Inaccurate: RNA from a vaccine would not be able to directly alter our DNA, in part because of the chemical differences between the two nucleic acids. RNA also would not persist long enough to cause autoimmunity. Autoimmune diseases are chronic in nature, whereas RNA has a very short lifespan, being quickly degraded after it has...
Tag: <span>proteins</span>
Moving the diagosis of rheumatic diseases into the era of precision medicine
by Delthia Ricks , Medical Xpress Many rheumatic conditions develop slowly and initially have inflammatory arthritis as the first sign that something is amiss. The trouble with such close similarity is the difficulty that clinicians have differentiating one condition from another in the early stages of the disease process. Dr. Rachel Knevel and colleagues at...
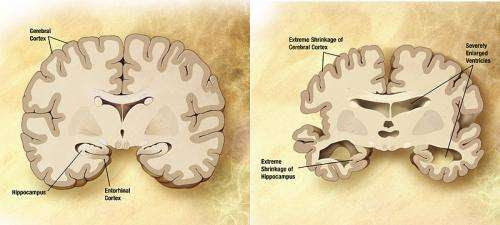
Effects of Cell Death on Neurodegeneration
By Christy Cheung, MRes Neuronal cell death in the nervous system is a major contribution to neurodegenerative diseases. Despite occasional neuronal deaths during the process of aging, extensive neuronal cell death is rare in adults with a mature central nervous system (CNS). Nevertheless, there is an increased neuronal loss in patients with neurodegenerative diseases compared...
Study hints at early sign of Alzheimer’s degeneration
by Maggie MacLellan, University of Western Ontario BrainsCAN researchers examined an area in the brain’s subcortical region called the basal forebrain that includes cholinergic neurons. These neurons are known to be severely damaged by Alzheimer’s disease. Credit: University of Western Ontario Researchers have moved one step closer to identifying targets for brain degeneration that occur...
Designer peptides show potential for blocking viruses, encourage future study
Research demonstrates how Rensselaer-made peptides can bind to cells and potentially block viruses Designer peptides show potential for blocking viruses, e TROY, N.Y. — Chemically engineered peptides, designed and developed by a team of researchers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, could prove valuable in the battle against some of the most persistent human health challenges. The...
It’s not just Alzheimer’s disease: Research highlights form of dementia
by University of Kentucky The long-running study on aging and brain health at the University of Kentucky’s Sanders-Brown Center on Aging Alzheimer’s Disease Center has once again resulted in important new findings—highlighting a complex and under-recognized form of dementia. The work was recently published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA): Neurology. “One...
What are Furin Proteases?
By Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc. Reviewed by Emily Henderson, B.Sc. In order to develop appropriate treatments and vaccines to combat the novel coronavirus, otherwise known as SARS-CoV-2 or COVID-19, researchers around the world have carefully examined every microscopic component of this potent virus. What is protease? The term protease is used to describe a large group...
Study finds protein in mitochondria appears to regulate health and longevity
by University of Southern California A new study led by researchers at the USC Leonard Davis School of Gerontology is the first to demonstrate that a tiny protein has a big impact on health and longevity in both animals and humans. The researchers examined humanin, a peptide encoded in the small genome of mitochondria—the powerhouses...
Different ‘subtypes’ of Alzheimer’s may be linked to different modifications of the tau protein
by Massachusetts General Hospital A new study reveals a possible biological reason that Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) progresses at different rates in different patients. The study, which was led by Massachusetts General Hospital researchers, focused on tau, a protein found in the neurofibrillary tangles in the brain that are a well-known sign of AD. Tau can...
Disrupted circadian rhythms linked to later Parkinson’s diagnoses
Researchers probe brain’s 24-hour biological clock for neurodegenerative risks UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – SAN FRANCISCO Older men who have a weak or irregular circadian rhythm guiding their daily cycles of rest and activity are more likely to later develop Parkinson’s disease, according to a new study by scientists at the UC San Francisco Weill Institute...