by Deborah Kotz, University of Maryland School of Medicine Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) have identified how certain gene mutations cause amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease. The pathway identified by the researchers may also be responsible for a certain form of dementia related to ALS....
Tag: <span>Protein</span>
Ways to disrupt protein synthesis in Staphylococcus aureus found
Kazan Federal University continues to research Staphylococcus aureus, one of the most dangerous bacteria causing nosocomial infections. It is well known that many strains of Staphylococcus are resistant to antibiotics, and research groups around the world seek new targets in the bacteria to decrease their infectious potential. Head of KFU research group, Leading Research Associate...
Essential components of dietary restriction revealed
by Monash University Led by Dr. Adam Rose , the recent finding, published in Nature Communications, shows that by reducing the amount of two amino acids—threonine and tryptophan—in young healthy mice, they were able to burn more calories than they consumed, without calorie reduction, keeping them lean and healthy and without the side-effect of lower...
Study uncovers link between psoriasis and joint disease
Reviewed by James Ives, M.Psych. (Editor) A team led by Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine researchers has made two major discoveries involving psoriasis, a chronic and debilitating skin disease with no known cure. The researchers found that an overabundance of a protein known as KLK6 can produce and worsen the skin inflammation characteristic...
‘It opens up a whole new universe’: Revolutionary microscopy technique sees individual atoms for first time
A game-changing technique for imaging molecules known as cryo-electron microscopy has produced its sharpest pictures yet — and, for the first time, discerned individual atoms in a protein. By achieving atomic resolution using cryogenic-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), researchers will be able to understand, in unprecedented detail, the workings of proteins that cannot easily be examined by...
Environmental pollutant in drinking water is more dangerous than previously understood
New research reveals environmental pollutant in drinking water is more dangerous than previously understood. Vanderbilt researchers have discovered that perchlorate, an environmental pollutant found in many sources of drinking water in the U.S., inhibits the uptake of iodide, an essential component of thyroid hormones, in a more pronounced and fundamental way than commonly considered. This...
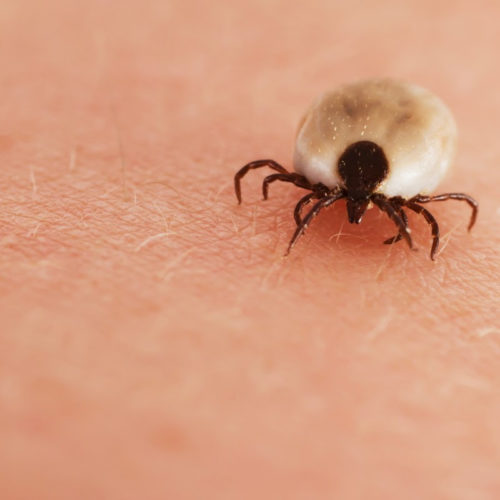
Synthetic tick-spit protein may save lives
By Ben Coxworth May 26, 2020 One of the creepy things about ticks is the fact that not only do they suck your blood, but they’re able to do so for a long time, undetected. Scientists have now synthesized the protein that lets them get away with it, and it may have life-saving medical applications....
First map of proinsulin’s ‘social network’ reveals new drug target for type 2 diabetes
Study reveals previously unknown protein that helps proinsulin fold and opens new avenues for diabetes research SANFORD BURNHAM PREBYS MEDICAL DISCOVERY INSTITUTE Scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute have mapped for the first time the vast network of proteins that interact with proinsulin, the protein the body normally processes into insulin. The study,...
Blocking tumor signals can hinder cancer’s spread
by University of Pennsylvania For most people who die of cancer, the spread of the initial tumor is to blame. “Metastasis is what kills most cancer patients,” says Serge Fuchs, a professor in Penn’s School of Veterinary Medicine. “Yet there are not many, if any, drugs that specifically target metastatic processes.” In a paper in...
Restoring nerve-muscle communication in ALS
by Karuna Meda, Thomas Jefferson University Patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, lose muscle control as nerve cells or neurons in the brain and spinal cord degenerate and can no longer send signals to muscles. Previous studies have identified that problems at the synapse, the point where signals jump...