Silky material uses magnetic particles to regrow bone By Ben Coxworth August 10, 2020 It was just a couple of months ago that we heard about an implantable material that electrically stimulates bone cells, causing them to reproduce. Now, scientists have created a similar substance that utilizes magnetism. There are already a number of experimental...
Tag: <span>scientific</span>
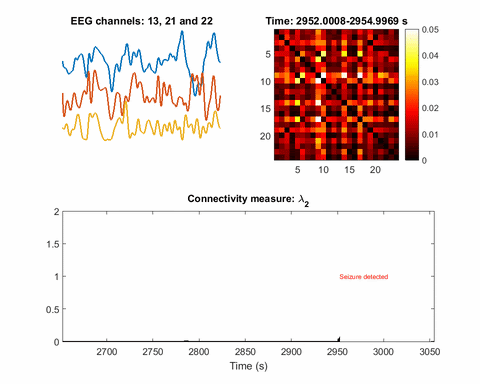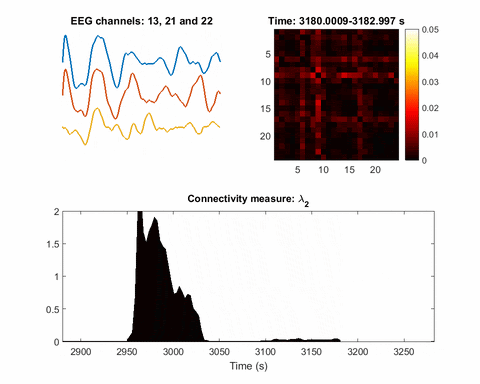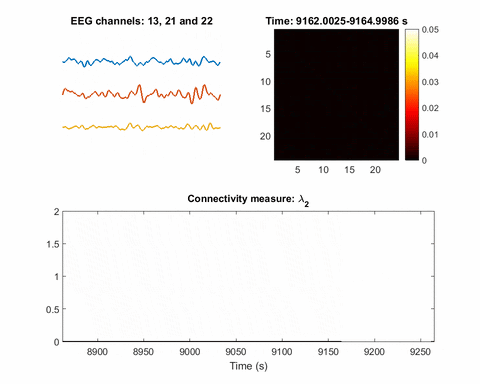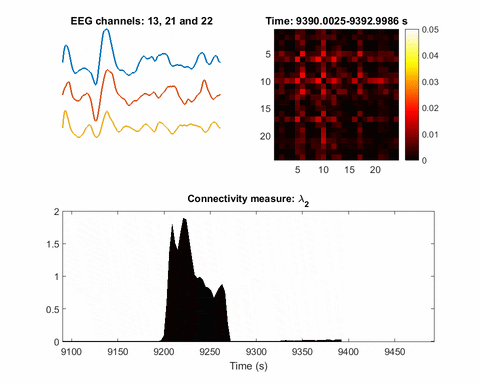
Artificial intelligence identifies, locates seizures in real-time
This gif was recorded during two seizures, one at 2950 seconds, the other at 9200. The top left animation is of EEG signals from three electrodes. The top right is a map of the inferred network. The third animation plots the Fiedler eigenvalue, the single value used to detect seizures using the network inference technique....
Genomes front and center of rare disease diagnosis
by National Institute for Health Research BioResource A research program pioneering the use of whole-genome sequencing in the NHS has diagnosed hundreds of patients and discovered new genetic causes of disease. Whole genome sequencing is the technology used by the 100,000 Genomes Project, a service set up by the government which aims to introduce routine...
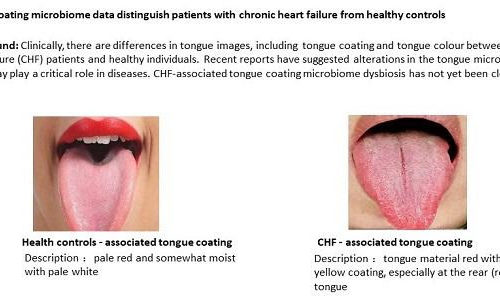
Tongue microbes provide window to heart health
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF CARDIOLOGY CLINICALLY, THERE ARE DIFFERENCES IN TONGUE IMAGES, INCLUDING TONGUE COATING AND TONGUE COLOUR BETWEEN CHRONIC HEART FAILURE (CHF) PATIENTS AND HEALTHY INDIVIDUALS. RECENT REPORTS HAVE SUGGESTED ALTERATIONS IN THE TONGUE… view more CREDIT: @EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF CARDIOLOGY 2020 Sophia Antipolis – 23 June 2020: Microorganisms on the tongue could help diagnose...
Wearable patch may provide new treatment option for skin cancer
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Conventional melanoma therapies, including chemotherapy and radiotherapy, suffer from the toxicity and side effects of repeated treatments due to the aggressive and recurrent nature of melanoma cells. Less invasive topical chemotherapies have emerged as alternatives, but their widespread uses have been hindered by both the painful size of the microneedles and...
Working in the sun—heating of the head may markedly affect safety and performance
by University of Copenhagen Prolonged exposure of the head to strong sunlight significantly impairs cognitively dominated functions and coordination of complex motor tasks, according to a new study from the Heat-Shield project coordinated by researchers from Department of Nutrition, Exercise and Sports at University of Copenhagen. This may have important implications for work safety and...
COVID-19: the number of antibodies neutralizing the virus decreases after six weeks
Neutralizing antibodies are thought to be key to the development of an efficient vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. Researchers at the University of Montreal Hospital Research Centre (CRCHUM) indicate that ensuring their presence over long periods of time might be required. “Our study shows that more than six infected people in ten generated neutralizing antibodies in only...
Cancer treatments significantly affected by diet, researchers find
By DONNA RACHEL EDMUNDS Changes in diet can increase the toxicity of a chemotherapeutic drug by up to 100-fold. What we eat has a direct effect on the outcome of medical treatments such as chemotherapy thanks to the interplay between our diets and the microbes in our gut, new research from the University of Virginia...
Potential biomarker identified to screen quality of donor’s stem cells before harvesting
Durham, NC – A new study released today in STEM CELLS addresses a significant problem that has been confronting human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) therapy. While hundreds of clinical trials involving thousands of patients are under way to test hMSCs’ ability to treat everything from heart disease to brain injury, there has been no way...
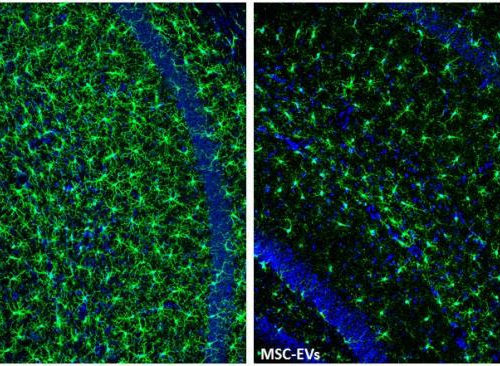
Intranasal delivery of MSCs provides hope for treating Alzheimer’s disease
Durham, NC – In the search for a cure for Alzheimer’s disease, mesenchymal stem cells and their derived extracellular vesicles (MSC-EVs) offer much promise, thanks to their protective and anti-inflammatory properties. The results from a new study done on mice, released today in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine, strengthens this idea by showing for the first...