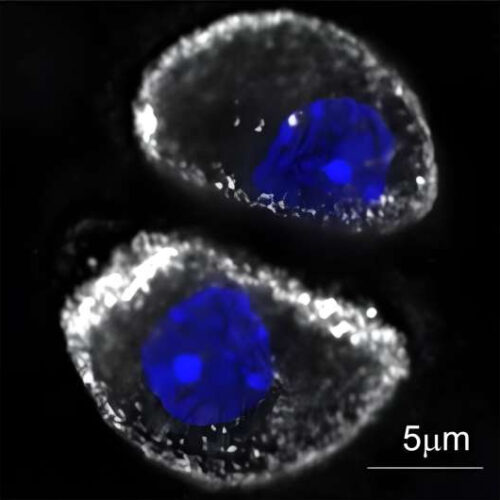
by University of Delaware The blue area is the cell nucleus, the white area is F-actin, the structural scaffolding of the cells. Researchers discovered adseverin regulates the amount of F-actin in the cells. In osteoarthritis loss of F-actin can eventually lead to cell death. Credit: University of Delaware A previously unstudied protein in the framework of...
Tag: <span>Osteoarthritis</span>
Joint disease: New therapeutic approach for osteoarthritis discovered
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF VIENNA Osteoarthritis was long considered to be the result of wear and tear in advanced age. In the meantime, more and more studies are linking the degradation of articular cartilage to inflammatory and metabolic processes in the joint. In researching these processes, a scientific team led by MedUni Vienna has made significant...
Changes in the composition of joint lubricant may be behind osteoarthritis
Share on PinterestScientists may have found a culprit behind osteoarthritis. Emotion Matters/Stocksy Synovial joints, one of the most common types of joints between bones, are characterized by the presence of a cavity filled with viscous synovial fluid between the two joint bones. The molecules in the synovial fluid form a lubricating film on the layer...
New injectable cell therapy could resolve osteoarthritis
by Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist Credit: CC0 Public Domain Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) scientists have created a promising injectable cell therapy to treat osteoarthritis that both reduces inflammation and also regenerates articular cartilage. Recently identified by the Food and Drug Administration as a public health crisis, osteoarthritis affects more than 520...
Composition of synovial fluid potential culprit behind osteoarthritis
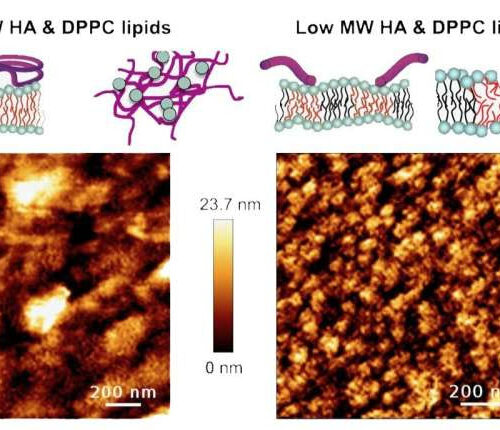
by American Institute of Physics The complex interplay between phospholipid and hyaluronic acid self-assembly in solution, and the molecular weight of hyaluronic acid, determine surface affinity and the formation of a protective film on cartilage. Credit: Kangdi Sun, Tooba Shoaib, Mark W. Rutland, Changwoo Do, and Rosa M. Espinosa-Marzal Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease caused...
Researchers uncover new cell types involved in osteoarthritis
by Valerie Goodwin, University of Michigan Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain A Michigan Medicine study has identified a new potential target for treating osteoarthritis—a debilitating joint disease that affects over 31 million Americans and is a leading cause of disability worldwide. A team of researchers led by Tristan Maerz, Ph.D., a biomedical engineer and assistant professor in the...
New mechanism uncovered behind osteoarthritis could inform new treatments
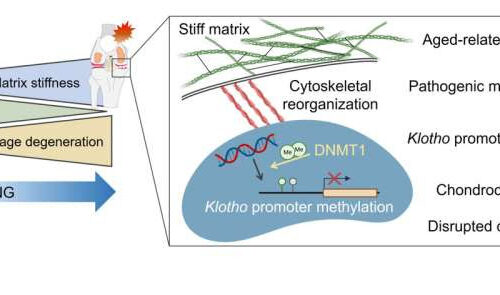
by Mass General Brigham Age-related matrix stiffening in articular cartilage initiates pathogenic mechanotransductive signaling, driving chondrocyte dysfunction as well as disrupted cartilage integrity through Klotho promoter hypermethylation. Portions of the figure were created with biorender.com. Credit: Ambrosio et al, Nature Communications Researchers in the United States and Japan have discovered a new mechanism that links age-related cartilage tissue...
New drug offers hope for people with hand osteoarthritis
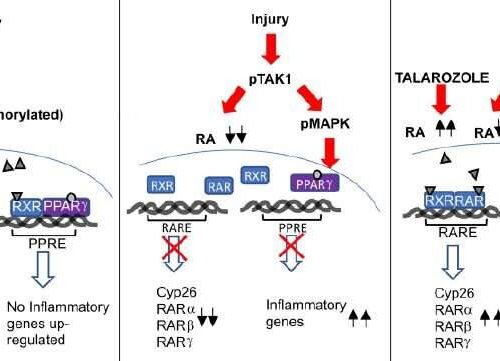
by University of Oxford Diagram illustrating the anti-inflammatory role of all-trans retinoic acid (atRA) after cartilage injury. Credit: Science Translational Medicine (2022). DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abm4054 A new study, published in Science Translational Medicine by researchers at the University of Oxford has identified that Talarozole, a drug that is known to increase retinoic acid, was able to prevent osteoarthritis (OA) in disease models. Tonia...
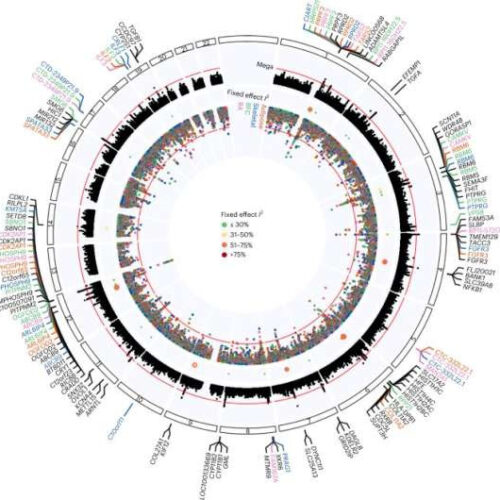
Ten new genetic loci linked to osteoarthritis found
by Bob Yirka , Medical Xpress Summary of osteoarthritis mega-GWAS and transcriptome-wide imputation results. Credit: Nature Genetics (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41588-022-01221-w A team of researchers affiliated with several institutions in Alabama has linked 10 genetic loci to the development of osteoarthritis. In their paper published in the journal Nature Genetics, the group describes their analysis of data from the...
CRTAC1 is a promising biomarker of osteoarthritis
DECODE GENETICS Scientists at deCODE genetics a subsidiary of Amgen report in Arthritis & Rheumatology that the level of cartilage acidic protein-1 (CRTAC1) in plasma is a potential biomarker of osteoarthritis (OA) through its association with OA risk and progression to joint replacement. The level of CRTAC1 in plasma was recently associated with osteoarthritis (OA)...