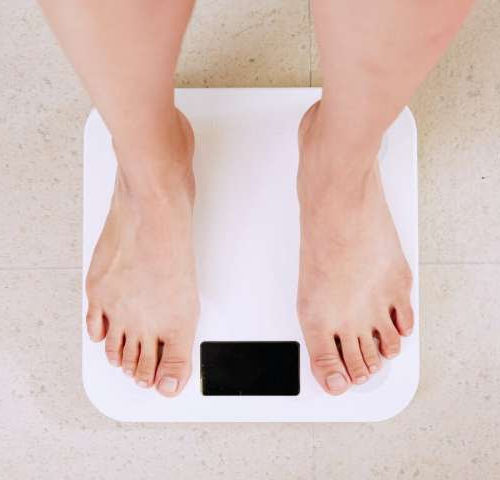
by Steve Lundeberg, Oregon State University A compound given as a dietary supplement to overweight but otherwise healthy people in a clinical trial caused many of the patients to slim down, research by Oregon State University and Oregon Health & Science University showed. The research, published in the Journal of Nutrition, analyzed the effects of...
Tag: <span>researchers</span>
Study finds parents can help kids eat healthier by knowing their own sense of self-control
University of Oregon study finds that parental views of lay theories influence what meals they serve to children and how children develop their food preferences EUGENE, Ore. – Aug. 7, 2020 – Young children naturally like sugar and salt in food and develop food preferences based on what their parents serve them, but new research...
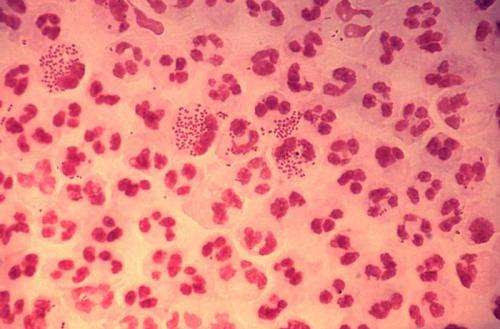
Test accurately IDs people whose gonorrhea can be cured with simple oral antibiotic
by University of California, Los Angeles A test designed by UCLA researchers can pinpoint which people with gonorrhea will respond successfully to the inexpensive oral antibiotic ciprofloxacin, which had previously been sidelined over concerns the bacterium that causes the infection was becoming resistant to it. In research published in the peer-reviewed journal Clinical Infectious Diseases,...
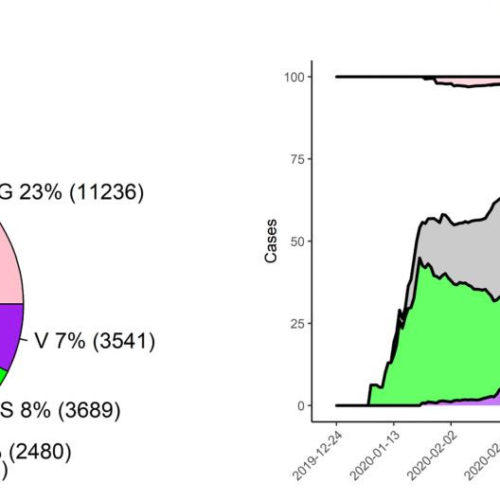
The six strains of SARS-CoV-2
THE MOST EXTENSIVE STUDY EVER CARRIED OUT ON SARS-COV-2 SEQUENCING REVEALED SIX STRAINS OF THE VIRUS. The virus causing the COVID-19 pandemic, SARS-CoV-2, presents at least six strains. Despite its mutations, the virus shows little variability, and this is good news for the researchers working on a viable vaccine. These are the results of the...
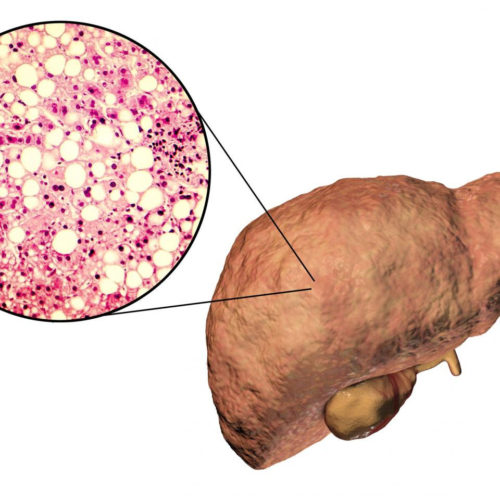
Osteopontin, a protein not always as bad as it is made out to be
The UPV/EHU-University of the Basque Country shows that maintaining osteopontin delays the onset of metabolic fatty liver disease during ageing UNIVERSITY OF THE BASQUE COUNTRY THE STUDY INDICATES THAT OSTEOPONTIN IS NECESSARY TO PREVENT THE EARLY ONSET OF NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE LINKED TO AGEING view more Metabolic fatty liver disease, known as non-alcoholic fatty...
Scientists discover the switch that makes human brown fat burn energy
UNIVERSITY OF COPENHAGEN THE FACULTY OF HEALTH AND MEDICAL SCIENCES An international research team have discovered how to activate brown fat in humans, which may lead to new treatments for type 2 diabetes and obesity. The results of the collaboration between the Centre de recherche du Centre hospitalier universitaire de Sherbrooke (CRCHUS) and the Novo...
Tool could improve success in translating drugs from animal studies to humans
by Kayla Wiles, Purdue University Doug Brubaker, a Purdue assistant professor of biomedical engineering, uses computational and experimental approaches to study host-microbiome interactions in cancers and inflammatory diseases. Credit: Purdue University /John Underwood About 50% of people who take the drug infliximab for inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn’s disease, end up becoming resistant or...
UCI researchers publish new guide for viral tracers in neural circuit mapping
Center for Neural Circuit Mapping established to disseminate molecular tools to the worldwide neuroscience community UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – IRVINE XU ET AL. REVIEW AND EVALUATE GENETICALLY MODIFIED VIRUSES DEVELOPED FOR NEURAL CIRCUIT MAPPING, INCLUDING HERPESVIRUS, RABIES VIRUS, ADENOVIRUSES, LENTIVIRUSES, AND ADENO-ASSOCIATED VIRUSES.view more CREDIT: UCI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Irvine, CA – August 4, 2020...
Fitness watches generate useful information, but increase patient anxiety
How does measuring our sleep, exercise and heart rates using various apps and fitness watches affect us? Self-quantifying may better the understanding of our individual health, but according to a new study, it also gives rise to anxiety. The researchers h UNIVERSITY OF COPENHAGEN PRINT E-MAIL Is my heart beating slightly fast? Is a heart...
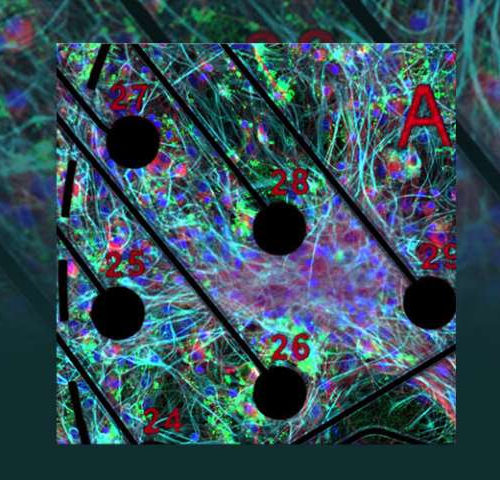
Neuronal cultures advance ‘brain-on-a-chip’ technology
by Jeremy Thomas, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Laboratory team cultured rodent-derived neurons on microelectrode arrays and allowed the cultures to form networks, supplementing them with astrocytes and oligodendrocytes — cell types that play a critical role in neuronal health and function. Pictured is an immunofluorescence image of a complex culture, showing neurons (stained red), astrocytes...