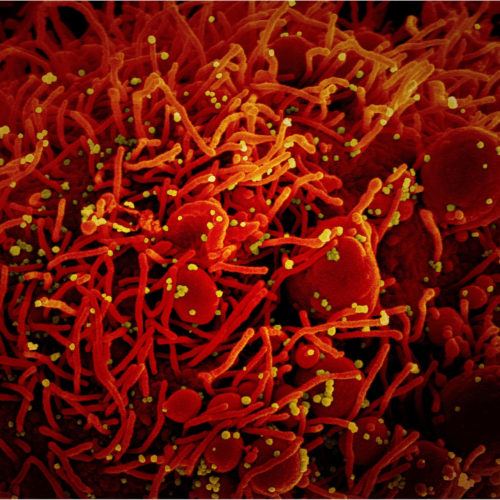
MIT engineers are using computing modeling to prevent microparticles from clogging during injections. Microparticles offer a promising way to deliver multiple doses of a drug or vaccine at once because they can be designed to release their payload at specific intervals. However, the particles, which are about the size of a grain of sand, can...
Tag: <span>potential drug</span>
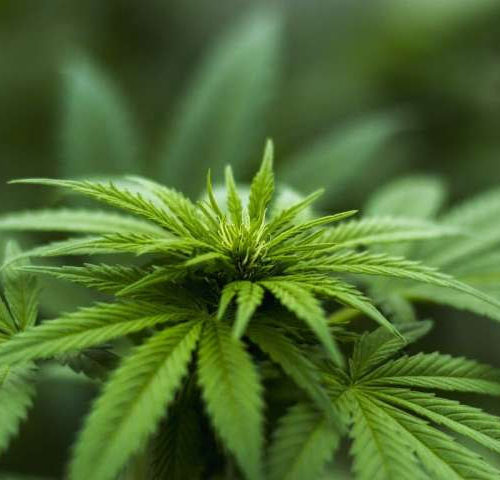
Cannabis shows potential for mitigating sickle cell disease pain
by University of California, Irvine Cannabis appears to be a safe and potentially effective treatment for the chronic pain that afflicts people with sickle cell disease, according to a new clinical trial co-led by University of California, Irvine researcher Kalpna Gupta and Dr. Donald Abrams of UC San Francisco. The findings appear in JAMA Network...
Why does coronavirus make people lose their sense of smell?
To begin with, it was just anecdotal reports. Ear, nose and throat specialists from around the world were sharing their experiences on online message boards – they were all seeing a spike in patients experiencing anosmia, a loss of smell. The link with coronavirus was brought to public attention by specialists in the UK in...
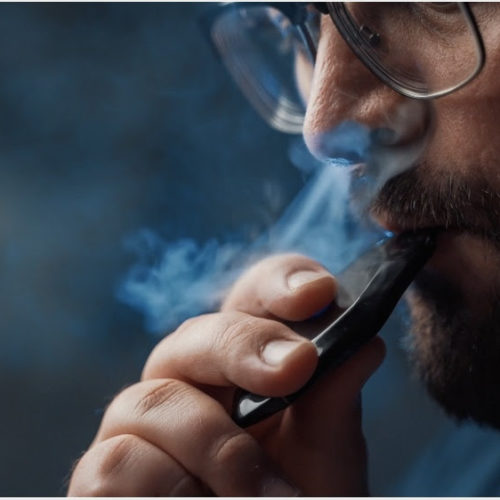
Tobacco smoking and vaping nicotine may exacerbate COVID-19 inflammation
By Sally Robertson, B.Sc. Researchers at the University of California San Diego have conducted a study showing that both smoking and the use of e-cigarettes containing nicotine and flavorings may critically exacerbate inflammation in cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and significantly worsen clinical outcomes. The use of e-cigs that do not contain nicotine or...
More evidence on vitamin D deficiency and death rates from COVID-19
By Sally Robertson, B.Sc. Physicians at the Complete Med Care clinic in Dallas, Texas, have conducted a study showing that the prevalence of severe vitamin D deficiency is strongly correlated with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) mortality rate in European countries. The researchers say the correlation also strengthened over time, making it even less likely to...
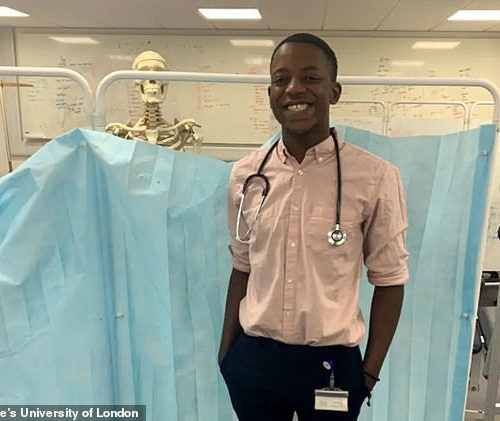
Black medical student creates a handbook to show how symptoms of disease appear on darker skin after he was only taught how to diagnose conditions on white patients
Malone Mukwende, a student at St George’s, London has written a handbook Future doctor said medical schools don’t teach how illnesses appear on dark skin It comes as 186,000 people signed petition to urge doctors to be trained in how rashes present on BAME people too A black medical student has created a handbook for...
THESE ARE THE BEST AND WORST MATERIALS FOR FACE MASKS
While research has shown masks are effective in reducing the spread of COVID-19, not all masks or mask materials are equally effective, according to new research. “WE KNEW THAT MASKS WORK, BUT WE WANTED TO KNOW HOW WELL AND COMPARE DIFFERENT MATERIALS’ EFFECTS ON HEALTH OUTCOMES.” In a study in the Journal of Hospital Infection,...
Reactive arthritis is fueled by amyloid protein during salmonella infection
by Temple University Like the infrastructure of an apartment building, a fibrous protein known as curli amyloid that is produced by bacteria provides the supportive framework for biofilms—thick extracellular substances made by bacteria that enable multiple bacterial cells to assemble, survive, and thrive together. Curli amyloid, however, is also a key factor in diarrheal illness...
COVID-19 can cause a rare and potentially lethal brain inflammation
The second wave of COVID-19 is slowly emerging and countries have to be prepared. However, this is still a fairly new disease, which scientists are still trying to figure out. Now researchers at UCL found that COVID-19 can have neurological complications, which include delirium, brain inflammation, stroke and nerve damage. Scientists looked through the cases...
Silencing of an ALS gene safely delivered to patients in new study
by Jim Fessenden, University of Massachusetts Medical School UMass Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital are the first to safely treat two research participants with a synthetic microRNA, delivered into the spinal fluid, designed to silence a human disease-causing gene. Details of the treatment, which targeted the mutant SOD1 gene that causes ALS, appear in...