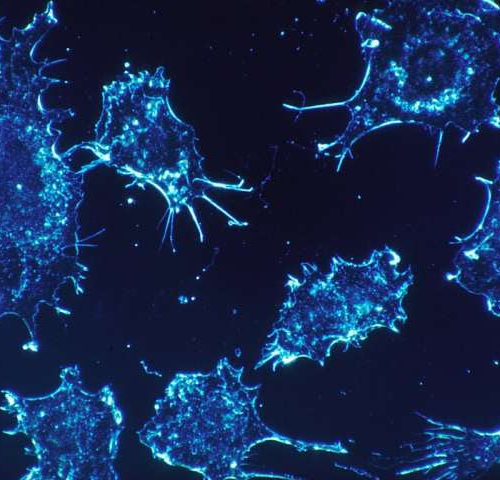
by Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Because of how aggressively they divide, cancer cells have an increased demand for building materials and energy. They meet these added demands by altering their metabolism—taking in larger amounts of fuel, for example. Historically, these metabolic changes have been considered a consequence rather than a cause of cancer, and...
Tag: <span>potential drug</span>
PSA screening affords men long-term benefits, study finds
The benefits of the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test to screen men for prostate cancer may be greater than the harm, according to a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine. Genitourinary cancer specialists from Seattle Cancer Care Alliance, University of Washington School of Medicine, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, and Weill Cornell Medicine...
Exercise may offer ‘profound’ benefits for Friedreich’s ataxia, research suggests
by Josh Barney, University of Virginia UVA researcher Zhen Yan studies the benefits of exercise. “You will benefit from just about any type of exercise as you age, as long as you’re not at risk of injury,” he said. Credit: Dan Addison, University Communications Atop exercise researcher at the University of Virginia School of Medicine...
New bandages could help to treat diabetic and burn wounds
by University of Sheffield New dressings that could be used to treat diabetic wounds and burns injuries more effectively have been developed by engineers from the University of Sheffield The cotton-based dressings, developed by Professor Sheila MacNeil from the University’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering, release an agent that promotes the formation of new...
T cells engineered to target senescence
Senescence is a hallmark of cellular ageing and contributes to many diseases. A new method enabling immune cells to target senescent cells might offer improved therapeutic options. Senescence is a form of cellular stress response. In some circumstances it can be harmful, and efforts are under way to develop therapies that target senescent cells. Writing...
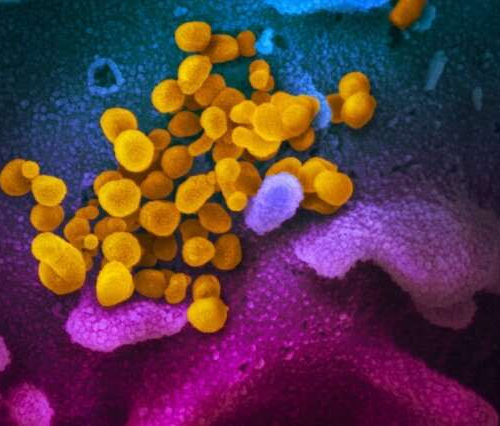
Researchers identify potent antibody cocktail with potential to treat COVID-19
by Deborah Kotz, University of Maryland School of Medicine Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) evaluated several human antibodies to determine the most potent combination to be mixed in a cocktail and used as a promising anti-viral therapy against the virus that causes COVID-19. Their research, conducted in collaboration with scientists...
CAR T cell therapy: potential for considerable savings
GERMAN CANCER RESEARCH CENTER (DEUTSCHES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENTRUM, DKFZ) Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy is a new and in some cases highly effective form of immunotherapy to treat certain types of cancer of the blood and lymph system. This promising treatment comes at a cost, however: The manufacturers charge up to EUR 320,000 for the...
Simple blood test could one day diagnose motor neurone disease
by University of Sussex Scientists at the University of Sussex have identified a potential pattern within blood which signals the presence of motor neuron disease; a discovery which could significantly improve diagnosis. Currently, it can take up to a year for a patient to be diagnosed with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis(ALS), more commonly known as motor...
A sugar hit to help destroy cancer cells
by University of Southern California The research team has discovered that akt-type cancer cells, which are common in breast cancer, above, can be killed by a common milk sugar, galactose. Credit: Wikimedia Commons Like any cells in the body, cancer cells need sugar—namely glucose—to fuel cell proliferation and growth. Cancer cells in particular metabolize glucose...
Novel antisense drug shows promise in slowing fatty liver disease
In Phase II trial, treatment inhibited key enzyme, resulting in lowered triglyceride production and slower progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease to its more dangerous form: non-alcoholic steatohepatitis UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – SAN DIEGO Using a first-of-its-class drug in a clinical trial, an international research effort headed by a scientist at University of California San...