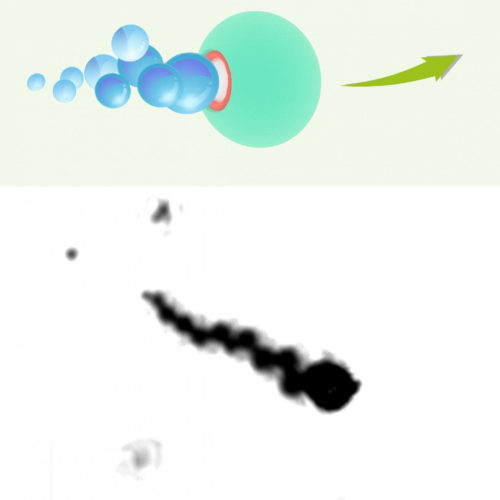
By Ben Coxworth February 24, 2021 An illustration of one of the micromotors (top), along with a microscope image of the genuine articleAdapted from Nano Letters 2021, DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c04438VIEW 1 IMAGES Although the drinking of hydrogen-gas-infused water can help treat rheumatoid arthritis, the effects are limited. Scientists have developed what could be a better alternative,...
Tag: <span>rheumatoid arthritis</span>
Treating rheumatoid arthritis with micromotors
AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY IMAGE: HYDROGEN-PROPELLED MICROMOTORS (ILLUSTRATION, TOP, AND MICROSCOPE IMAGE, BOTTOM) IMPROVED RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS SYMPTOMS WHEN INJECTED INTO RATS’ JOINTS. SCALE BAR, 20 ΜM. CREDIT: ADAPTED FROM NANO LETTERS 2021, DOI: 10.1021/ACS.NANOLETT.0C04438 Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder marked by joint pain, swelling and damage. Although medications, such as steroids, anti-inflammatory drugs and immunosuppressants, can...
A new approach to study autoimmune diseases
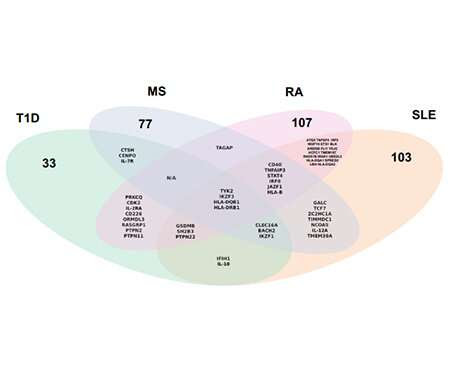
by Indiana Biosciences Research Institute Venn diagrams of risk genes expressed in the target tissues of the fourautoimmune diseases (type 1 diabetes, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis) shows shared candidate genes among them. Credit: Indiana Biosciences Research Institute A team of researchers led by the Indiana Biosciences Research Institute Diabetes Center’s Scientific Director Decio L. Eizirik, MD, Ph.D., has found...
Opening a new door into kinder, gentler therapies for chronic inflammation
by Delthia Ricks , Medical Xpress A structural model of TNFR2 and the antibody agonist. Credit: H. Torrey et al., Science Signaling (2020) Credit: H. Torrey et al., Science Signaling (2020) A naturally occurring antibody capable of stimulating the body’s immune-suppressing regulatory T cells has been discovered by a team of Harvard scientists, a finding...
New therapeutic target pinpointed for stomach cancer
by Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain WEHI researchers have identified a key molecular regulator involved in the progression and spread of stomach cancer, suggesting a potential new approach to treat this devastating disease. The team discovered that removing the inflammatory signaling protein TNF in a laboratory model prevented early...
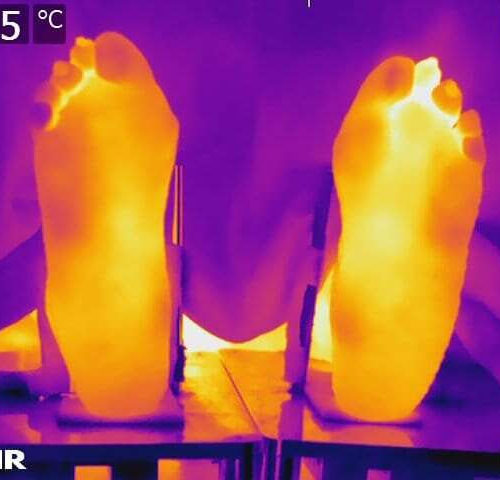
Higher body temperatures still a factor in patients in remission from rheumatoid arthritis
by Staffordshire University Thermal image showing temperatures in the different regions of the foot. Credit: Staffordshire University A pioneering study carried out among patients in remission from Rheumatoid Arthritis has determined that they display significantly higher temperatures than healthy individuals. The work, published in PLOSONE and undertaken by University of Malta and Staffordshire University, compares...
New breakthrough in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
by University of Oxford Credit: University of Oxford People with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) could soon benefit from a new drug treatment that not only suppresses inflammation but also significantly reduces patient reported pain scores. Otilimab is a monoclonal antibody, biologic drug, which targets and suppresses the inflammatory cytokine GM-CSF. In a multicentre, dose-ranging trial, led by...
Scientists pinpoint two new potential therapeutic targets for rheumatoid arthritis
by Trinity College Dublin Dr Achilleas Floudas, front right, and Professor Ursula Fearon, left, with members of Trinity College Dublin’s Molecular Rheumatology Group. A collaborative team of scientists has pinpointed two new potential therapeutic targets for rheumatoid arthritis—a painful inflammatory disease that affects an estimated 350 million people worldwide. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the most common...
New research predicts whether rheumatoid arthritis patients will respond to treatment
by Queen Mary, University of London A new study led by researchers at Queen Mary University of London provides potential novel biomarkers for predicting patient responsiveness to disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) patients are commonly treated with disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) despite the fact that up to 50% of patients are unresponsive to treatment....
Is rheumatoid arthritis two different diseases?
by Public Library of Science While disease activity improves over time for most rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, long-term outcomes only improve in RA patients with autoantibodies, according to a new study published this week in PLOS Medicine by Xanthe Matthijssen of Leiden University Medical Center, Netherlands, and colleagues. The findings add to a growing body of evidence that...