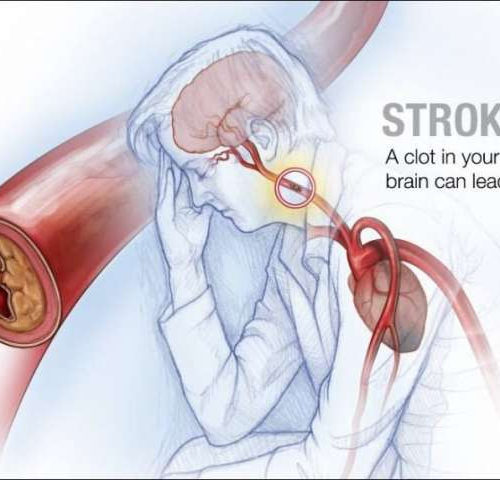
by Lynda De Widt, Mayo Clinic Researchers at Mayo Clinic in Florida and collaborators have found that a biomarker in the blood may determine the extent of brain injury from different types of strokes and predict prognosis in these patients. Their findings are reported in Science Translational Medicine. The blood biomarker is a protein known as neurofilament light...
Tag: <span>Protein</span>
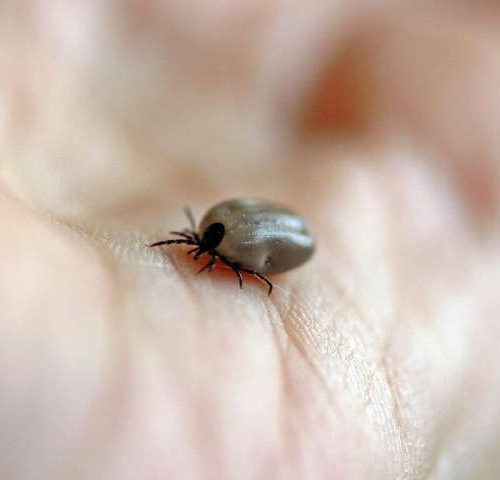
Scientists identify protein that protects against Lyme
by Yale University Yale researchers have discovered a protein that helps protect hosts from infection with the tick-borne spirochete that causes Lyme Disease, a finding that may help diagnose and treat this infection, they report Nov. 11 in the journal PLOS Pathogens. Lyme Disease is the most common vector-borne disease in North America and is transmitted by ticks infected...
That’s a wrap: Protein ‘burritos’ stabilize vaccines
by Kelley Christensen, Michigan Technological University Half of vaccines are wasted annually because they aren’t kept cold. Chemical engineers have discovered a way to stabilize viruses in vaccines with proteins instead of temperature. Ever receive a vaccination that seemed to burn while it was injected? The vaccine solution likely contained a lot of salt or sugar—natural...
Protein by which common skin bacteria trigger eczema identified
A decade-long study has identified the factor produced by a common species of skin bacteria that triggers eczema, in a breakthrough of our understanding of the condition. The discovery of a missing link by an international team led by University of Manchester scientists could lead to new treatments for the sometimes debilitating skin condition which...
Discovery of a druggable pocket in the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein could stop virus in its tracks
by University of Bristol A druggable pocket in the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein that could be used to stop the virus from infecting human cells has been discovered by an international team of scientists led by the University of Bristol. The researchers say their findings, published today in the journal Science, are a potential ‘game changer’ in defeating the current...
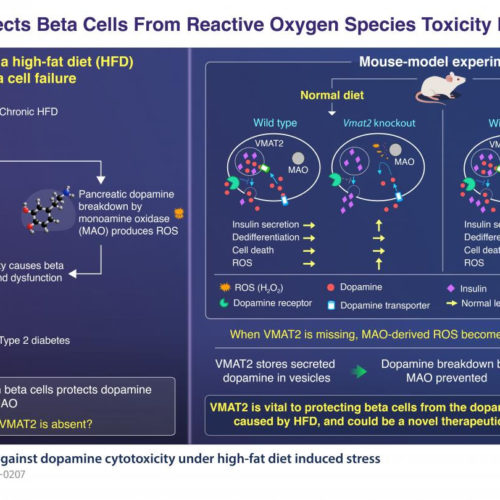
A ferry protein in the pancreas protects it from the stress induced by a high-fat diet
TOKYO INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY IMAGE: VMAT2 CONTROLS THE AMOUNT OF DOPAMINE IN BETA-CELLS THEREBY PROTECTING PANCREATIC BETA-CELLS FROM EXCESSIVE OXIDATIVE STRESS. Every time we eat, the glucose level in our body goes up. This spurs our pancreatic machinery into action and through intricate physiological mechanisms, appropriate amounts of insulin are produced, our blood glucose levels...
Across the cell membrane
This news or article is intended for readers with certain scientific or professional knowledge in the field. Some of the most essential processes on the planet involves water and energy entering and leaving cells. The cellular doormen responsible for this access are known as aquaporins and glucose transporters, two families of proteins that facilitate the...
How antibiotics interact with each other
by University of Cologne It is usually difficult to predict how well drugs will work when they are combined. Sometimes, two antibiotics increase their effect and inhibit the growth of bacteria more efficiently than expected. In other cases, the combined effect is weaker. Since there are many different ways of combining drugs—such as antibiotics—it is...
Protein discovery could improve type 2 diabetes treatment
by University of Melbourne A world first discovery of how a protein works in the liver could lead to a more effective type 2 diabetes drug. The University of Melbourne-led study found that the SMOC1 protein, which is naturally produced by the liver, can decrease blood glucose levels. An engineered form of SMOC1 could therefore...
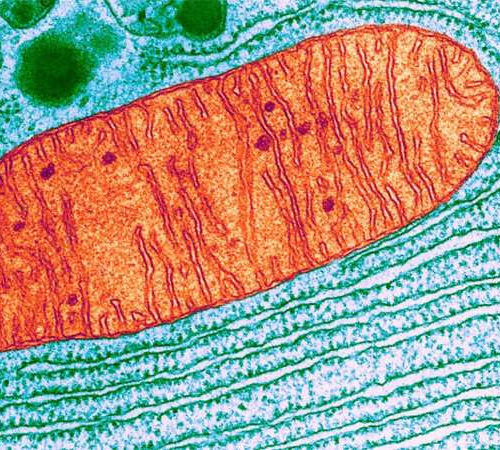
Scientists look to cell recycling tools for new ways to treat Parkinson’s disease
by Vanessa Wasta, Johns Hopkins University Photomicrograph of a mitochondrion, the energy-generating powerhouse in a human cell. Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers are studying how to recycle these organelles and perhaps, lead to new treatments for Parkinson’s disease. Credit: University of Wisconsin-Madison College of Agricultural and Life Sciences Researchers at Johns Hopkins Medicine are taking a...