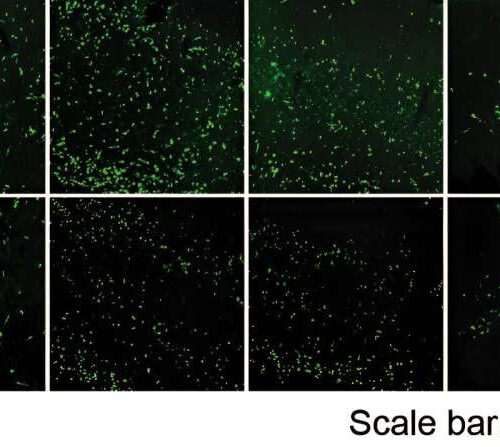
by Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Second row shows how rapamycin dampens alpha-synuclein protein production in a magnified area of a mouse brain. Credit: Mohammed Khan and Ted Dawson, Johns Hopkins Medicine A so-called pathological protein long associated with Parkinson’s disease has been found in a new study to trigger cells to increase protein synthesis,...
Tag: <span>novel therapies</span>
Exercise Enhancement
Loss of a specific enzyme increases fat metabolism and exercise endurance in mice. Sugars and fats are the primary fuels that power every cell, tissue, and organ. For most cells, sugar is the energy source of choice, but when nutrients are scarce, such as during starvation or extreme exertion, cells will switch to breaking down...
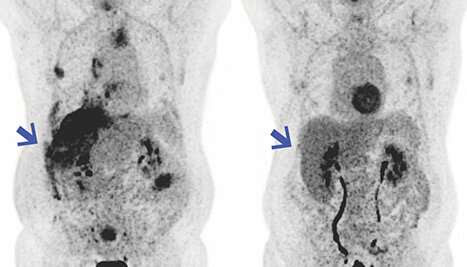
Study finds drug beneficial for shrinking mesothelioma tumors
by National Cancer Institute A drug that is designed to boost the immune system against mesothelioma, when combined with immunotherapy, was found to be beneficial in a small study involving ten patients. The results, which appeared July 1, 2020, in Science Translational Medicine, suggest that the drug LMB-100 could prolong the life of some patients...
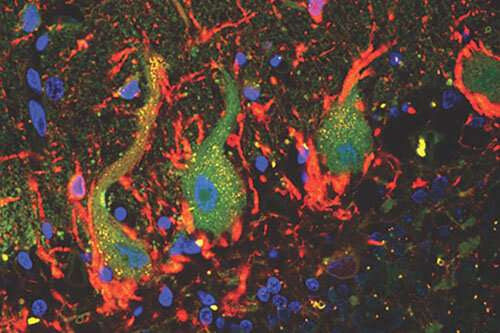
Novel pathology could improve diagnosis and treatment of Huntington’s and other diseases
by University of Bristol Bristol scientists have discovered a novel pathology that occurs in several human neurodegenerative diseases, including Huntington’s disease. The article, published in Brain Pathology, describes how SAFB1 expression occurs in both spinocerebellar ataxias and Huntington’s disease and may be a common marker of these conditions, which have a similar genetic background. SAFB1...
Wearable patch may provide new treatment option for skin cancer
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Conventional melanoma therapies, including chemotherapy and radiotherapy, suffer from the toxicity and side effects of repeated treatments due to the aggressive and recurrent nature of melanoma cells. Less invasive topical chemotherapies have emerged as alternatives, but their widespread uses have been hindered by both the painful size of the microneedles and...
How do we disconnect from the environment during sleep and under anesthesia?
In normal sleep states, sounds fail to penetrate brain regions mediating consciousness and memory, and this natural disconnection is caused by low noradrenaline activity, say Tel Aviv University researchers During sleep and under anesthesia, we rarely respond to such external stimuli as sounds even though our brains remain highly active. Now, a series of new...
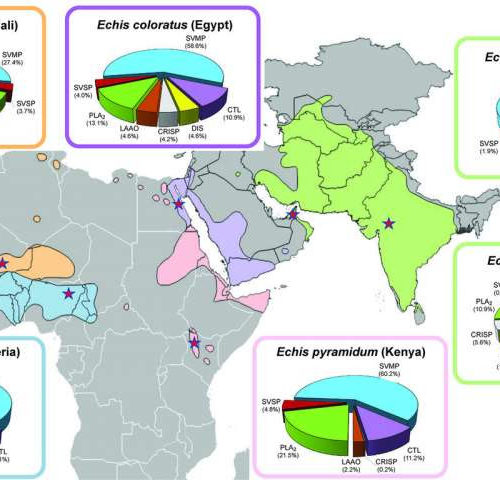
Researchers demonstrate a novel way to treat snakebite
by Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine Snakebite is one of the world’s biggest hidden health problems with up to 138 000 victims dying every year, and around 400 000 victims left with permanent physical disabilities or disfigurements. Those most affected live in some of the world’s poorest communities in sub-Saharan Africa, Asia and Latin America...
Novel necklace detects abnormal heart rhythm
“The wearable necklace-ECG (electrocardiogram) provides a new and easy method for detecting an abnormal heart rhythm called atrial fibrillation, which is a fast-growing public health problem,” said study author Mr. Elmeri Santala, a medical student at the University of Eastern Finland. One of the major causes of stroke is unrecognised and untreated atrial fibrillation. Approximately...
U of G researchers discover potential drug to treat heart attacks
A potential drug to treat heart attacks and to prevent heart failure — for which no cure currently exists — may result from pioneering research by a University of Guelph professor UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH A potential drug to treat heart attacks and to prevent heart failure – for which no cure currently exists — may...
A new role for an old immune cell may lead to novel therapies for infection and cancer
A new study has identified a previously undescribed role for a type of unconventional T cell with the potential to be used in the development of new therapies for infection and cancer. The study, published today in Nature Communications, shows that Gamma Delta T cells are able to generate immunological memory against previous infections and cancerous...