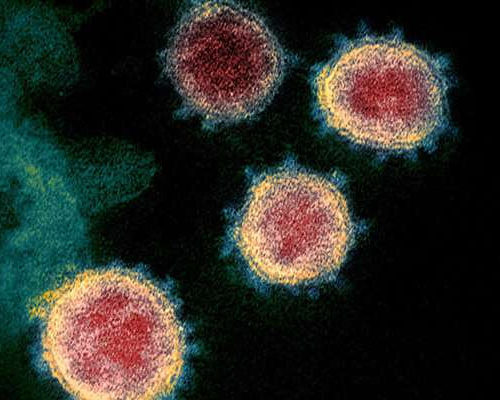
by German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases An infection with the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 can affect multiple organs. With this in mind, researchers of the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE) and Cornell University in the US have investigated cellular factors that could be significant for an infection. To this end, they analyzed the activity of 28...
Tag: <span>RNA</span>
Heart repair factor boosted by RNA-targeting compound
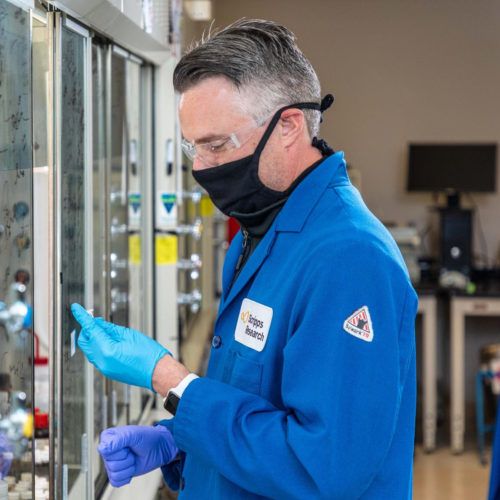
Disney lab collaboration reawakens heart cells’ silenced VEGF-A healing system by targeting non-coding RNA SCRIPPS RESEARCH INSTITUTE CHEMISTRY PROFESSOR MATTHEW DISNEY, PHD, IN HIS LAB AT SCRIPPS RESEARCH IN JUPITER, FLORIDA. DISNEY AND HIS GRADUATE STUDENT, HAFEEZ HANIFF, DEVELOPED A COMPOUND THAT ACTS ON NON-CODING RNA TO… view more CREDIT: MATTHEW STURGESS FOR SCRIPPS RESEARCH...
RNA quality control system goes awry in frontotemporal lobar degeneration
by Osaka University Researchers at Osaka University have identified a fault in the RNA quality control system of cells that leads to the haywire production of toxic proteins in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (FTLD/ALS). Their new study, published in the EMBO Journal, shows that an abnormality of the C9orf72 gene produces toxic...
Deciphering the largest CRISPR system
Interview conducted by Emily Henderson, B.Sc. Professor Guillermo Montoya spoke to News-Medical on his research that involved visualizing the largest and most complex CRISPR system, which could have potential applications in biomedical diagnostics. What provoked your research into CRISPR? My interest in protein-DNA interactions and genome editing started a while ago when I collaborated with...
New treatment targets found for blinding retinal disease
by Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University When the eye isn’t getting enough oxygen in the face of common conditions like premature birth or diabetes, it sets in motion a state of frenzied energy production that can ultimately result in blindness, and now scientists have identified new points where they may be able to...
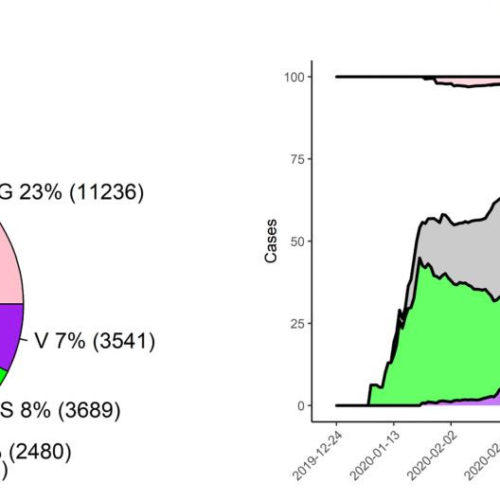
The six strains of SARS-CoV-2
THE MOST EXTENSIVE STUDY EVER CARRIED OUT ON SARS-COV-2 SEQUENCING REVEALED SIX STRAINS OF THE VIRUS. The virus causing the COVID-19 pandemic, SARS-CoV-2, presents at least six strains. Despite its mutations, the virus shows little variability, and this is good news for the researchers working on a viable vaccine. These are the results of the...
RNA scientists advance early detection of Duchene muscular dystrophy
by University at Albany The devastating effects of Duchene muscular dystrophy (DMD) can be mitigated if detection takes place in early childhood. Sadly, early diagnosis is rare. Now, University RNA researchers have discovered a novel method that could solve this long-standing problem. The research team, from the UAlbany laboratories Professor Igor Lednev of Chemistry and...
ENCODE 3 project details the inner workings of the human and mouse genome
by NIH/National Human Genome Research Institute The Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) Project is a worldwide effort to understand how the human genome functions. With the completion of its latest phase, the ENCODE Project has added millions of candidate DNA “switches” from the human and mouse genomes that appear to regulate when and where genes...
People with SARS-CoV-2 most infectious in days 0-5, no evidence of transmission after day 9
By Sally Robertson, B.Sc. A study conducted by researchers in the UK and Italy suggests that individuals with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) are probably at their most infectious during the first week of illness. The systematic review and meta-analysis of data available on the viral dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 found that although viral...
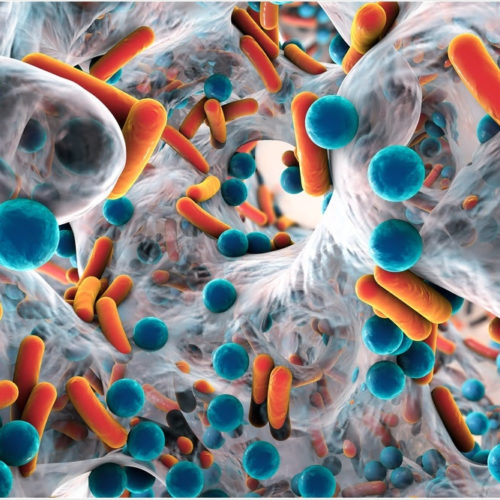
Phage therapy shows potential for treating prosthetic joint infections
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Bacteriophages, or phages, may play a significant role in treating complex bacterial infections in prosthetic joints, according to new Mayo Clinic research. The findings suggest phage therapy could provide a potential treatment for managing such infections, including those involving antibiotic-resistant microbes. The research is published in the July issue of Clinical Infectious...