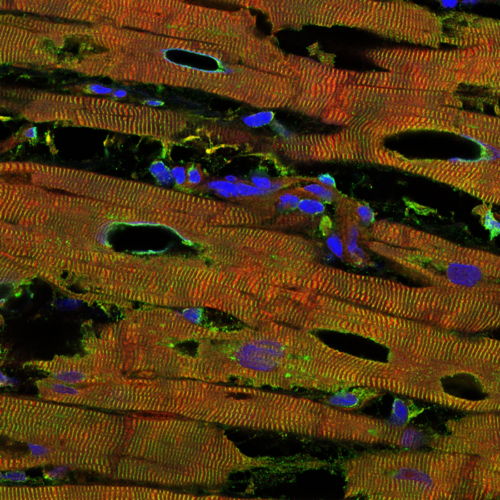
UNIVERSITY OF MÜNSTER IMAGE: RED STAINING INDICATES TITIN, GREEN ANOTHER PROTEIN OF THE CONTRACTILE UNITS, AND BLUE THE NUCLEI. THE HOLES ARE INDICATIVE OF DISEASE-INDUCED TISSUE DAMAGE. CREDIT: AG LINKE Titin is a “titanically large” protein – the largest in the human body – which enables elastic movements of our muscles, including the heart. Mutations...
Tag: <span>Pathomechanisms</span>
Osteopontin, a protein not always as bad as it is made out to be
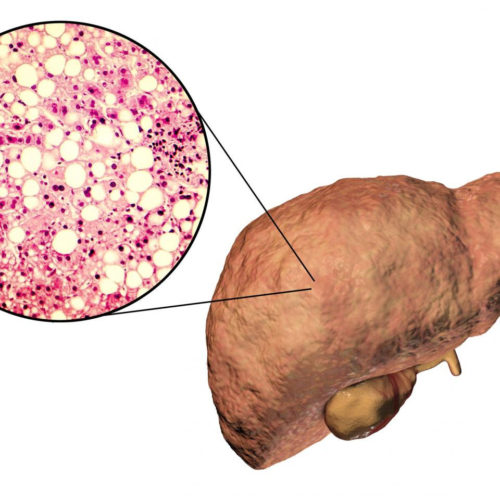
The UPV/EHU-University of the Basque Country shows that maintaining osteopontin delays the onset of metabolic fatty liver disease during ageing UNIVERSITY OF THE BASQUE COUNTRY THE STUDY INDICATES THAT OSTEOPONTIN IS NECESSARY TO PREVENT THE EARLY ONSET OF NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE LINKED TO AGEING view more Metabolic fatty liver disease, known as non-alcoholic fatty...
Pathomechanisms deciphered for the two most common age-related eye disorders
Population aging is a global phenomenon with profound medical implications. Tissue dysfunction associated with aging affects all vital organs, including the eyes. Various ocular structures are affected by aging, such as the macula, the functional center of the retina responsible for precise central vision. Idiopathic epiretinal membrane (iEMR) and macular hole (MH) affect millions of...