by Peter Rüegg, ETH Zurich Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain ETH Zurich researchers have found that a set of proteins have different shapes in the spinal fluid of healthy individuals and Parkinson’s patients. These could be used in the future as a new type of biomarker for this disease. Many human diseases can be detected and...
Tag: <span>Parkinson’s disease</span>
Genomic transposable elements modify the progression of Parkinson’s disease
A study involving researchers from the University of Liverpool describes how transposable elements are associated with Parkinson’s subtypes and impact disease trajectory. The study, published in Experimental Biology and Medicine, analysed the variation of transposable elements – DNA sequences that can change their position within a genome – and their impact on different trajectories of Parkinson’s disease....
Alzheimer’s drug candidate may have potential for treating Parkinson’s disease
disease A recent study showed that itanapraced disrupted genetic mutations associated with Parkinson’s disease and reduced loss of neurons in cell culture and mouse models. ImagesBazaar/Getty Images Mutations that enhance the activity of the LRRK2 enzyme are one of the most common mutations in inherited and sporadic Parkinson’s disease. A recent study showed that mutations...
Trans-auricular VNS ‘Very Clever’ for Parkinson’s Disease
Pauline Anderson September 23, 2022 Trans-auricular vagus nerve stimulation (taVNS) is feasible, well-tolerated, and may improve motor function in patients with Parkinson’s Disease (PD), new research suggests. The field of noninvasive brain stimulation in PD is in its infancy, but emerging research shows it is a promising approach for some patients, lead study author Vanessa...
Epigenetic changes linked to Parkinson’s disease differ in men and women
by Rutgers University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain The epigenetic changes linked to Parkinson’s disease—a nervous system disorder that afflicts nearly 1 million Americans—are different in men and women, according to a new Rutgers study published in npj Parkinson’s Disease. In a postmortem analysis of brain neurons, researchers compared samples from 50 people who died with Parkinson’s...
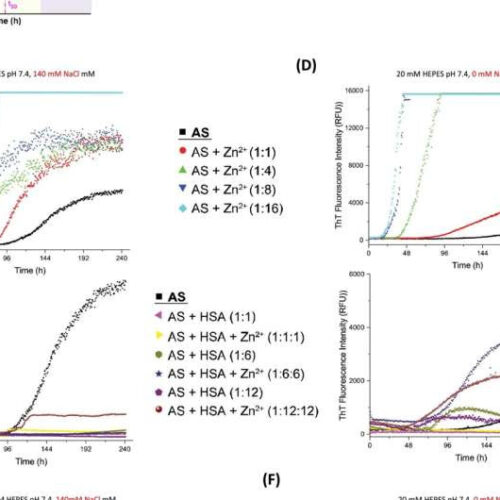
Zinc enhances albumin’s protective role against Parkinson’s disease
by King Abdullah University of Science and Technology Fig. 1. Fibrillization kinetics of AS under pH 7.4, low and high ionic strength in the presence and absence of Zn2+ and/or defatted human serum albumin (DE-HSA). (A) The nucleation dependent polymerization reaction of amyloid fibril formation causes a sigmoidal growth curve with nucleation, elongation, and saturation phases. (B)...
11 Symptoms That Could Be Early Signs of Parkinson’s Disease
Written by Cherilyn Cecchini, MD | Reviewed by Katie E. Golden, MDPublished on August 25, 2022 Key takeaways: Parkinson’s disease symptoms can be subtle in the early stages of the condition. They include stiffness, loss of smell, trouble sleeping, and constipation. As Parkinson’s disease progresses, many of the movement symptoms become more apparent. This includes...
Discovery illuminates how Parkinson’s disease spreads in the brain
by Weill Cornell Medical College Weill Cornell Medicine. Credit: Sharma Lab Aggregates of the protein alpha-synuclein spread in the brains of people with Parkinson’s disease through a cellular waste-ejection process, suggests a new study led by Weill Cornell Medicine researchers. During the process, called lysosomal exocytosis, neurons eject protein waste they cannot break down and recycle....
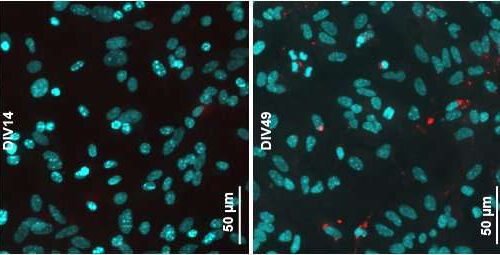
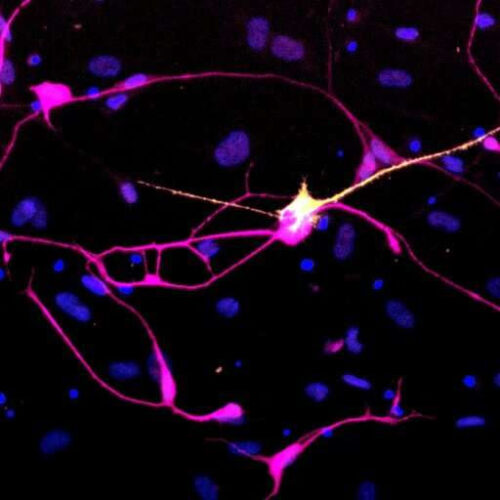
Aged neurons generated directly from skin more accurately model Parkinson’s disease
by International Society for Stem Cell Research Induced dopaminergic neurons directly reprogrammed from the skin cells of a patient with idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease. Credit: Janelle Drouin-Ouellet, University of Montreal, Canada The possibility to make virtually all cell types of the human body from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which are embryonic-like cells generated from a...
Exercise hormone halts Parkinson’s disease symptoms in mouse study
JOHNS HOPKINS MEDICINE FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Researchers from Johns Hopkins Medicine and the Dana Farber Cancer Institute in Boston have shown that a hormone secreted into the blood during endurance, or aerobic, exercise reduces levels of a protein linked to Parkinson’s disease and halts movement problems in mice. Parkinson’s disease, a neurologic condition that causes...