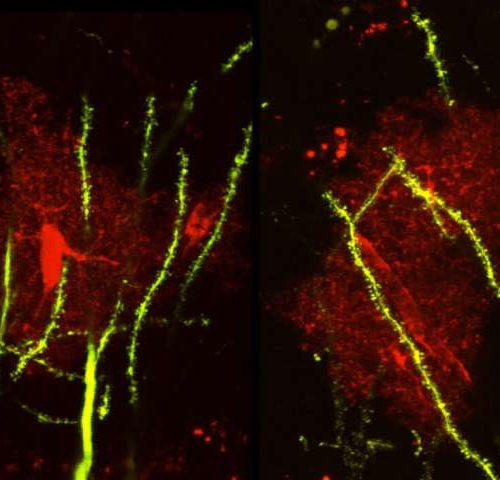
by Iqbal Pittalwala, University of California – Riverside Confocal image of a mouse brain tissue shows the astrocytes (red) and neurons (green). Credit: Ethell lab, UC Riverside. A team led by a biomedical scientist at the University of California, Riverside has found a new mechanism responsible for the abnormal development of neuronal connections in the...
Tag: <span>Schizophrenia</span>
Schizophrenia: Nurture cannot overcome nature
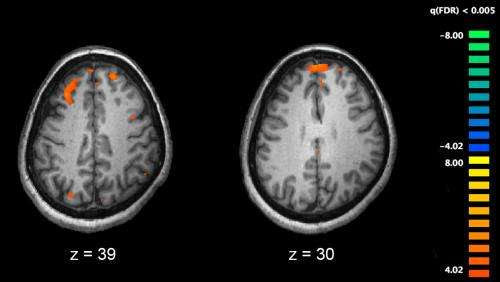
by Nicole Feldman, University of California, Irvine Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and other brain imaging technologies allow for the study of differences in brain activity in people diagnosed with schizophrenia. The image shows two levels of the brain, with areas that were more active in healthy controls than in schizophrenia patients shown in orange,...
Aging memories may not be ‘worse,’ just ‘different’
by Brandie Jefferson, Washington University in St. Louis “Older adults might be representing events in different ways, and transitions might be picked up differently than, say, a 20-year-old,” said Zachariah Reagh, assistant professor of psychological and brain sciences in Arts & Sciences. Reagh looked at fMRI images to study memory differences in different age groups....
Cannabidiol improves blood flow to brain’s hippocampus
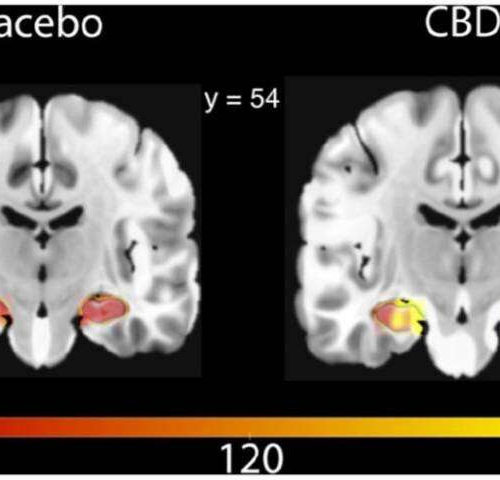
by University College London A single dose of cannabidiol (CBD) helped increase blood flow to the hippocampus, an important area of the brain associated with memory and emotion, finds a new study led by UCL researchers. Researchers say the findings could be an important discovery for conditions which affect memory, such as Alzheimer’s disease and...
Fish maze experiment provides new hope for degenerative diseases
by University of Portsmouth Zebrafish in the maze. Credit: University of Portsmouth A test of fish behavior in a maze has shed light on human degenerative conditions, heralding new hope for treatments. Fish swimming through a simple maze has shown ‘exceptional’ potential to improve progress in developing treatments for brain and psychiatric disorders, including Alzheimer’s...
Synapse-saving proteins discovered, opening possibilities in Alzheimer’s, schizophrenia
UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS HEALTH SCIENCE CENTER AT SAN ANTONIO GEK-MING SIA, PHD, AND COLLEAGUES IN THE LONG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AT UT HEALTH SAN ANTONIO DISCOVERED A NEW CLASS OF PROTEINS THAT SPARE SYNAPSES FROM ELIMINATION. INCREASING THE NUMBERS… view more CREDIT: UT HEALTH SAN ANTONIO Researchers at The University of Texas Health Science Center...
Is what I see, what I imagine? Study finds neural overlap between vision and imagination
by Catherine Bridges, Medical University of South Carolina An ibis as “seen” by a machine, 2015. This processed image, which is based on a photograph by Dr. Zachi Evenor, is courtesy of software engineer Guenther Noack, 2015, and is reproduced from Wikimedia Commons (CC BY 4.0). Credit: Dr. Guenther Noack, 2015, reproduced from Wikimedia Commons...
Complement genes add to sex-based vulnerability in lupus and schizophrenia
Variants in a gene of the human immune system cause men and women to have different vulnerabilities to the autoimmune diseases lupus and Sjögren’s syndrome, according to findings published in the journal Nature. This extends recent work that showed the gene variants could increase risk for schizophrenia. The gene variants are a member of the...
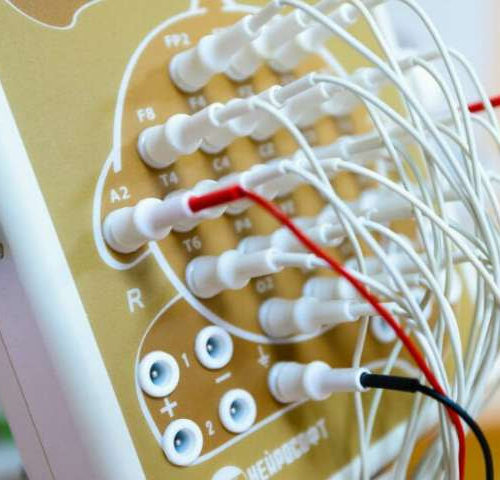
Scientists develop technique for more accurate brain diagnoses
by South Ural State University, South Ural State University Scientists of South Ural State University have developed a technique to identify the functional state of the brain with absolute accuracy. The results of the study will contribute to medical and physiological diagnostics. Electroencephalography is a study of the brainbased on the recording of its bioelectric...
‘Cell pores’ discovery gives hope to millions of brain and spinal cord injury patients
by Aston University Scientists have discovered a new treatment to dramatically reduce swelling after brain and spinal cord injuries, offering hope to 75 million victims worldwide each year. The breakthrough in treating such injuries—referred to as central nervous system (CNS) edema—is thought to be hugely significant because current options are limited to putting patients in...