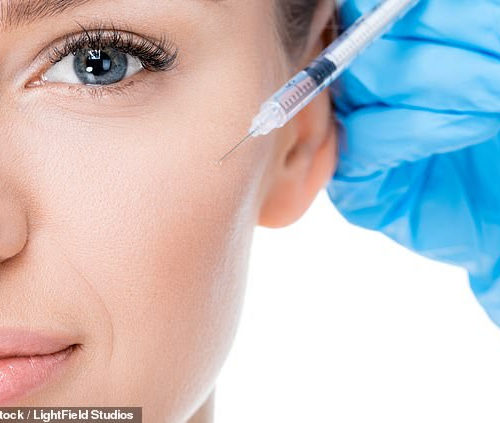
Botox is a muscle-relaxing toxin used cosmetically and for other purposes Researchers mined a US database of side-effects experienced from medications Patients given Botox were compared with those using alternative treatments The team found that the former were 40–88% less likely to report depression Further tests will be needed to confirm if and how Botox...
Tag: <span>potential drug</span>
Study in mice finds potential therapy to reverse memory loss from Alzheimer’s
by Macquarie University Researchers from Macquarie University have discovered a world-first new treatment that reverses the effects of memory loss associated with Alzheimer’s disease in a study of mice with advanced dementia. The research, co-led by two brothers, Dr. Arne Ittner and Professor Lars Ittner, from Macquarie University Dementia Research Center, builds on their work...
Immune cell steroids help tumours suppress the immune system, offering new immunotherapy targets
by Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute A study has revealed that tumors can evade the immune system by telling immune cells to produce immunosuppressive steroids. Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Department of Pathology, University of Cambridge, and MRC Cancer Unit, discovered that immune T cells from mouse skin and breast tumors secrete steroids, and that...
A never-before-seen cell state may explain cancer’s ability to resist drugs
MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENTER Cancer’s knack for developing resistance to chemotherapy has long been a major obstacle to achieving lasting remissions or cures. While tumors may shrink soon after chemotherapy, many times they eventually grow back. Scientists once thought that unique genetic mutations in tumors underlay this drug resistance. But more and more, they...
The immune system: Knocked off balance
by Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich The immune system: Knocked off balanceInstead of protecting us, the immune system can sometimes go awry, as in the case of autoimmune diseases and allergies. An LMU team has dissected how mast cells regulate their calcium levels to keep the immune response under control. Credit: IMCES UK Essen/LMU Instead...
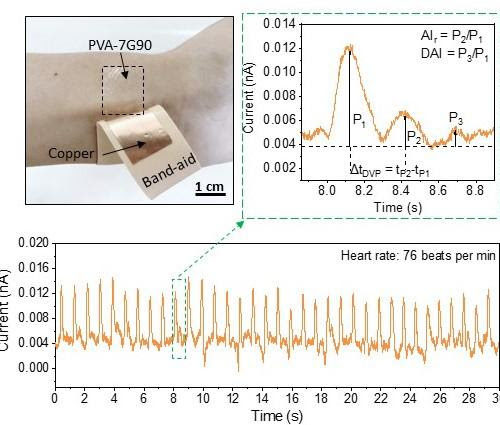
Invention offers new option for monitoring heart health
PURDUE UNIVERSITY A TEAM FROM PURDUE UNIVERSITY DEVELOPED SELF-POWERED WEARABLE TRIBOELECTRIC NANOGENERATORS WITH POLYVINYL ALCOHOL-BASED CONTACT LAYERS FOR MONITORING CARDIOVASCULAR HEALTH.view more CREDIT: WENZHUO WU/PURDUE UNIVERSITY WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – An invention may turn one of the most widely used materials for biomedical applications into wearable devices to help monitor heart health. A team from...
A micro-lab on a chip detects blood type within minutes
A novel lab-on-a-chip device reveals the blood type within minutes, holding much potential for use in an emergency TOKYO UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE Blood transfusion, if performed promptly, is a potentially life-saving intervention for someone losing a lot of blood. However, blood comes in several types, some of which are incompatible with others. Transfusing an incompatible...
Adults with obesity more likely to develop H1N1 influenza
Adults with obesity are more susceptible to influenza A/H1N1pdm—the swine flu virus, according to a new study that did not, however, find a similar association with the seasonal flu. The results could be relevant in understanding the mechanisms by which infectious diseases such as influenza or the ongoing coronavirus pandemic might affect different segments of...
Study finds that special filters in glasses can help the color blind see colors better
Effect persists even when glasses are not worn UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – DAVIS HEALTH JOHN S. WERNER OF UC DAVIS HEALTH HAS LED A STUDY OF GLASSES WITH SPECIAL FILTERS DESIGNED TO ADDRESS COLORBLINDNESS. view more CREDIT: UC REGENTS / UC DAVIS HEALTH A new UC Davis Eye Center study, conducted in collaboration with France’s...
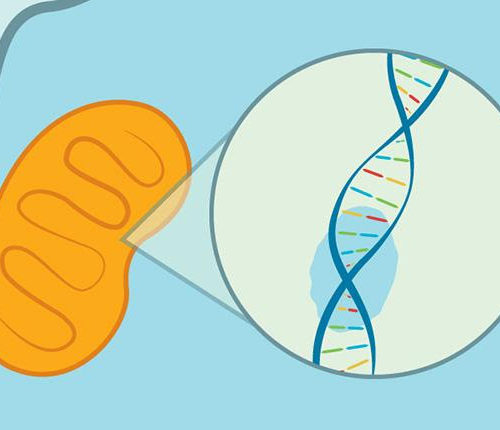
New molecular tool precisely edits mitochondrial DNA
UW microbiologists discovered a bacterial toxin that, when engineered, is a key part of a gene editor that can make single-base changes in human mitochondria. The genome in mitochondria — the cell’s energy-producing organelles — is involved in disease and key biological functions, and the ability to precisely alter this DNA would allow scientists to...