorganization is quantified as the average (across subjects) of the within-subject difference in regional FC weighted degree (sum of each region’s positive connections) between task-free fMRI scans at baseline and under...
Research team proves how neurotransmitter may be key in controlling Alzheimer’s toxicity
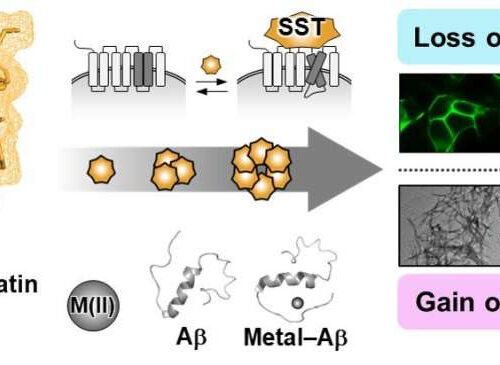
by KAIST Functional shift of somatostatin (SST) by factors in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Credit: KAIST With nearly 50 million dementia patients worldwide, Alzheimers’s disease is the most common neurodegenerative disease. Its main symptom is the impairment of general cognitive abilities, including the ability to speak or to remember. The importance of finding a...
Dopamine’s many roles, explained
ROCKEFELLER UNIVERSITY VIDEO: RESEARCHERS RECORD THE ACTIVITY OF NEURONS IN THE BRAIN’S OLFACTORY LEARNING CENTER (BOTTOM), AS THE FLY RECEIVES A DROP OF SUCROSE. CREDIT: LABORATORY OF NEUROPHYSIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR AT THE ROCKEFELLER UNIVERSITY Among the neurotransmitters in the brain, dopamine has gained an almost mythical status. Decades of research have established its contribution to...
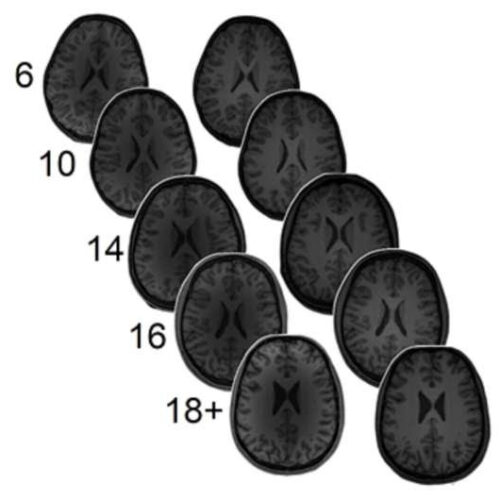
Neurotransmitter levels predict math ability
by Public Library of Science Scanning was completed both during Time 1 and Time 2 (approximately 1.5 years later) in each of the 5 age groups (6-year-olds, 10-year-olds, 14-year-olds, 16-year-olds, and 18+-year-olds). Credit: Zacharopoulos G, et al., 2021, PLOS Biology The neurotransmitters GABA and glutamate have complementary roles—GABA inhibits neurons, while glutamate makes them more active....
Unexpected discovery leads to better understanding of migraine
by University of Utah Health Sciences Credit: CC0 Public Domain Massive “plumes” of glutamate, a key neurotransmitter, surging in the brain could help explain the onset of migraine with aura—and potentially a broad swath of neurologic disease, including stroke and traumatic brain injury—according to an international study led by University of Utah Health scientists. The study,...
Gold nanoparticles to save neurons from cell death
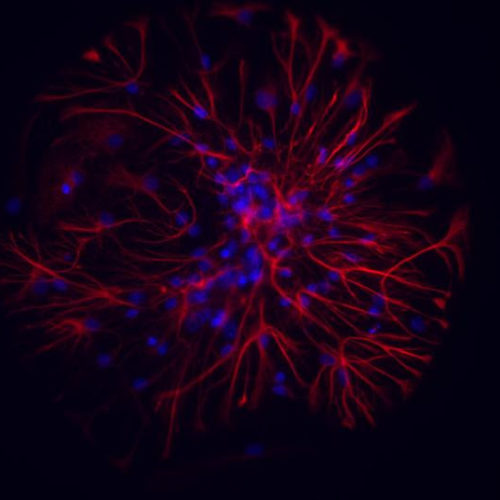
Published on ACS Nano, journal of the American Chemical Society, the study opens important perspectives for treatment of diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s disease, but also epilepsy, brain trauma and stroke. NEURONS AND ATROCYTES UNDER A FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPE view more CREDIT: IIT-ISTITUTO ITALIANO DI TECNOLOGIA Lecce, 25th June 2020 – Gold nanoparticles have been...
Gold nanoparticles to save neurons from cell death
Published on ACS Nano, journal of the American Chemical Society, the study opens important perspectives for treatment of diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s disease, but also epilepsy, brain trauma and stroke. ISTITUTO ITALIANO DI TECNOLOGIA – IIT CREDIT: IIT-ISTITUTO ITALIANO DI TECNOLOGIA Lecce, 25th June 2020 – Gold nanoparticles have been developed in the...
Stanford researchers develop artificial synapse that works with living cells
CREDIT: L.A. CICERO/STANFORD NEWS SERVICE In 2017, Stanford University researchers presented a new device that mimics the brain’s efficient and low-energy neural learning process. It was an artificial version of a synapse – the gap across which neurotransmitters travel to communicate between neurons – made from organic materials. In 2019, the researchers assembled nine of...