by NYU Langone Health After a brain injury, cells that normally nourish nerves may actually kill them instead, a new study in rodents finds. This “reactive” phenomenon may be the driving factor behind neurodegenerative diseases like glaucoma, a leading cause of blindness. Led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, the study examined what...
Tag: <span>physiology</span>
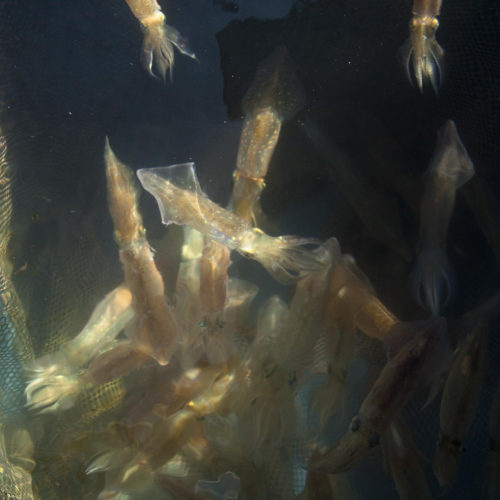
Squid studies illuminate neural dysfunction in ALS; suggest new route to therapy
CREDIT: DANIEL COJANU WOODS HOLE, Mass. — Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is one of the most devastating adult-onset neurodegenerative diseases. Patients, including the late actor/playwright Sam Shepard, become progressively weaker and eventually paralyzed as their motor neurons degenerate and die. To find a cure for ALS, which is fatal, scientists need a deeper understanding of...
Missing sodium-channel component may protect against diet-induced artery stiffening
by American Physiological Society New research in mice finds that deficiency in one small component of a signaling pathway may protect against artery stiffening and subsequent kidney disease associated with a high-fat, high-sugar diet. The study is published in the American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology. Consuming a western diet—typically high in fat and refined carbohydrates,...
Caveolin binding motif in Na/K-ATPase required for stem cell differentiation in animals
HUNTINGTON, W.Va. – New findings reveal the importance of the Na/K-ATPase protein in stem cell differentiation and organogenesis, in a study led by scientists at Marshall University that involves the scaffolding function of the Na/K-ATPase. The research, published today in Science Advances, indicates that a sequence in the Na/K-ATPase, also known as the sodium pump,...
Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone (CRH)
Corticotropin–releasing hormone (CRH), also called corticotropin–releasing factor (CRF), is a peptide hormone that activates the synthesis and release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from the pituitary gland. In this way, CRH affects our response to stress, addiction and depression, among others. What is Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone? CRH is a neuropeptide hormone that regulates neuroendocrine, sympathetic, and behavioral functions in response to stress. It consists of 41 amino acids...
New method uses just a drop of blood to monitor lung cancer treatment
Dr. Tasuku Honjo won the 2018 Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine for discovering the immune T-cell protein PD-1. This discovery led to a set of anti-cancer medications called checkpoint inhibitors, one of the first of which was nivolumab (Opdivo). Nivolumab helps T-cells fight tumors, however, different patients respond in different ways. It now appears...
- 1
- 2