Hydroxychloroquine is a medication that doctors prescribe to treat a variety of conditions, including malaria, arthritis, and lupus. Recently, some doctors had been using hydroxychloroquine to treat severe cases of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients. Its use for this purpose has been controversial and conflicting, with some researchers reporting heart problems among those taking the drug....
Tag: <span>researchers</span>
Covid 19 outstanding questions
Six months of coronavirus: the mysteries scientists are still racing to solve From immunity to the role of genetics, Nature looks at five pressing questions about COVID-19 that researchers are tackling. In late December 2019, reports emerged of a mysterious pneumonia in Wuhan, China, a city of 11 million people in the southeastern province of...
Chemist develops potential drug to treat type 2 diabetes without harsh side effects
Credit: Syracuse University Syracuse, N.Y. – Syracuse University chemistry professor Dr. Robert P. Doyle has developed a new drug lead to treat type 2 diabetes in millions of patients who are seeking to better control their blood sugar without the common side effects of nausea, vomiting, and in select cases, undesired weight loss. Doyle’s research...
Scientists discover protective Alzheimer’s gene and develop rapid drug-testing platform
by Queen Mary, University of London A gene has been discovered that can naturally suppress the signs of Alzheimer’s Disease in human brain cells, in research led by Queen Mary University of London. The scientists have also developed a new rapid drug-screening system for treatments that could potentially delay or prevent the disease. The main...
Spatial mapping method pinpoints potential new therapeutic targets in lupus
by Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia A team of researchers from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) used a new method of pinpointing potential disease-causing changes in the genome to identify two new potential therapeutic targets for lupus, while also paving the way for more accurately identifying disease-causing variations in other autoimmune disorders. The findings were published...
UBC research shows hearing persists at end of life
Hearing is widely thought to be the last sense to go in the dying process. Now UBC researchers have evidence that some people may still be able to hear while in an unresponsive state at the end of their life. This research, published recently in Scientific Reports, is the first to investigate hearing in humans...
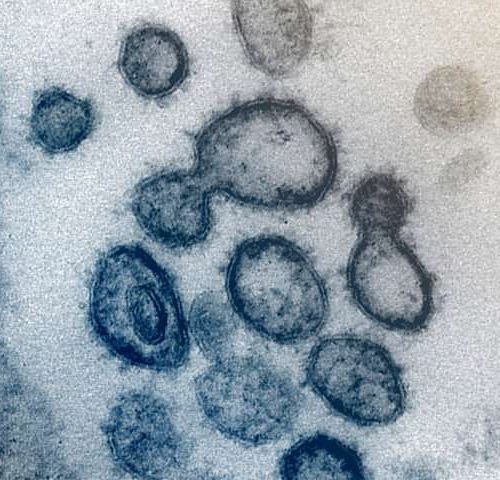
Increase in delirium, rare brain inflammation and stroke linked to COVID-19
by University College London This transmission electron microscope image shows SARS-CoV-2 — also known as 2019-nCoV, the virus that causes COVID-19 — isolated from a patient in the US. Virus particles are shown emerging from the surface of cells cultured in the lab. The spikes on the outer edge of the virus particles give coronaviruses...
Team develops new approach to treat certain neurological diseases
This news or article is intended for readers with certain scientific or professional knowledge in the field. Research produces dramatic results in laboratory studies involving fatal myelin disease that strikes children. A team led by Case Western Reserve University medical researchers has developed a potential treatment method for Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease (PMD), a fatal neurological disorder...
Coronavirus Discovery: Indigestion and Heartburn Drugs May Increase Chances of COVID-19 by Two-Fold
By Nhx T. Tech Time Until now, scientists are still trying to understand COVID-19 fully to help ensure people’s safety. A new study suggests that popular indigestion and heartburn drugs could increase the risks of getting coronavirus infection. People who take certain indigestion and heartburn medicines are more likely to contract COVID-19. Higher Risk of...
Study shows harmful elements prevalent in suicide posts on social media while protective elements are rare
by Bob Yirka , Medical Xpress A trio of researchers, two with Facebook, the other the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, has found that posts that feature elements considered harmful to people at risk of committing suicide are prevalent on shared social media sites, but those with protective elements are rare. In their paper...