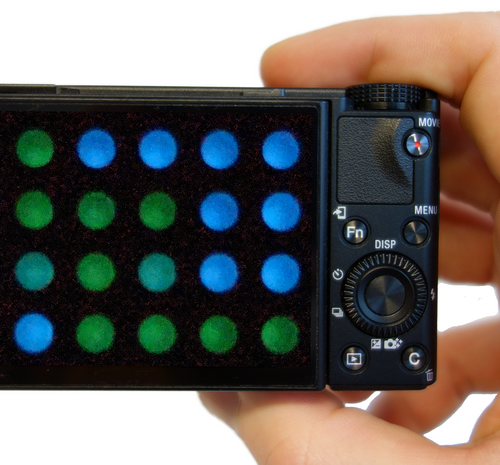
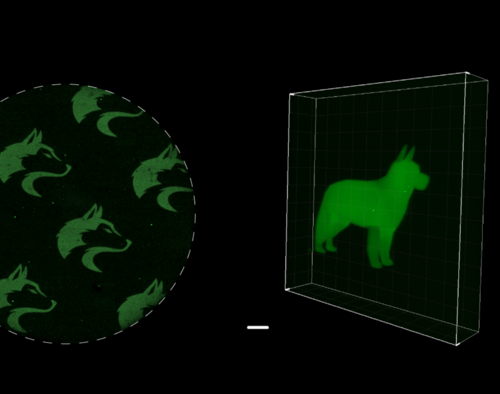
UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON SCHOOL OF MEDICINE/UW MEDICINE IMAGE: MICROSCOPIC 2D AND 3D IMAGES OF UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON HUSKY LOGOS AND A DOG WERE MADE WITH A NEW CHEMISTRY TECHNIQUE, SPYLIGATION, THAT PRECISELY CONTROLS WHEN AND WHERE PROTEINS TURN ON. CREDIT: COLE DEFOREST RESEARCH GROUP Scientists can now use light to activate protein functions both inside and outside...
Tag: <span>proteins</span>
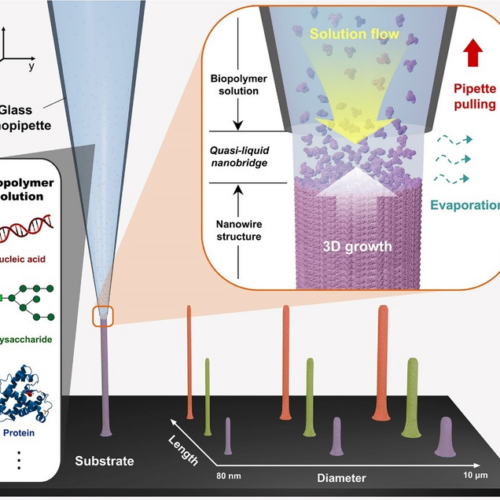
Entering an ERA of 3D printing even for DNAs and proteins
POHANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY (POSTECH) IMAGE: 3D PRINTING OF BIOPOLYMERS (NUCLEIC ACIDS, POLYSACCHARIDES, PROTEINS) WITH NANOSCALE RESOLUTION CREDIT: POSTECH Three-dimensional (3D) bioprinting is a useful technique that has been widely utilized in our lives, ranging from reconstructive plastic surgery to artificial organ production. However, many biopolymers, such as nucleic acids, polysaccharides, and proteins,...
‘Glow-in-the-dark’ proteins could help diagnose viral diseases
AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY IMAGE: PROTEINS THAT GLOW BRIGHT BLUE OR GREEN, AS PICTURED HERE, COULD MAKE DISEASE DIAGNOSIS QUICKER AND EASIER. CREDIT: MAARTEN MERKX Despite recent advancements, many highly sensitive diagnostic tests for viral diseases still require complicated techniques to prepare a sample or interpret a result, making them impractical for point-of-care settings or areas...
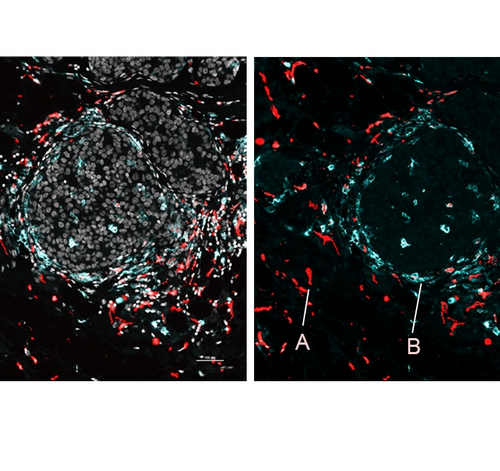
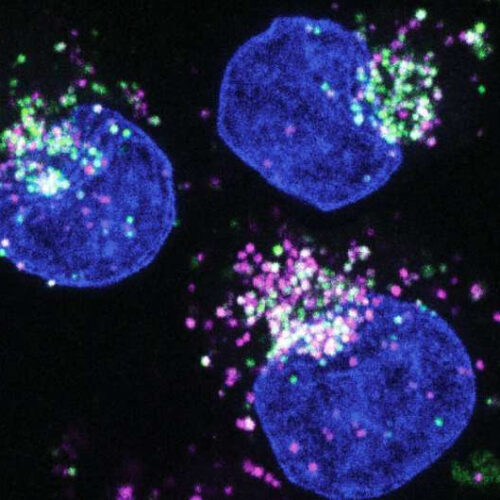
New method precisely locates gene activity and proteins across tissues
WEILL CORNELL MEDICINE IMAGE: IMAGE OF HUMAN BREAST CANCER CELLS SHOWING A) IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVE MACROPHAGES NEAR TUMOR CONNECTIVE TISSUE, AND B) IMMUNOSTIMULATORY MACROPHAGES NEAR TUMOR NESTS. CREDIT: NIR BEN CHETRIT. A new method can illuminate the identities and activities of cells throughout an organ or a tumor at unprecedented resolution, according to a study co-led by researchers at...
Detecting the undetected: Measuring levels of three proteins in the blood can aid detection of undiagnosed prediabetes
by University of Cambridge Credit: CC0 Public Domain Scientists have used a proteomics approach to identify a three-protein signature in the blood that can improve detection of isolated impaired glucose tolerance, a form of prediabetes. The research, led by scientists from the Medical Research Council (MRC) Epidemiology Unit at the University of Cambridge, U.K., and Berlin...
Breaking down proteins: How starving cancer cells switch food sources
by German Cancer Research Center Human cancer cells (cell nucleus in blue) feeding on protein (Albumin, labeled in green). The proteins are digested and broken down into amino acids in the lysosomes (magenta). Credit: W. Palm / DKFZ Cancer cells often grow in environments that are low in nutrients, and they cope with this challenge...
Activated surface proteins may reverse development of malignant neuroblastoma cells
by Karolinska Institutet Credit: CC0 Public Domain In a new study, researchers at Karolinska Institutet show that the activation of specific cell surface proteins—cortisol, estrogen and vitamin A—in mice with human neuroblastoma cells results in the neuronal differentiation of cancer cells which leads to reduced mortality. The results, published in the Journal of Experimental & Clinical...
Nanobiotics: Model predicts how nanoparticles interact with proteins
Nanoengineered drugs that stop harmful bacteria and viruses could be on the horizon. With antibiotic-resistant infections on the rise and a continually morphing pandemic virus, it’s easy to see why researchers want to be able to design engineered nanoparticles that can shut down these infections. A new machine learning model that predicts interactions between nanoparticles...
Artificial intelligence system rapidly predicts how two proteins will attach
The machine-learning model could help scientists speed the development of new medicines. Antibodies, small proteins produced by the immune system, can attach to specific parts of a virus to neutralize it. As scientists continue to battle SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes Covid-19, one possible weapon is a synthetic antibody that binds with the virus’ spike proteins to...
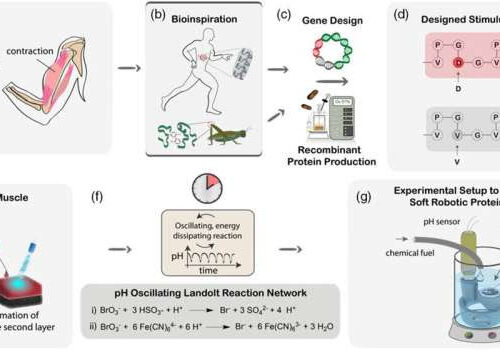
Artificial muscles made of proteins
by University of Freiburg Scheme of the artificial protein muscle design, fabrication, and application. a) Natural muscle characteristics. Inspired by nature’s high-performance materials elastin and resilin. b) Novel protein genes are designed to biotechnologically produce the corresponding recombinant proteins. c) Yielding a pH-responsive protein (DSY)16 d) upper sequence in red) and a temperature-responsive protein (VRY)16...