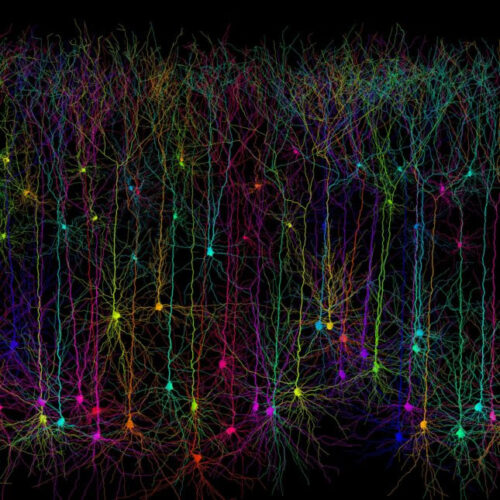
By Megan Molteni Scientists in Japan modified pyramidal neurons in mice so that when shined with a laser they couldn’t make the new connections needed to form and solidify new memories. The synthetic pyramidal neurons pictured here were simulated by a software called the TREES toolbox.WELLCOME Amouse finds itself in a box it’s seen before; inside,...
Tag: <span>optogenetics</span>
How a memory game could help us understand brain injury
After a traumatic brain injury, why do some people regain skills quickly while others face long-lasting setbacks? Boston University neuroscientist Jerry Chen of BU’s Center for Systems Neuroscience and colleagues have been trying to answer this question by understanding which parts of the brain process sensory information and which remember different skills. The latest research...
The ‘love hormone’ oxytocin can also give rise to aggressive behavior
by Max Planck Society During the pandemic lockdown, as couples have been forced to spend days and weeks in one another’s company, some have found their love renewed while others are on their way to divorce court. Oxytocin, a peptide produced in the brain, is complicated in that way: A neuromodulator, it may bring hearts...
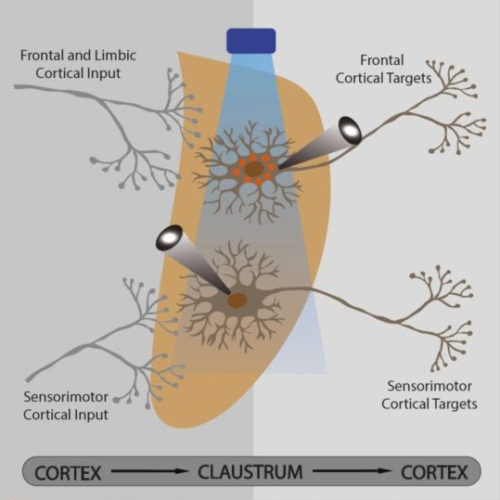
New findings redefine organisation of the claustrum
Researchers from Karolinska Institutet and Nanyang Technological University (NTU) in Singapore have found that the claustrum is organized into functional connectivity modules rather than a hub-like structure, which up until now, was the prevailing idea. The study was recently published in Current Biology. “We found that the synaptic connectivity between the cortex and claustrum is...
How do we disconnect from the environment during sleep and under anesthesia?
In normal sleep states, sounds fail to penetrate brain regions mediating consciousness and memory, and this natural disconnection is caused by low noradrenaline activity, say Tel Aviv University researchers During sleep and under anesthesia, we rarely respond to such external stimuli as sounds even though our brains remain highly active. Now, a series of new...
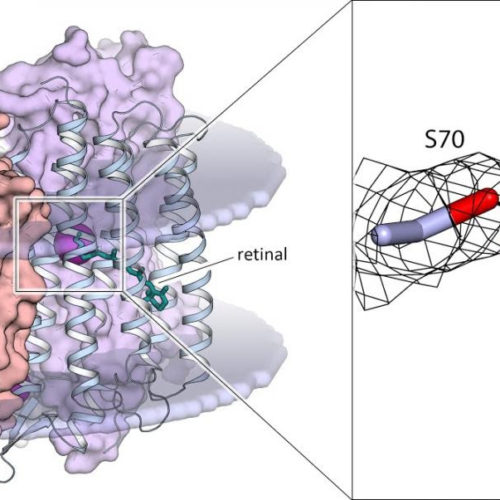
Biophysicists reveal how optogenetic tool works
An international research team has for the first time obtained the structure of the light-sensitive sodium-pumping KR2 protein in its active state. The discovery provides a description of the mechanism behind the light-driven sodium ion transfer across the cell membrane. The paper came out in Nature Communications. KR2 is a member of a very large...
It’s the yeast they can do
UC Riverside engineers are transforming yeast, both the domesticated kind used to make bread and beer and lesser-known wild species, so it can be used in a variety of new ways — including fighting cancer. Yanran Li, a UC Riverside assistant professor of chemical and environmental engineering, is working with the yeast species Saccharomyces cerevisiae...
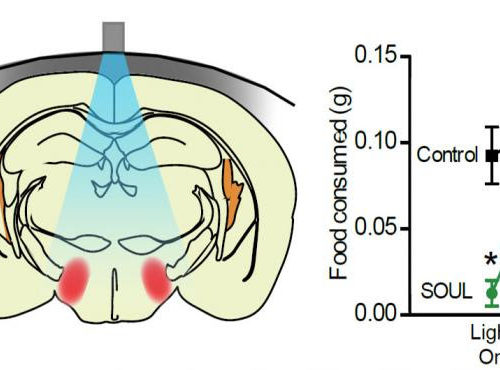
Implant-free optogenetics minimizes brain damage during neuronal stimulation
A minimally invasive optogenetic technique that does not require brain implants successfully manipulated the activity of neurons in mice and monkeys, researchers report April 29th in the journal Neuron. The researchers first genetically engineered neurons to produce a newly developed, extremely light-sensitive protein called SOUL. They then demonstrated that it is possible to shine light...
Optogenetics in Cellular Biology and Human Disease Models
By Clare Knight, B.Sc.Reviewed by Dr. Liji Thomas, MD What is Optogenetics?Optogenetics is a combination of the manipulation of genes and optics in living tissues. This technique uses light-responsive proteins called opsins. This allows scientists to switch selective neurons on or off precisely and selectively. The involvement of these proteins within cultured cells of the...
Brain-mimicking chip uses different-colored light to learn and forget
The human brain is still a far more powerful computer than anything it itself has created so far. It’s no wonder then that engineers have recently focused on trying to emulate the structure of the brain with artificial synapses. Now, a team of researchers has made a new artificial synapse design that works using a light-based biotechnology technique called optogenetics. The field...
- 1
- 2