New LJI discovery could help explain patterns of cell death in many autoimmune diseases LA JOLLA INSTITUTE FOR IMMUNOLOGY LA JOLLA–Your pancreas is a little sweet potato-shaped organ that sits snug behind your stomach. The pancreas is studded with islets, the cell clusters that house insulin-producing beta cells. In people with type 1 diabetes, the...
Tag: <span>postdoctoral</span>
Developing a blood test for prostate cancer
Interview conducted by Emily Henderson, B.Sc. Professor Pockley among other researchers from the John van Geest Cancer Research Centre have recently developed a blood test for the detection of prostate cancer. News-Medical spoke to Professor Pockley to find out more! What provoked your research into the detection of prostate cancer? Why is there an urgent...
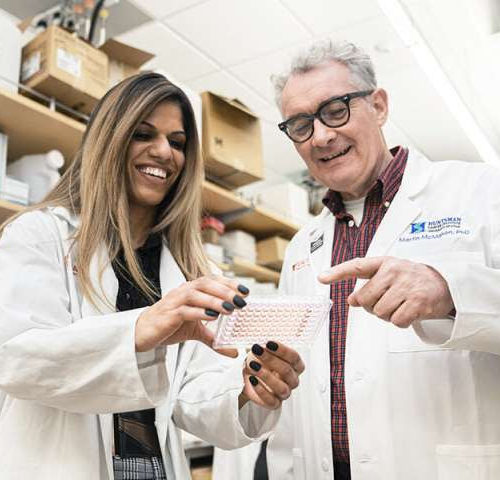
Scientists accelerate progress in preventing drug resistance in lung and pancreas cancers
by Huntsman Cancer Institute Scientists at Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah report today the development of new models to study molecular characteristics of tumors of the lung and pancreas that are driven by mutations in a gene named NTRK1. The findings were published today in the journal Cell Reports. Credit: Huntsman Cancer...
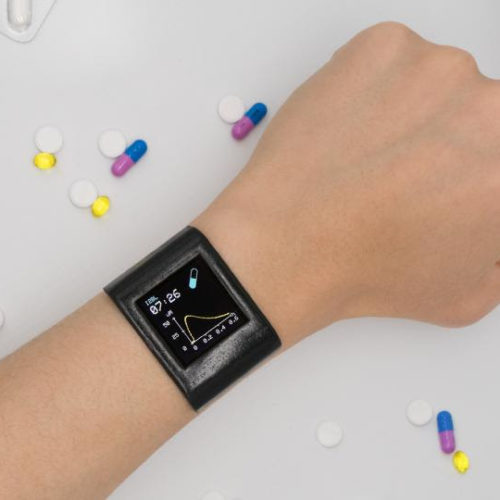
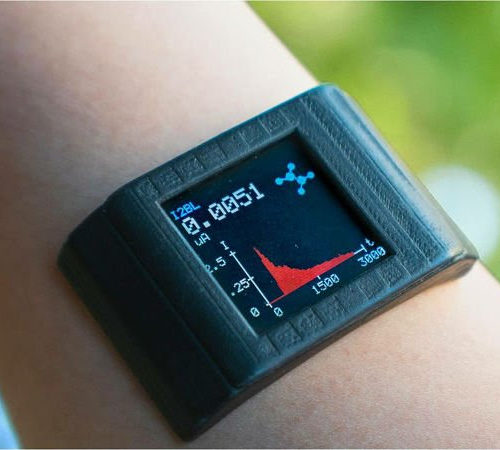
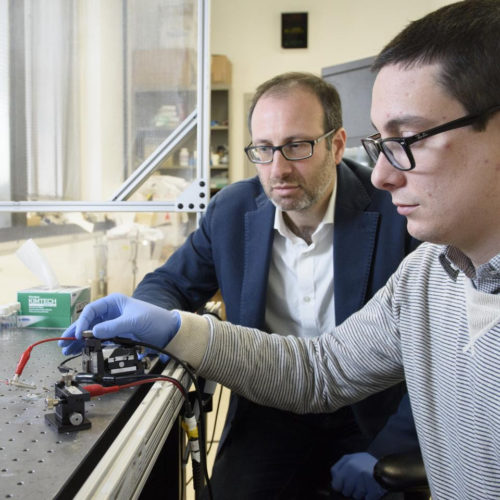
Smartwatch tracks medication levels to personalize treatments
Advance could help doctors choose the right drug at the right dose for the right person UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – LOS ANGELES SMARTWATCH TO TRACK MEDICATION LEVELS view more CREDIT: JIALUN ZHU, SHUYU LIN, AND YICHAO ZHAO (I²BL/UCLA) Engineers at the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering and their colleagues at Stanford School of Medicine have...
Scientists decipher key mechanism in hypoxia
by Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares Carlos III (F.S.P.) The figure illustrates the role of the mitochondrial Ca2+/Na+ exchanger (NCLX) in the early adaptation to low oxygen concentrations (hypoxia) through the entry of sodium into the mitochondrial interior. This role is exemplified by hypoxic vasoconstriction of the pulmonary artery, which connects the heart to the...
Immune response to COVID-19’s spike protein – the secret to a successful vaccine?
by Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity Scientists have uncovered how a crucial component of the immune system responds to the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19—important information for future validation of vaccine candidates. Coronavirus particles have a corona (crown) of proteins that resemble spikes, which enable the virus to attach and...
Brain benefits of exercise can be gained with a single protein
by University of California, San Francisco A little-studied liver protein may be responsible for the well-known benefits of exercise on the aging brain, according to a new study in mice by scientists in the UC San Francisco Eli and Edythe Broad Center for Regeneration Medicine and Stem Cell Research. The findings could lead to new...
Virginia Tech scientists confirm usually harmless virus attacks the heart’s electrical system
Fralin Biomedical Research Institute scientists show adenovirus disrupts electrical signaling, impedes new communication channels. Credit: Fralin Biomedical Research Institute Adenovirus, which typically can cause a common cold, has a far more dangerous impact if it reaches the heart. When the virus commandeers gap junctions, it can slow production of connexin43, disturbing the electrical system that...
Stanford researchers develop artificial synapse that works with living cells
CREDIT: L.A. CICERO/STANFORD NEWS SERVICE In 2017, Stanford University researchers presented a new device that mimics the brain’s efficient and low-energy neural learning process. It was an artificial version of a synapse – the gap across which neurotransmitters travel to communicate between neurons – made from organic materials. In 2019, the researchers assembled nine of...
Adhesive film turns smartwatch into biochemical health monitoring system
UCLA engineers have designed a thin adhesive film that could upgrade a consumer smartwatch into a powerful health monitoring system. The system looks for chemical indicators found in sweat to give a real-time snapshot of what’s happening inside the body. A study detailing the technology was published in the journal Science Advances. Smartwatches can already...
- 1
- 2