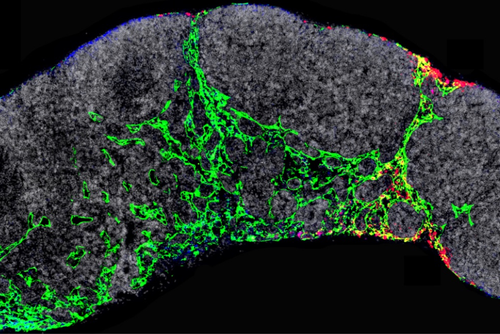
What happens inside neurons when we memorize a password or learn the cello? Some of our basic understanding about learning and memory comes from the study of conditions in which cognitive development is disrupted. For example, FMRP, a protein whose loss causes fragile X syndrome, intellectual disability, and some forms of autism has been shown to play...
Tag: <span>new mechanism</span>
Research team identifies new mechanism for protecting DNA
Discovery offers hope to better understand how diseases like cancer, premature aging can be prevented. Researchers from Case Western Reserve University have identified a new mechanism by which a protein known for repairing damaged DNA also protects the integrity of DNA by preserving its structural shape. The discovery, involving the protein 53BP1, offers insight into understanding how...
Researchers uncover new mechanism for deadly blood clots
BRIGHAM AND WOMEN’S HOSPITAL Nearly 80 percent of deaths from type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are associated with thrombosis, a condition that occurs when blood clots block a vein or artery. Traditionally, it’s been thought that proteins released by damaged blood vessels may lead to inappropriate blood clotting, but a new study from investigators at...
CNIO researchers discover a new mechanism involved in early melanoma metastasis
CENTRO NACIONAL DE INVESTIGACIONES ONCOLÓGICAS (CNIO) IMAGE: LYMPH NODE OF A MOUSE IN WHICH LYMPHATIC VESSELS (GREEN) AND TUMOR EXOSOMES (RED) THAT WILL DIRECT THE EARLY STAGES OF MELANOMA METASTASIS ARE VISUALIZED CREDIT: CNIO “We must not only look inside the tumour but also outside of it,” says Héctor Peinado, a researcher at the Spanish National...
Findings reveal new mechanism of activation for ALK
by St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital Credit: CC0 Public Domain ALK is a receptor tyrosine kinase that regulates important functions in the central nervous system. Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital have used leading-edge structural biology techniques to reveal in more detail how ALK is activated by the binding of ligands. ALK is an...
New mechanism involving the protein Scribble helps maintain cell polarity
Reviewed by Emily Henderson, B.Sc. Nov 12 2021 A previously unknown mechanism involving the protein Scribble helps maintain polarity in cells, according to a Northwestern Medicine study published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry. This new mechanism sheds light on the complex web of systems that keep cells pointing in the correct direction, according to Sergey...
The mRNA alphabet: Identification of a new mechanism to cancer metastasis
by Université libre de Bruxelles Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain When cancers metastasize, cells from the primary tumor break away, travel through the blood or lymph system and form new tumors in other body parts. Although metastasis is responsible for more than 90% of all cancer deaths, limited progress has been made in treating cancers that have...
Scientists uncover new mechanism that enables development of cancer
UNC LINEBERGER COMPREHENSIVE CANCER CENTER IMAGE: “Because similar gene fusions have been observed in other malignancies, the mechanism we elucidated could explain other types of cancer as well,” said UNC Lineberger’s Douglas H. Phanstiel, Ph.D. “We believe that our research could open up new and innovative avenues to attack cancer cells.” CREDIT: UNIVERSITY OF NORTH...
Researchers discover a new mechanism that regulates cholesterol levels
by University of Oulu Credit: CC0 Public Domain A research team at the University of Oulu, Finland, has discovered a new mechanism in cells that causes an increase in harmful LDL cholesterol. The observation made by the researchers may explain the adverse effects of certain environmental chemicals and medicinal substances on cardiovascular health. At the heart of the finding...
Study led by Penn Medicine reveals new mechanism of lung tissue regeneration
UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE PHILADELPHIA– New research performed in mice models at Penn Medicine shows, mechanistically, how the infant lung regenerates cells after injury differently than the adult lung, with alveolar type 1 (AT1) cells reprograming into alveolar type 2 (AT2) cells (two very different lung alveolar epithelial cells), promoting cell regeneration, rather than AT2...