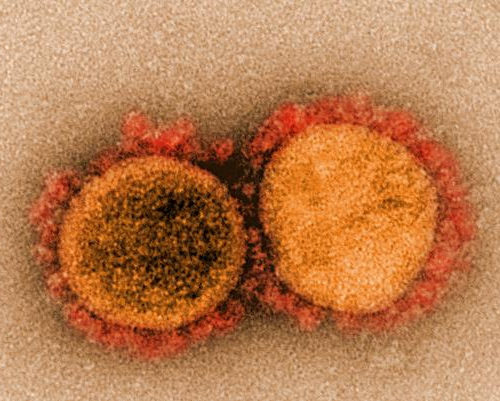
LA JOLLA INSTITUTE FOR IMMUNOLOGY IMAGE: TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROGRAPH OF SARS-COV-2 VIRUS PARTICLES, ISOLATED FROM A PATIENT. IMAGE CAPTURED AND COLOR-ENHANCED AT THE NIAID INTEGRATED RESEARCH FACILITY (IRF) IN FORT DETRICK, MARYLAND. CREDIT: NIAID LA JOLLA–A new study led by scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) suggests that T cells try to fight...
Tag: <span>SARS-CoV-2</span>
Cancer Drug Shows Potent Activity in the Lab Against SARS-CoV-2, Including B.1.1.7
By Pete Farley Plitidepsin was 27.5-fold more potent against SARS-CoV-2 than remdesivir, a drug that received FDA emergency use authorization in 2020 for the treatment of COVID-19, according to new research. Image by NIH Scientists at UC San Francisco’s Quantitative Bioscience Institute (QBI) and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mt. Sinai (ISMMS) in New York have shown that plitidepsin...
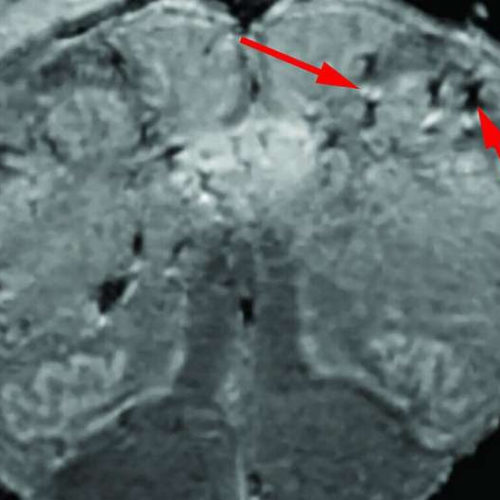
How does SARS-CoV-2 get in your head and destroy your sense of smell?
by John Hewitt , Medical Xpress Credit: National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, NIH One of the early indicators of imminent SARS-CoV-2 infection is a sudden and complete loss of smell and taste. Often, these symptoms persist long after infection has been seemingly cleared. How might a virus like this get into the nervous...
Researchers engineer antibody that acts against multiple SARS-like viruses
AMERICAN ASSOCIATION FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF SCIENCE Researchers have engineered an antibody that neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 with a potency that “rivals” current lead SARS-CoV-2 clinical neutralizing antibodies, and that also broadly neutralizes a range of clade 1 sarbecoviruses. Their antibody, ADG-2, studied in mice, represents a “promising candidate” for the prevention and treatment of not only COVID-19,...
‘A bloody mess’: Confusion reigns over naming of new COVID variants
Ewen Callaway New variants of the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 are being identified around the world.Credit: David Talukdar/NurPhoto/Getty Would a virus by any other name spread so fast? As scientists identify more and more potentially worrying variants of the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, they are grappling with just what to call them. At a 12 January World Health Organization...
Extract of medicinal plant Artemisia annua interferes with replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro
By Sally Robertson, B.Sc. Jan 11 2021 Researchers in the United States have shown that extracts of an aromatic herb called Artemisia annua inhibit the replication of severe acute respiratory coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) – the agent responsible for the current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Also known as “Sweet wormwood,” Artemisia annua (A. annua) is an herb from Asia that produces...
Could Ivermectin be an effective antiviral against SARS-CoV-2?
By Dr. Sanchari Sinha Dutta, Ph.D. Jan 11 2021 A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial conducted at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, India, has recently demonstrated that Ivermectin, an anti-parasitic drug, can reduce in-hospital mortality rate of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients. The study is currently available on the medRxiv* preprint server. Study: Ivermectin as a...
Some transmission of SARS-CoV-2 occurs after seven, 10 days
There is some onward transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) from household contacts released from quarantine after seven or 10 days, according to research published in the Jan. 1 issue of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Melissa A. Rolfes, Ph.D., from the CDC COVID-19 Response...
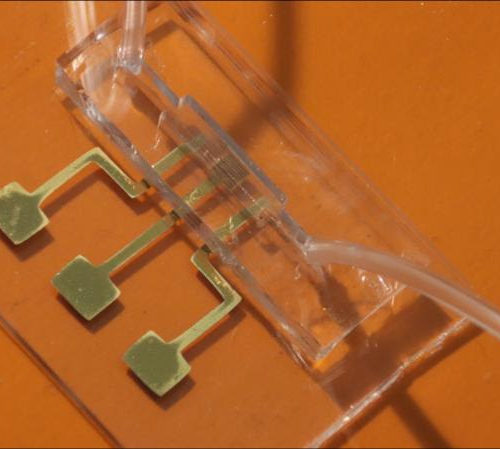
Detecting COVID-19 antibodies in 10-12 seconds
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CARNEGIE MELLON UNIVERSITY IMAGE: AN IMAGE OF THE COVID-19 TEST CHIP MADE BY AEROSOL JET NANOPARTICLE 3D PRINTING. CREDIT: ADVANCED MANUFACTURING AND MATERIALS LAB, COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CARNEGIE MELLON UNIVERSITY PITTSBURGH–Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University report findings on an advanced nanomaterial-based biosensing platform that detects, within seconds, antibodies specific to SARS-CoV-2, the virus...
Disulfide-reducing agents demonstrate potential antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2
By Dr. Sanchari Sinha Dutta, Ph.D. Jan 6 2021 A team of scientists from the University of Saskatchewan, Canada, has recently demonstrated that chemical agents capable of reducing disulfide (S-S) bonds can be potentially used as antiviral drugs against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative pathogen of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Their...