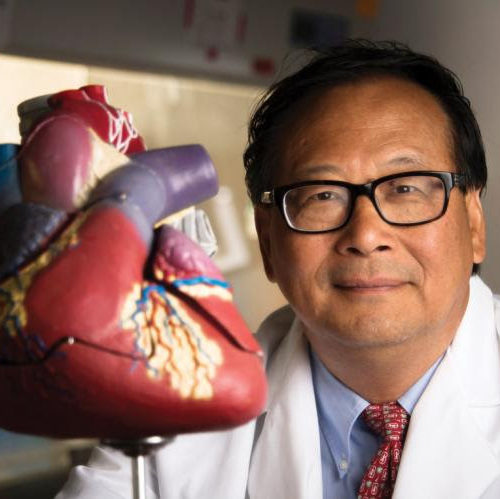
Injections of two chemicals in a slow-release form significantly reduced the size of dead heart tissue and improved the function of the left ventricle. UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA AT BIRMINGHAM BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – A novel treatment reduces heart damage after serious heart attacks in two animal models. Injections of two chemicals in a slow-release form significantly...
Tag: <span>Protection</span>
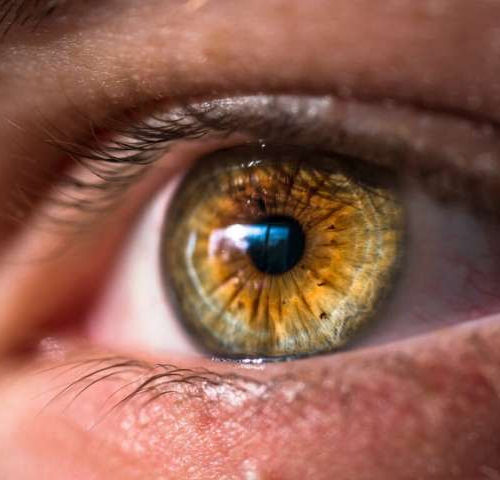
Clinicians identify pink eye as possible primary symptom of COVID-19
by University of Alberta Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry A case of pink eye is now reason to be tested for COVID-19, according to University of Alberta researchers. Coughing, fever and difficulty breathing are common symptoms of the illness, but a recent case study involving an Edmonton woman and published in the Canadian Journal of...
An aspirin a day keeps the bowel doctor away
by Newcastle University A regular dose of aspirin to reduce the risk of inherited bowel cancer lasts at least 10 years after stopping treatment, research has revealed. The international trial—known as CAPP2—involved patients with Lynch syndrome from around the world and revealed that two aspirins a day, for an average of two and a half...
Coronavirus antibodies may last only two to three months after infection, study suggests
Berkeley Lovelace Jr. @BERKELEYJR Coronavirus antibodies may last only two to three months after a person becomes infected with Covid-19, according to a new study published Thursday in Nature Medicine. Researchers in the Wanzhou District of China compared the antibody response of 37 asymptomatic people with that of 37 symptomatic people. The researchers found people...
Working in the sun—heating of the head may markedly affect safety and performance
by University of Copenhagen Prolonged exposure of the head to strong sunlight significantly impairs cognitively dominated functions and coordination of complex motor tasks, according to a new study from the Heat-Shield project coordinated by researchers from Department of Nutrition, Exercise and Sports at University of Copenhagen. This may have important implications for work safety and...
Missing sodium-channel component may protect against diet-induced artery stiffening
by American Physiological Society New research in mice finds that deficiency in one small component of a signaling pathway may protect against artery stiffening and subsequent kidney disease associated with a high-fat, high-sugar diet. The study is published in the American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology. Consuming a western diet—typically high in fat and refined carbohydrates,...
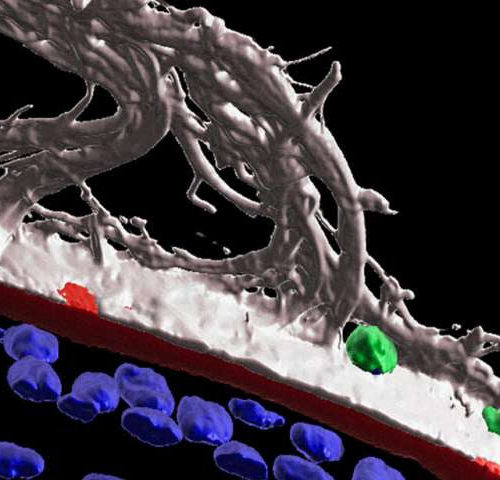
Eye injury sets immune cells on surveillance to protect the lens
by Thomas Jefferson University 3D surface structure imaging at one day post-corneal wounding shows immune cells (CD45+, green) migrating along within ciliary zonule fibrils (MAGP1+, white) that extend along the surface of the matrix capsule that surrounds the lens (perlecan+, red). Also seen are the ciliary zonules (white) that link the lens to the ciliary...
Scientists in China believe new drug can stop pandemic ‘without vaccine’
by Qian Ye and Matthew Knight A Chinese laboratory has been developing a drug it believes has the power to bring the coronavirus pandemic to a halt. The outbreak first emerged in China late last year before spreading across the world, prompting an international race to find treatments and vaccines. A drug being tested by...
Repurposed Drug for Brain Protection
Drug that reduces swelling may help protect against brain and spinal cord injury. Every year, millions of people around the world suffer brain and spinal cord injuries resulting from trauma, accidents, infections, or stroke. These injuries trigger swelling that can lead to death or long-lasting disabilities, but current treatment options are limited and can be...