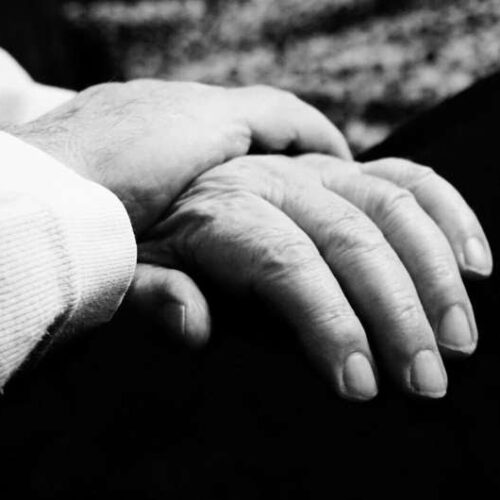
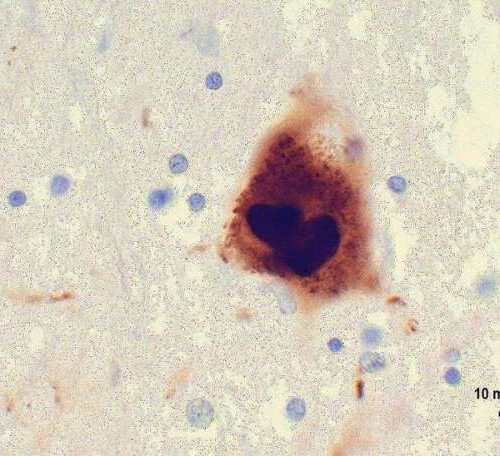
by Haley Wasserman, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Researchers at Johns Hopkins Medicine have pinpointed the section of a brain protein called alpha-synuclein that enables it to latch onto neurons and likely drives the development of Parkinson’s disease, a progressively worsening neurological disorder. The photomicrograph shows an aggregation of alpha-synuclein in brain tissue taken from...
Tag: <span>Parkinson’s disease</span>
Fruit compound may have potential to prevent and treat Parkinson’s disease
by Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they have added to evidence that the compound farnesol, found naturally in herbs, and berries, and other fruits, prevents and reverses brain damage linked to Parkinson’s disease in mouse studies. The compound, used in flavorings and perfume-making, can prevent the...
Dancing to music may halt progression of Parkinson’s disease
New research highlights the importance of dancing to music for halting Parkinson’s disease. Raymond Forbes/Stocksy A study investigated how dancing to music affects various symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. The results suggest that dancing to music can halt the progression of physical and psychological symptoms of Parkinson’s. The researchers say the results could aid in developing...
UCPH researchers prove powerhouse malfunction as the major cause of Parkinson’s Disease
UNIVERSITY OF COPENHAGEN – THE FACULTY OF HEALTH AND MEDICAL SCIENCES 12,000 people in Denmark and 7 to 10 million people worldwide suffer from Parkinson’s Disease (PD). It is the second most common neurogenerative disorder of aging and the most common movement disorder, but the cause of the disease is largely unknown. In a new...
Tetanus toxin fragment may treat depression, Parkinson’s disease and ALS
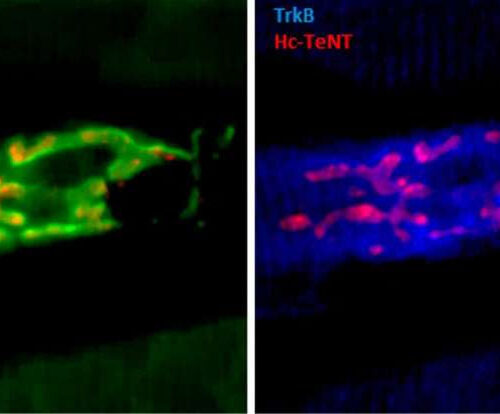
by Autonomous University of Barcelona Mice neuromuscular junction in a tibialis anterior muscle slice. Microscope images were obtained for the research. Credit: UAB Researchers at the UAB describe the mechanism through which a non-toxic derivative of the tetanus neurotoxin (Hc-TeTx) may serve to treat depression and neurodegenerative diseases, as has already been demonstrated in animal models. Depression...
New study gives clue to the cause, and possible treatment of Parkinson’s Disease
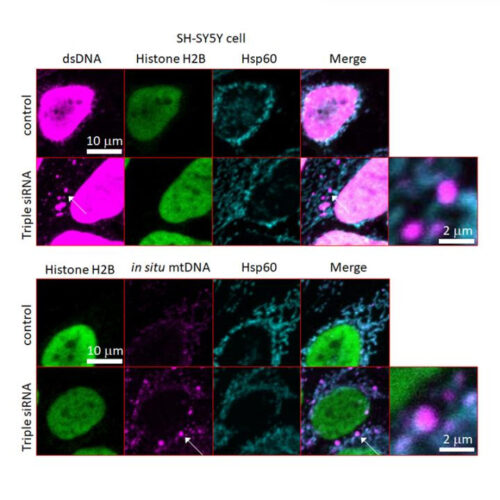
NIIGATA UNIVERSITY IMAGE: Immunostaining: Top panel SH-SY5Y cells transfected with GBA are stained for dsDNA (magenta), histone H2B (green), and Hsp60 (turquoise). White arrows indicate cytosolic dsDNA of mitochondrial origin. Triple siRNA: Knockdown of GBA, ATP13A2, and PINK1 expression with siRNAs. Coimmunostaining: Bottom panel In situ hybridization of mitochondrial DNA and coimmunostaining for histone H2B...
Protein simulation, experiments unveil clues on origins of Parkinson’s disease
Parkinson’s disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disease and affects more than 10 million people around the world. To better understand the origins of the disease, researchers from Penn State College of Medicine and The Hebrew University of Jerusalem have developed an integrative approach, combining experimental and computational methods, to understand how individual proteins...
Low blood flow in the brain may be an early sign of Parkinson’s disease
AARHUS UNIVERSITY Patients who suffer from REM sleep behaviour disorder have altered blood flow in the brain, which can lead to a lack of oxygen in the brain tissue. In the long term, this may cause symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. This is shown by research from Aarhus University and Aarhus University Hospital. Do you sleep restlessly and...
One step closer to nasal spray drug delivery for Parkinson’s disease
by University of York Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Scientists at the University of York have made significant progress in the development of a nasal spray treatment for patients with Parkinson’s disease. Researchers have developed a new gel that can adhere to tissue inside the nose alongside the drug levodopa, helping deliver treatment directly to the brain. Levodopa is...
Researchers reveal mechanism for α-syn deposition in familial Parkinson’s disease
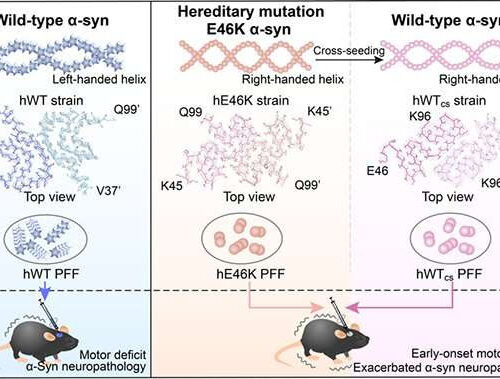
by Zhang Nannan, Chinese Academy of Sciences Fig.1. Schematic summary of the exacerbated α-syn neuropathology in heterozygous familial PD. Credit: SIOC Amyloid deposition of α-synuclein (α-syn) is a hallmark of Parkinson’s disease (PD). α-Syn fibrillation and cell-to-cell transmission in the brain play an essential role in disease progression. To date, eight single-point mutations of SNCA have...